A changing paradigm: management and treatment of the HCV/HIV-co-infected patient
- PMID: 30238230
- PMCID: PMC6471674
- DOI: 10.1007/s12072-018-9896-4
A changing paradigm: management and treatment of the HCV/HIV-co-infected patient
Abstract
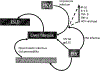
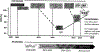
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) treatment in HIV/HCV co-infected individuals has renewed relevance given the ongoing opioid crisis and rise of new HIV and HCV infections associated with injection drug use. Patients co-infected with HIV and HCV demonstrate increased rates of hepatic fibrosis, progression to liver failure, and liver-related mortality. HIV co-infection does not impact outcomes of current HCV treatments, and patients should be treated the same as HCV mono-infected persons, though attention to drug:drug interactions is required. In this review, we discuss the mechanisms mediating injury to the liver in HIV mono-infection and HIV/HCV co-infection, and present the landmark trials of HCV treatment in HIV-infected individuals.
Keywords: Co-infection; DAA; Drug–drug interactions; HCV; HIV.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
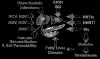
Similar articles
-
HIV-1 tropism and liver fibrosis in HIV-HCV co-infected patients.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e50289. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050289. Epub 2012 Nov 30. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23226258 Free PMC article.
-
Current treatment options for hepatitis C patients co-infected with HIV.Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016 Jun;10(6):689-95. doi: 10.1586/17474124.2016.1145545. Epub 2016 Feb 12. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 26799571 Review.
-
HCV mono-infected and HIV/HCV co-infected individuals treated with direct-acting antivirals: to what extent do they differ?Int J Infect Dis. 2017 Sep;62:64-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2017.07.001. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Int J Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28728927
-
Optimal therapy of HIV/HCV co-infected patients with direct acting antivirals.Liver Int. 2015 Jan;35 Suppl 1:51-5. doi: 10.1111/liv.12721. Liver Int. 2015. PMID: 25529087 Review.
-
Optimum combination therapy regimens for HIV/HCV infection.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2016;14(3):299-309. doi: 10.1586/14787210.2016.1147952. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2016. PMID: 26822803 Review.
Cited by
-
Toxoplasma gondii, HBV, and HCV co-infection and their correlation with CD4 cells among Iranian HIV-positive patients.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023 Feb;11(2):e794. doi: 10.1002/iid3.794. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023. PMID: 36840494 Free PMC article.
-
Management and Treatment of Hepatitis C: Are There Still Unsolved Problems and Unique Populations?Viruses. 2021 Jun 1;13(6):1048. doi: 10.3390/v13061048. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34205966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of sofosbuvir and daclastavir on health-related quality of life in patients co-infected with hepatitis C and human immunodeficiency virus.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2021 May 26;19(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s12955-021-01777-x. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2021. PMID: 34039353 Free PMC article.
-
Successful HCV Therapy Reduces Liver Disease Severity and Inflammation Biomarkers in HIV/HCV-Coinfected Patients With Advanced Cirrhosis: A Cohort Study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Feb 1;8:615342. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.615342. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33598470 Free PMC article.
-
Real-world efficacy of direct acting antiviral therapies in patients with HIV/HCV.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 13;15(2):e0228847. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228847. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32053682 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hepatitis C [Internet]; 2017. []. http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-c. Accessed 12 July 2018.
-
- HIV and hepatitis coinfections [Internet]. 2017. http://www.who.int/hiv/topics/hepatitis/en/. Accessed 12 July 2018.
-
- Benhamou Y, Bochet M, Di Martino V, Charlotte F, Azria F, Coutellier A, et al. Liver fibrosis progression in human immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis C virus coinfected patients. The multivirc group. Hepatology 1999;30(4):1054–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

