Resurfacing with Ablation of Periorbital Skin Technique: Indications, Efficacy, Safety, and 3D Assessment from a Pilot Study
- PMID: 30234414
- PMCID: PMC6199626
- DOI: 10.1089/pho.2018.4479
Resurfacing with Ablation of Periorbital Skin Technique: Indications, Efficacy, Safety, and 3D Assessment from a Pilot Study
Abstract
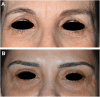
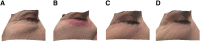
Objectives and background: Nowadays, several approaches for skin rejuvenation of the lower eyelid are available. We present a new technique of resurfacing with ablation of periorbital skin (RAP) performed in a single session.
Methods: This is a retrospective study involving 20 patients showing skin elastosis with or without evidence of the nasojugal fold and atrophic and dyschromic skin or needing a combined approach of transconjuntival lower blepharoplasty for fat bag removal. RAP technique is assessed in terms of efficacy, safety, and 3D evaluation of results at 6 months' follow-up.
Results: Global Assessment Improvement Scale results highlighted an improvement in all cases, for both physicians (blinded to treatment) and individual subjects. Only minor adverse events (edema, erythema, and discoloration) were reported in almost all patients, lasting 2-3 weeks after treatment, and were resolved without intervention. A 3D imaging tool revealed the reduction of medium protrusions and depressions and an improved texture at 2 months. Skin recovery was inversely correlated with hemoglobin reduction.
Conclusions: RAP seems to offer expert dermatologists a safe and clinically effective technique for skin rejuvenation of lower eyelids, without significant adverse events. Further studies will be performed to confirm our results.
Keywords: CO2 laser; lower eyelid; resurfacing.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Giovanni D'Alessandro received honoraria from Deka M.E.L.A. for speaker activities. Disclosure for all other authors: none reported. Declaration of funding interests: Deka M.E.L.A. provided support for publication fees.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Power of the pinch: pinch lower lid blepharoplasty.Ann Plast Surg. 2008 May;60(5):532-7. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0b013e318172f60e. Ann Plast Surg. 2008. PMID: 18434828
-
Continuous Wave Fractional CO2 Laser for the Treatment of Upper Eyelid Dermatochalasis and Periorbital Rejuvenation.Photomed Laser Surg. 2017 May;35(5):278-281. doi: 10.1089/pho.2016.4225. Epub 2017 Jan 12. Photomed Laser Surg. 2017. PMID: 28085575 Free PMC article.
-
"Split-Face" Evaluation of Collagen Changes Induced by Periorbital Fractional CO2 Laser Resurfacing.Aesthet Surg J. 2022 Feb 15;42(3):239-248. doi: 10.1093/asj/sjab357. Aesthet Surg J. 2022. PMID: 34618888
-
Laser blepharoplasty and laser resurfacing of the periorbital area.Clin Plast Surg. 1998 Jan;25(1):95-108. Clin Plast Surg. 1998. PMID: 9507800 Review.
-
Eyelid tightening by CO2 fractional laser, alternative to blepharoplasty.Dermatol Surg. 2014 Dec;40 Suppl 12:S137-41. doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000000165. Dermatol Surg. 2014. PMID: 25417564 Review.
Cited by
-
TFOS Lifestyle: Impact of cosmetics on the ocular surface.Ocul Surf. 2023 Jul;29:77-130. doi: 10.1016/j.jtos.2023.04.005. Epub 2023 Apr 13. Ocul Surf. 2023. PMID: 37061220 Free PMC article.
-
Laser Treatment Monitoring with Reflectance Confocal Microscopy.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 May 28;59(6):1039. doi: 10.3390/medicina59061039. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37374244 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Morphometric and Histometric Evaluation of Power-Dependent Tissue Ablation Using Fractional Carbon Dioxide Laser.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2025 Aug 7;18:1901-1907. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S534637. eCollection 2025. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 40791847 Free PMC article.
-
Laser-assisted blepharoplasty: An innovative safe and effective technique.Skin Res Technol. 2023 May;29(5):e13351. doi: 10.1111/srt.13351. Skin Res Technol. 2023. PMID: 37231919 Free PMC article.
-
Modern blepharoplasty: From bench to bedside.World J Clin Cases. 2023 Mar 16;11(8):1719-1729. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i8.1719. World J Clin Cases. 2023. PMID: 36969996 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tamatsu Y, Tsukahara K, Sugawara Y, Shimada K. New finding that might explain why the skin wrinkles more on various parts of the face. Clin Anat 2015;28:745–752 - PubMed
-
- Maria Kołodziejczak A, Rotsztejn H. Mexametric and cutometric assessment of the signs of aging of the skin area around the eyes after the use of non-ablative fractional laser, non-ablative radiofrequency and intense pulsed light. Dermatol Ther 2017;30:e12470 - PubMed
-
- Bonan P, Campolmi P, Cannarozzo G, et al. . Eyelid skin tightening: a novel “Niche” for fractional CO2 rejuvenation. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2012;26:186–193 - PubMed
-
- Rossi E, Farnetani F, Trakatelli M, Ciardo S, Pellacani G. Clinical and confocal microscopy study of plasma exeresis for non-surgical blepharoplasty of the upper eyelid: a pilot study. Dermatol Surg 2017. [Epub ahead of print] - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
