Outcome Analysis of Lateral Pinning for Displaced Supracondylar Fractures in Children Using Three Kirschner Wires in Parallel and Divergent Configuration
- PMID: 30237614
- PMCID: PMC6142790
- DOI: 10.4103/ortho.IJOrtho_462_17
Outcome Analysis of Lateral Pinning for Displaced Supracondylar Fractures in Children Using Three Kirschner Wires in Parallel and Divergent Configuration
Abstract
Background: Supracondylar humerus fracture is the most common fracture around elbow in children. Closed reduction and percutaneous Kirschner wire (pin) fixation is the standard method of managing displaced extension type (Gartland Type II and Type III) supracondylar humerus fractures. The configuration of wires is debatable. Although two crossed K-wires are mechanically stable, there is an inherent risk of ulnar nerve injury. Lateral K-wires - parallel or divergent - are good alternative. This study was aimed at identifying the best configuration for the lateral wires.
Materials and methods: Patients with Gartland type 3 supracondylar humerus fractures were randomized by envelope method to receive closed reduction and K-wire fixation in either a parallel or divergent fashion. The patients were followed up at 3 weeks for wire removal and at 6 weeks and 3 months after surgery. Baumann's angle, functional outcome as per Flynn's criteria, and range of motion were recorded in each visit. Effect of delay in surgery was also evaluated as a secondary outcome.
Results: Nineteen patients received fixation with parallel wires and 11 patients had divergent fixation. No loss of reduction was seen in any patient at 3 months. No statistically significant difference was seen in the Baumann's angles and outcome according to Flynn's criteria irrespective of the wire configuration (divergent or parallel). Furthermore, the delay in surgery was also found not to have a significant effect on the functional outcome.
Conclusions: Both parallel and divergent K-wire configurations provide satisfactory stability when accurate reduction and adequate fixation of the fracture has been done. Based on the limited number of patients in this study, one configuration cannot be judged to be superior to the other.
Keywords: Baumann's angle; Flynn's criteria; Gartland's Type 3; Pediatrics; closed reduction; humeral fractures; humerus; supracondylar humerus fracture.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


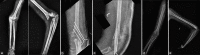
References
-
- Otsuka NY, Kasser JR. Supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1997;5:19–26. - PubMed
-
- Beaty JH, Kasser JR. Fractures about the elbow. Instr Course Lect. 1995;44:199–215. - PubMed
-
- Boyd HB, Altenberg AR. Fractures about the elbow in children. Arch Surg. 1944;49:213.
-
- Swenson AL. The treatment of supracondylar fractures of the humerus by Kirschner-wire transfixion. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1948;30A:993–7. - PubMed
-
- Casiano E. Reduction and fixation by pinning “banderillero” style-fractures of the humerus at the elbow in children. Mil Med. 1960;125:262–4. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
