The usefulness of selected biomarkers in aortic regurgitation
- PMID: 30234893
- PMCID: PMC8084396
- DOI: 10.5603/CJ.a2018.0108
The usefulness of selected biomarkers in aortic regurgitation
Abstract
Background: The aim of the study was to investigate the prognostic value of selected biomarkers in patients with aortic regurgitation undergoing valve surgery.
Methods: A prospective study was conducted on a group of consecutive patients with hemodynamically significant aortic regurgitation that underwent elective aortic valve surgery. The primary endpoint was 30-day mortality and any major adverse event within 30 days.
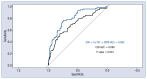
Results: The study group included 205 consecutive patients who underwent replacement or repair of the aortic valve. The primary endpoint occurred in 72 patients. At multivariate analysis red cell distribution width (RDW; p = 0.03) and high-sensitivity troponin T (hs-TnT; p = 0.02) remained independent predictors of the major complications including death.
Conclusions: Elevated preoperative RDW and hs-TnT were associated with a poorer outcome following aortic valve surgery.
Keywords: EuroSCORE II; aortic regurgitation; biomarkers; high-sensitivity troponin T; risk stratification.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Grąbczewska Z, Dębski R, Góralczyk K, et al. Associations between selected angiographic parameters and the number of CD34+ cells and plasma levels of vascular endothelial growth factor and angiogenin in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 2015;125(3):132–140. - PubMed
-
- Kawahara C, Tsutamoto T, Nishiyama K, et al. Prognostic role of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T in patients with nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy. Circ J. 2011;75(3):656–661. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources