Peripheral neuropathy in children and adolescents treated for cancer
- PMID: 30236383
- PMCID: PMC6287277
- DOI: 10.1016/S2352-4642(18)30236-0
Peripheral neuropathy in children and adolescents treated for cancer
Abstract
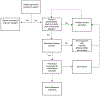
Peripheral neuropathy is a well recognised treatment-related toxicity in children with cancer, associated with exposure to neurotoxic chemotherapy agents. Acute damage can occur in sensory, motor, or autonomic neurons, with symptoms that are rarely life threatening, but often severe enough to interfere with function during therapy and after treatment ends. The type of neuropathy and specific symptoms are associated with multiple factors including age at time of therapy, genetic predisposition, chemotherapy type and cumulative dose, and exposure to other agents during therapy. In this Review, we describe the peripheral neuropathy phenotype in children during cancer therapy and among survivors who have completed therapy, to summarise genetic and treatment-related risk factors for neuropathy, and to outline strategies to monitor and detect neuropathy during and after therapy. Additionally, we outline strategies for medical management of neuropathy during treatment and potential rehabilitation interventions to prevent or remediate functional loss.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests
The authors declare no competing financial or personal interests.
Figures

References
-
- Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2013. http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2013/ (accessed 5/18/2017).
-
- Reinders-Messelink HA, Van Weerden TW, Fock JM, et al. Mild axonal neuropathy of children during treatment for acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 2000; 4: 225–33. - PubMed
-
- Gilchrist LS, Tanner LR, Ness KK. Short-term recovery of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy after treatment for pediatric non-CNS cancer. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2017; 64: 180–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

