Proximity Ligation Assay (PLA)
- PMID: 30238640
- PMCID: PMC6205916
- DOI: 10.1002/cpim.58
Proximity Ligation Assay (PLA)
Abstract
Proximity ligation assay (PLA), also referred to as Duolink® PLA technology, permits detection of protein-protein interactions in situ (at distances <40 nm) at endogenous protein levels. It exploits specific antibodies identifying (either directly or indirectly) the two proteins of interest and utilizes specific DNA primers covalently linked to the antibodies. A hybridization step followed by DNA amplification with fluorescent probes permit visualization of spots of proximity by fluorescence microscopy. Since the development of PLA in 2002, it has been increasingly used to detect the interaction between two proteins with high sensitivity and specificity. It is a simple and sensitive technique to study protein-protein interaction in cells. © 2018 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Keywords: Duolink®; antibody; in situ assays; protein-protein interaction.
© 2018 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Figures
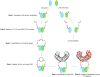
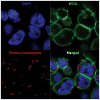
References
-
- Berggård T, Linse S, James P. Methods for the detection and analysis of protein-protein interactions. Proteomics. 2007;7:2833–2842. - PubMed
-
- Braun P, Gingras AC. History of protein-protein interactions: from egg-white to complex networks. Proteomics. 2012;12:1478–1498. - PubMed
-
- Cheng P-C. In: The Contrast Formation in Optical Microscopy Handbook of Biological Confocal Microscopy. Pawley JB, editor. Boston, MA: Springer US; 2006. pp. 162–206.
-
- Collins SR, Kemmeren P, Zhao XC, Greenblatt JF, Spencer F, Holstege FC, Weissman JS, Krogan NJ. Toward a comprehensive atlas of the physical interactome of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2007;6:439–450. - PubMed
-
- Edidin M. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer: techniques for measuring molecular conformation and molecular proximity. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2003;Chapter 18(Unit 18.10) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

