LNMAT1 promotes lymphatic metastasis of bladder cancer via CCL2 dependent macrophage recruitment
- PMID: 30237493
- PMCID: PMC6148066
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-06152-x
LNMAT1 promotes lymphatic metastasis of bladder cancer via CCL2 dependent macrophage recruitment
Abstract
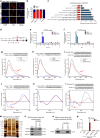
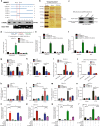
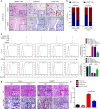
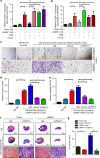
Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are the most abundant inflammatory infiltrates in the tumor microenvironment and contribute to lymph node (LN) metastasis. However, the precise mechanisms of TAMs-induced LN metastasis remain largely unknown. Herein, we identify a long noncoding RNA, termed Lymph Node Metastasis Associated Transcript 1 (LNMAT1), which is upregulated in LN-positive bladder cancer and associated with LN metastasis and prognosis. Through gain and loss of function approaches, we find that LNMAT1 promotes bladder cancer-associated lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis. Mechanistically, LNMAT1 epigenetically activates CCL2 expression by recruiting hnRNPL to CCL2 promoter, which leads to increased H3K4 tri-methylation that ensures hnRNPL binding and enhances transcription. Furthermore, LNMAT1-induced upregulation of CCL2 recruits macrophages into the tumor, which promotes lymphatic metastasis via VEGF-C excretion. These findings provide a plausible mechanism for LNMAT1-modulated tumor microenvironment in lymphatic metastasis and suggest that LNMAT1 may represent a potential therapeutic target for clinical intervention in LN-metastatic bladder cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Re: LNMAT1 Promotes Lymphatic Metastasis of Bladder Cancer via CCL2 Dependent Macrophage Recruitment.J Urol. 2019 Apr;201(4):669. doi: 10.1097/01.JU.0000553307.75692.ff. J Urol. 2019. PMID: 30652991 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

