Predicting medication nonadherence risk in a Chinese inflammatory rheumatic disease population: development and assessment of a new predictive nomogram
- PMID: 30237698
- PMCID: PMC6136915
- DOI: 10.2147/PPA.S159293
Predicting medication nonadherence risk in a Chinese inflammatory rheumatic disease population: development and assessment of a new predictive nomogram
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of this study was to develop and internally validate a medication nonadherence risk nomogram in a Chinese population of patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases.
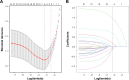
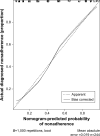
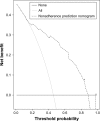
Patients and methods: We developed a prediction model based on a training dataset of 244 IRD patients, and data were collected from March 2016 to May 2016. Adherence was evaluated using 19-item Compliance Questionnaire Rheumatology. The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression model was used to optimize feature selection for the medication nonadherence risk model. Multivariable logistic regression analysis was applied to build a predicting model incorporating the feature selected in the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression model. Discrimination, calibration, and clinical usefulness of the predicting model were assessed using the C-index, calibration plot, and decision curve analysis. Internal validation was assessed using the bootstrapping validation.
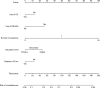
Results: Predictors contained in the prediction nomogram included use of glucocorticoid (GC), use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, number of medicine-related questions, education level, and the distance to hospital. The model displayed good discrimination with a C-index of 0.857 (95% confidence interval: 0.807-0.907) and good calibration. High C-index value of 0.847 could still be reached in the interval validation. Decision curve analysis showed that the nonadherence nomogram was clinically useful when intervention was decided at the nonadherence possibility threshold of 14%.
Conclusion: This novel nonadherence nomogram incorporating the use of GC, the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, the number of medicine-related questions, education level, and distance to hospital could be conveniently used to facilitate the individual medication nonadherence risk prediction in IRD patients.
Keywords: Compliance Questionnaire Rheumatology; inflammatory rheumatic diseases; noadherence; nomogram; predictors.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Osterberg L, Blaschke T. Adherence to medication. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(5):487–497. - PubMed
-
- Burkhart PV, Sabate E. Adherence to long-term therapies: evidence for action. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2003;35(3):207. - PubMed
-
- Costedoat-Chalumeau N, Tamirou F, Piette JC. Treatment adherence in systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis: time to focus on this important issue: treatment adherence in SLE and RA. Rheumatology (Oxford, England) 2017 Sep;:11. Epub. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

