Health-related quality of life compared between kidney transplantation and nocturnal hemodialysis
- PMID: 30235331
- PMCID: PMC6147724
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204405
Health-related quality of life compared between kidney transplantation and nocturnal hemodialysis
Abstract
Background: Health-related quality of life (HRQOL) is an important outcome measure in patients with end-stage renal disease. HRQOL is assumed to improve with kidney transplantation and also with nocturnal hemodialysis compared to conventional hemodialysis. However, there is no evidence regarding HRQOL to support the optimal treatment choice for patients on nocturnal hemodialysis who hesitate opting for transplantation. We therefore compared HRQOL between patients who were treated with kidney transplantation or nocturnal hemodialysis for one year.
Methods: We assessed HQROL using the Kidney Disease Quality of Life-Short Form questionnaire in a cross-sectional sample of patients who were treated with kidney transplantation (n = 41) or nocturnal hemodialysis (n = 31) for one year. All patients on nocturnal hemodialysis were transplantation candidates. Using linear regression, we compared HRQOL between kidney transplantation and nocturnal hemodialysis, and adjusted for age, sex, dialysis duration, cardiovascular disease, and presence of residual urine production.
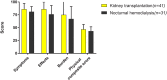
Results: At one year follow-up, mean age of the study population was 54 ±13 years, and median dialysis duration was 3.2 (IQR 2.1-5.0) years. Kidney transplantation was associated with significantly higher HRQOL on the domain "effects" compared to nocturnal hemodialysis (adjusted difference 12.0 points, 95% CI 3.9; 20.1). There were potentially clinically relevant differences between kidney transplantation and nocturnal hemodialysis on the domains "burden" (adjusted difference 11.1 points, 95% CI -2.6; 24.8), "social support" (adjusted difference 6.2, 95% CI -6.6; 19.1), and the physical composite score (adjusted difference 3.0, 95% CI -2.0; 8.1), but these were not significant.
Conclusions: After kidney transplantation, HRQOL is especially higher on the domain "effects of kidney disease" compared to nocturnal hemodialysis. This can be useful when counseling patients on nocturnal hemodialysis who may opt for transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
The NOCTx study is supported by unrestricted grants from Amgen, Baxter, Fresenius Medical Care, Novartis, Roche, and Shire Pharmaceuticals. B.C. van Jaarsveld reports research grants from Fresenius Medical Care, Baxter, Vifor Fresenius Medical Care Renal Pharma, and Nipro outside the submitted work. There are no patents, products in development or marketed products to declare. This does not alter our adherence to all the PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials, as detailed online in the guide for authors.
Figures
References
-
- Mapes DL, Lopes AA, Satayathum S, McCullough KP, Goodkin DA, Locatelli F, et al. Health-related quality of life as a predictor of mortality and hospitalization: the Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS). Kidney Int. 2003;64(1):339–49. 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00072.x . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lowrie EG, Curtin RB, LePain N, Schatell D. Medical outcomes study short form-36: a consistent and powerful predictor of morbidity and mortality in dialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;41(6):1286–92. . - PubMed
-
- Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kopple JD, Block G, Humphreys MH. Association among SF36 quality of life measures and nutrition, hospitalization, and mortality in hemodialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001;12(12):2797–806. . - PubMed
-
- Mittal SK, Ahern L, Flaster E, Maesaka JK, Fishbane S. Self-assessed physical and mental function of haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2001;16(7):1387–94. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

