Identification of endogenous normalizing genes for expression studies in inguinal ring tissue for scrotal hernias in pigs
- PMID: 30235332
- PMCID: PMC6147718
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204348
Identification of endogenous normalizing genes for expression studies in inguinal ring tissue for scrotal hernias in pigs
Abstract
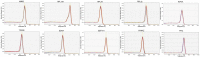
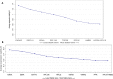
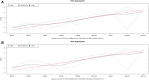
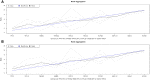
The use of reference genes is required for relative quantification in gene expression analysis and since the stability of these genes could be variable depending on the experimental design, it has become indispensable to test the reliability of endogenous genes. Therefore, this study evaluated 10 reference candidate genes in two different experimental conditions in order to obtain stable genes to be used as reference in expression studies related to scrotal hernias in pigs. Two independent experiments were performed: one with 30 days-old MS115 pigs and the other with 60 days-old Landrace pigs. The inguinal ring/canal was collected, frozen and further submitted to real-time PCR analysis (qPCR). For the reference genes stability evaluation, four tools were used: GeNorm in the SLqPCR, BestKeeper, NormFinder and Comparative CT. A general ranking was generated using the BruteAggreg function of R environment. In this study, the RPL19 was one of the most reliable endogenous genes for both experiments. The breed/age effects influenced the expression stability of candidate reference genes evaluated in the inguinal ring of pigs. Therefore, this study reinforces the importance of evaluating the stability of several endogenous genes previous their use, since a consensual set of reference genes is not easily obtained. Here, two sets of genes are recommended: RPL19, RPL32 and H3F3A for 30-days MS115 and PPIA and RPL19 for the 60 days-old Landrace pigs. This is the first study using the inguinal ring tissue and the results can be useful as an indicative for other studies working with gene expression in this tissue.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- de L Rebouças E, do N Costa JJ, Passos MJ, de S Passos JR, van den Hurk R, Silva JRV. Real time PCR and importance of housekeepings genes for normalization and quantification of mRNA expression in different tissues. Brazilian Arch Biol Technol. 2013;56: 143–154. 10.1590/S1516-89132013000100019 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

