A partial reconstitution implicates DltD in catalyzing lipoteichoic acid d-alanylation
- PMID: 30237166
- PMCID: PMC6240853
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004561
A partial reconstitution implicates DltD in catalyzing lipoteichoic acid d-alanylation
Abstract
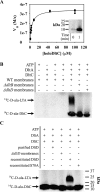
Modifications to the Gram-positive bacterial cell wall play important roles in antibiotic resistance and pathogenesis, but the pathway for the d-alanylation of teichoic acids (DLT pathway), a ubiquitous modification, is poorly understood. The d-alanylation machinery includes two membrane proteins of unclear function, DltB and DltD, which are somehow involved in transfer of d-alanine from a carrier protein inside the cell to teichoic acids on the cell surface. Here, we probed the role of DltD in the human pathogen Staphylococcus aureus using both cell-based and biochemical assays. We first exploited a known synthetic lethal interaction to establish the essentiality of each gene in the DLT pathway for d-alanylation of lipoteichoic acid (LTA) and confirmed this by directly detecting radiolabeled d-Ala-LTA both in cells and in vesicles prepared from mutant strains of S. aureus We developed a partial reconstitution of the pathway by using cell-derived vesicles containing DltB, but no other components of the d-alanylation pathway, and showed that d-alanylation of previously formed lipoteichoic acid in the DltB vesicles requires the presence of purified and reconstituted DltA, DltC, and DltD, but not of the LTA synthase LtaS. Finally, based on the activity of DltD mutants in cells and in our reconstituted system, we determined that Ser-70 and His-361 are essential for d-alanylation activity, and we propose that DltD uses a catalytic dyad to transfer d-alanine to LTA. In summary, we have developed a suite of assays for investigating the bacterial DLT pathway and uncovered a role for DltD in LTA d-alanylation.
Keywords: DLT pathway; DltB; MBOAT; Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus); acyltransferase; cell wall; membrane protein; pathway reconstitution; teichoic acid.
© 2018 Wood et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures


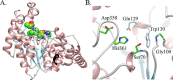


References
-
- Kovács M., Halfmann A., Fedtke I., Heintz M., Peschel A., Vollmer W., Hakenbeck R., and Brückner R. (2006) A functional dlt operon, encoding proteins required for incorporation of d-alanine in teichoic acids in Gram-positive bacteria, confers resistance to cationic antimicrobial peptides in Streptococcus pneumoniae. J. Bacteriol. 188, 5797–5805 10.1128/JB.00336-06 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

