Costs, outcome and cost-effectiveness of neurocritical care: a multi-center observational study
- PMID: 30236140
- PMCID: PMC6148794
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-018-2151-5
Costs, outcome and cost-effectiveness of neurocritical care: a multi-center observational study
Abstract
Background: Neurocritical illness is a growing healthcare problem with profound socioeconomic effects. We assessed differences in healthcare costs and long-term outcome for different forms of neurocritical illnesses treated in the intensive care unit (ICU).
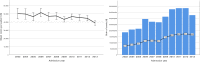
Methods: We used the prospective Finnish Intensive Care Consortium database to identify all adult patients treated for traumatic brain injury (TBI), intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH), subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) and acute ischemic stroke (AIS) at university hospital ICUs in Finland during 2003-2013. Outcome variables were one-year mortality and permanent disability. Total healthcare costs included the index university hospital costs, rehabilitation hospital costs and social security costs up to one year. All costs were converted to euros based on the 2013 currency rate.
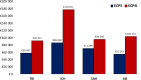
Results: In total 7044 patients were included (44% with TBI, 13% with ICH, 27% with SAH, 16% with AIS). In comparison to TBI, ICH was associated with the highest risk of death and permanent disability (OR 2.6, 95% CI 2.1-3.2 and OR 1.7, 95% CI 1.4-2.1), followed by AIS (OR 1.9, 95% CI 1.5-2.3 and OR 1.5, 95% CI 1.3-1.8) and SAH (OR 1.8, 95% CI 1.5-2.1 and OR 0.8, 95% CI 0.6-0.9), after adjusting for severity of illness. SAH was associated with the highest mean total costs (€51,906) followed by ICH (€47,661), TBI (€43,916) and AIS (€39,222). Cost per independent survivor was lower for TBI (€58,497) and SAH (€96,369) compared to AIS (€104,374) and ICH (€178,071).
Conclusion: Neurocritical illnesses are costly and resource-demanding diseases associated with poor outcomes. Intensive care of patients with TBI or SAH more commonly result in independent survivors and is associated with lower total treatments costs compared to ICH and AIS.
Keywords: Acute ischemic stroke; Finland; Intracerebral hemorrhage; Neurocritical care; neurointensive care; costs; Outcome; cost-effectiveness; Subarachnoid hemorrhage; Traumatic brain injury.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The research committee of the of Helsinki University Hospital (HUS/26/2018 §37), the Finnish National Institute for Health and Welfare (THL/2034/5.05.00/2017), Statistics Finland (TK-53-1047-14), the Social Insurance Institution (Kela 23/522/2018), the Office of the Data Protection Ombudsman (2794/402/2015) and all of the participating university hospitals’ ethics committees approved this study and waived the need for informed consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- GBD 2015 Neurological Disorders Collaborator Group VL. Abajobir AA, Abate KH, Abd-Allah F, Abdulle AM, Abera SF, et al. Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders during 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Neurol. 2017;16:877–897. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(17)30299-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Feigin VL, Roth GA, Naghavi M, Parmar P, Krishnamurthi R, Chugh S, et al. Global burden of stroke and risk factors in 188 countries, during 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15:913–924. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(16)30073-4. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

