Snyder-Robinson syndrome
- PMID: 30237987
- PMCID: PMC6140707
- DOI: 10.4322/acr.2018.031
Snyder-Robinson syndrome
Abstract
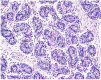
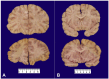
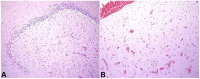
Snyder-Robinson syndrome, also known as spermine synthase deficiency, is an X-linked intellectual disability syndrome (OMIM #390583). First described by Drs. Snyder and Robinson in 1969, this syndrome is characterized by an asthenic body habitus, facial dysmorphism, broad-based gait, and osteoporosis with frequent fractures. We report here a pediatric autopsy of a 4 year old male with a history of intellectual disability, gait abnormalities, multiple fractures, and seizures previously diagnosed with Snyder-Robinson syndrome with an SMS gene mutation (c.831G>T:p.L277F). The cause of death was hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy secondary to prolonged seizure activity. Although Snyder-Robinson syndrome is rare, the need to recognize clinical findings in order to trigger genetic testing has likely resulted in under diagnosis.
Keywords: Intellectual Disability; Mental Retardation, X-linked; Snyder-Robinson syndrome; Spermine Synthase.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None
Figures

References
-
- Albert J, Schwartz CE, Boerkoel CF, Stevenson RE. Snyder-Robinson syndrome. In: Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, et al., editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle: University of Washington; 2013. [cited 2013 Jun 27]. p. 1993-2018. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK144284/ - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

