Neurofeedback for the enhancement of dynamic balance of judokas
- PMID: 30237667
- PMCID: PMC6135976
- DOI: 10.5114/biolsport.2018.71488
Neurofeedback for the enhancement of dynamic balance of judokas
Abstract
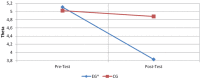
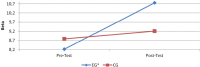
Physical balance is an important factor in sport. Neurofeedback (EEG biofeedback) can be used to improve concentration and focus. The present study investigated and determined the impact of neurofeedback training on dynamic balance in judo. Eighteen judokas voluntarily participated in this study. The participants were divided into two groups: experimental (EG) and control (CG). In the experimental group subjects were trained to inhibit 3-8 Hz while they were also trained to reinforce 14-19 Hz brainwave activities at points O1 and O2 for ten sessions and 25 minutes per session. The participants in the control group were exposed to the same conditions but instead were provided with sham feedback. EEG and dynamic balance tests were executed before and at the end of the fifteenth session of training. The one-way ANOVA with repeated measures revealed that dynamic balance scores significantly improved at the post-test (F=12.4, p=0.001) in the EG group. The findings demonstrate that neurofeedback training can enhance dynamic balance of judokas.
Keywords: Biofeedback; Dynamic balance; EEG; Judo; Neurofeedback.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Use of Neurofeedback in Sports Training: Systematic Review.Brain Sci. 2023 Apr 14;13(4):660. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13040660. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37190625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of Neurofeedback Training on the Visual Processing Efficiency in Judo Athletes.J Hum Kinet. 2020 Jan 31;71:219-227. doi: 10.2478/hukin-2019-0097. eCollection 2020 Jan. J Hum Kinet. 2020. PMID: 32148586 Free PMC article.
-
Neurofeedback training aimed to improve focused attention and alertness in children with ADHD: a study of relative power of EEG rhythms using custom-made software application.Clin EEG Neurosci. 2013 Jul;44(3):193-202. doi: 10.1177/1550059412458262. Clin EEG Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23820311
-
Erratum.Mult Scler. 2016 Oct;22(12):NP9-NP11. doi: 10.1177/1352458515585718. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Mult Scler. 2016. PMID: 26041800
-
Preventing relapse in alcohol disorder with EEG-neurofeedback as a neuromodulation technique: A review and new insights regarding its application.Addict Behav. 2020 Jul;106:106391. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2020.106391. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Addict Behav. 2020. PMID: 32197211 Review.
Cited by
-
Electroencephalography Neurofeedback Training with Focus on the State of Attention: An Investigation Using Source Localization and Effective Connectivity.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Sep 19;24(18):6056. doi: 10.3390/s24186056. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39338801 Free PMC article.
-
Could Ankle Muscle Activation be Used as a Simple Measure of Balance Exercise Intensity?J Hum Kinet. 2019 Nov 30;70:47-59. doi: 10.2478/hukin-2019-0037. eCollection 2019 Nov. J Hum Kinet. 2019. PMID: 31915475 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in Anthropometric Traits and Body Composition Over a Four-Year Period in Elite Female Judoka Athletes.J Hum Kinet. 2019 Nov 30;70:145-155. doi: 10.2478/hukin-2019-0115. eCollection 2019 Nov. J Hum Kinet. 2019. PMID: 31915484 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of Neurofeedback in Sports Training: Systematic Review.Brain Sci. 2023 Apr 14;13(4):660. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13040660. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37190625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in Injury Risk Mechanisms after Soccer-Specific Fatigue in Male Youth Soccer Players.J Hum Kinet. 2018 Jun 13;62:33-42. doi: 10.1515/hukin-2017-0157. eCollection 2018 Jun. J Hum Kinet. 2018. PMID: 29922375 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hammond DC. Neurofeedback treatment of depression and anxiety. J Adult Dev. 2005:12(2–3):131-137.
-
- Hammond DC. Neurofeedback to improve physical balance, incontinence, and swallowing. J. Neurother. 2005;9(1):27–36.
-
- Walker JE, Kozolowsky GP. Neurofeedback treatmaent of epilepsy. Child Adol Psych Cl. 2005;14(1):163–176. - PubMed
-
- Monastra VJ. Electroencephalographic biofeedback (neurotherapy) as a treatment for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: Rationale and empirical foundation. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am. 2005;14(1):55–82. - PubMed
-
- Chung-Hee C, Byoung-Jun K, Chang-Yong J, Eun-Kyu C. Effects of Concentration Training with Brainwave Biofeedback on Tennis Performance. J Phys Ther Sci. 2016;28(10):2938–2941. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources