Market penetration of Xpert MTB/RIF in high tuberculosis burden countries: A trend analysis from 2014 - 2016
- PMID: 30234198
- PMCID: PMC6139378
- DOI: 10.12688/gatesopenres.12842.2
Market penetration of Xpert MTB/RIF in high tuberculosis burden countries: A trend analysis from 2014 - 2016
Abstract
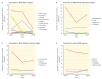
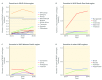
Background: Xpert® MTB/RIF, a rapid tuberculosis (TB) molecular test, was endorsed by the World Health Organization in 2010. Since then, 34.4 million cartridges have been procured under concessional pricing. Although the roll out of this diagnostic is promising, previous studies showed low market penetration. Methods: To assess 3-year trends of market penetration of Xpert MTB/RIF in the public sector, smear and Xpert MTB/RIF volumes for the year 2016 were evaluated and policies from 2014-2016 within 22 high-burden countries (HBCs) were studied. A structured questionnaire was sent to representatives of 22 HBCs. The questionnaires assessed the total smear and Xpert MTB/RIF volumes, number of modules and days of operation of GeneXpert machines in National TB Programs (NTPs). Data regarding the use of NTP GeneXpert machines for other diseases and GeneXpert procurement by other disease control programs were collected. Market penetration was estimated by the ratio of total sputum smear volume for initial diagnosis divided by the number of Xpert MTB/RIF tests procured in the public sector. Results: The survey response rate was 21/22 (95%). Smear/Xpert ratios decreased in 17/21 countries and increased in four countries, since 2014. The median ratio decreased from 32.6 (IQR: 44.6) in 2014 to 6.0 (IQR: 15.4) in 2016. In 2016, the median GeneXpert utilization was 20%, however seven countries (7/19; 37%) were running tests for other diseases on their NTP-procured GeneXpert systems in 2017, such as HIV, hepatitis-C virus (HCV), Chlamydia trachomatis, and Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Five (5/15; 33%) countries reported GeneXpert procurement by HIV or HCV programs in 2016 and/or 2017. Conclusions: Our results show a positive trend for Xpert MTB/RIF market penetration in 21 HBC public sectors. However, GeneXpert machines were under-utilized for TB, and inadequately exploited as a multi disease technology.
Keywords: Xpert MTB/RIF; access; diagnostics; market penetration; tuberculosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: SK and CD are employed by FIND. FIND is a not-for-profit foundation that supports the evaluation of publicly prioritized tuberculosis assays and the implementation of WHO-approved (guidance and prequalification) assays using donor grants. FIND has product evaluation agreements with several private sector companies, including Cepheid Inc, that design diagnostics and related products for treatment of tuberculosis and other diseases. These agreements strictly define FIND’s independence and neutrality vis-a-vis the companies whose products get evaluated and describe roles and responsibilities. MP previously consulted for the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. He serves on the Access Advisory Committee of FIND, Geneva. The other authors have no conflicts to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization: Global Tuberculosis Report 2017.2017; [cited 2018 February 5, 2018]. Reference Source
-
- World Health Organization: Next Generation Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra assay recommended by WHO.2017; [cited 2018 March 29]. Reference Source
-
- World Health Organization: Global Tuberculosis Report 2015.2015; [cited 2017]. Reference Source
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

