The usefulness of selected biomarkers in aortic regurgitation
- PMID: 30234893
- PMCID: PMC8084396
- DOI: 10.5603/CJ.a2018.0108
The usefulness of selected biomarkers in aortic regurgitation
Abstract
Background: The aim of the study was to investigate the prognostic value of selected biomarkers in patients with aortic regurgitation undergoing valve surgery.
Methods: A prospective study was conducted on a group of consecutive patients with hemodynamically significant aortic regurgitation that underwent elective aortic valve surgery. The primary endpoint was 30-day mortality and any major adverse event within 30 days.
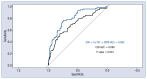
Results: The study group included 205 consecutive patients who underwent replacement or repair of the aortic valve. The primary endpoint occurred in 72 patients. At multivariate analysis red cell distribution width (RDW; p = 0.03) and high-sensitivity troponin T (hs-TnT; p = 0.02) remained independent predictors of the major complications including death.
Conclusions: Elevated preoperative RDW and hs-TnT were associated with a poorer outcome following aortic valve surgery.
Keywords: EuroSCORE II; aortic regurgitation; biomarkers; high-sensitivity troponin T; risk stratification.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
High-sensitivity troponin T in asymptomatic severe aortic stenosis.Biomarkers. 2019 Jun;24(4):334-340. doi: 10.1080/1354750X.2019.1567818. Epub 2019 Feb 6. Biomarkers. 2019. PMID: 30632403
-
1-Year Results in Patients Undergoing Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement With Failed Surgical Bioprostheses.JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2017 May 22;10(10):1034-1044. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2017.03.018. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2017. PMID: 28521921
-
Valve-sparing root replacement and composite valve graft replacement in patients with aortic regurgitation: From the Japan Cardiovascular Surgery Database.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2019 Dec;158(6):1501-1511.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2019.01.122. Epub 2019 Feb 15. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2019. PMID: 30952541
-
Risk factors for recurrence of aortic regurgitation after aortic valve repair.J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2021 Feb;62(1):25-34. doi: 10.23736/S0021-9509.20.11579-9. Epub 2020 Sep 10. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2021. PMID: 32909707 Review.
-
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement for Pure Native Aortic Valve Regurgitation: A Systematic Review.Cardiology. 2018;141(3):132-140. doi: 10.1159/000491919. Epub 2018 Dec 5. Cardiology. 2018. PMID: 30517917
Cited by
-
Postoperative myocardial fibrosis assessment in aortic valvular heart diseases-a cardiovascular magnetic resonance study.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2023 Jun 21;24(7):851-862. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jead041. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36935401 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive Value of Red Blood Cell Distribution Width for 1-Year All-Cause Mortality in Critically Ill Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction.Int J Gen Med. 2022 Jan 11;15:465-471. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S345109. eCollection 2022. Int J Gen Med. 2022. PMID: 35046707 Free PMC article.
-
Low Prevalence of Cardiomyopathy in Patients with Mitochondrial Disease and Neurological Manifestations.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2022 Jul 9;9(7):221. doi: 10.3390/jcdd9070221. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2022. PMID: 35877583 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting the One-Year Prognosis and Mortality of Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke Using Red Blood Cell Distribution Width Before Intravenous Thrombolysis.Clin Interv Aging. 2020 Feb 20;15:255-263. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S233701. eCollection 2020. Clin Interv Aging. 2020. PMID: 32110004 Free PMC article.
-
The long-term impact of increased red blood cell distribution width detected during hospitalization for heart failure.Biomark Med. 2024;18(19):831-842. doi: 10.1080/17520363.2024.2395237. Epub 2024 Sep 10. Biomark Med. 2024. PMID: 39254358
References
-
- Grąbczewska Z, Dębski R, Góralczyk K, et al. Associations between selected angiographic parameters and the number of CD34+ cells and plasma levels of vascular endothelial growth factor and angiogenin in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 2015;125(3):132–140. - PubMed
-
- Kawahara C, Tsutamoto T, Nishiyama K, et al. Prognostic role of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T in patients with nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy. Circ J. 2011;75(3):656–661. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources