Measurement invariance of the Spanish Launay-Slade Hallucinations Scale-Extended version between putatively healthy controls and people diagnosed with a mental disorder
- PMID: 30238666
- PMCID: PMC6877181
- DOI: 10.1002/mpr.1741
Measurement invariance of the Spanish Launay-Slade Hallucinations Scale-Extended version between putatively healthy controls and people diagnosed with a mental disorder
Abstract
Objectives: The current study aimed at evaluating the reliability, convergent and divergent validity, and factor structure of the Spanish Launay-Slade Hallucinations Scale-Extended version (LSHS-E) in people with mental disorders and healthy controls.
Methods: Four hundred and twenty-two individuals completed the Spanish LSHS-E and the Spanish Community Assessment of Psychic Experiences. The convergent and divergent validity of the LSHS-E was assessed with the three dimensions of the Community Assessment of Psychic Experiences (positive, negative, and depressive dimensions) in healthy controls and people with a mental disorder. Factor structure of the LSHS-E was assessed using confirmatory factor analysis and measurement invariance.
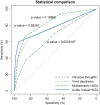
Results: The LSHS-E had a good reliability in healthy controls and people with a mental disorder (Cronbach's = 0.83 and 0.91, respectively). The LSHS-E was more strongly associated with positive psychotic-like experiences than with depressive and negative symptoms. Four factors were found: (a) "intrusive thoughts"; (b) "vivid daydreams"; (c) "multisensory hallucination-like experiences"; and (d) "auditory-visual hallucination-like experiences" that were invariant between the group of healthy controls and people with a mental disorder.
Conclusion: The Spanish version of the LSHS-E possesses adequate psychometric properties, and the confirmatory factor analysis findings provide further support for the multidimensionality of proneness to hallucination in clinical and nonclinical samples.
Keywords: Launay-Slade Hallucination Scale; factor analysis; hallucinatory proneness; measurement invariance; sensitivity and specificity analyses.
© 2018 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Aleman, A. , Nieuwenstein, M. R. , Böcker, K. B. E. , & De Haan, E. H. F. (2001). Multi‐dimensionality of hallucinatory predisposition: Factor structure of the Launay–Slade Hallucination Scale in a normal sample. Personality and Individual Differences, 30(2), 287–292. 10.1016/S0191-8869(00)00045-3 - DOI
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th edition (DSM‐5). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 4th Edition TR (ed., Vol. 280). Washington: American Psychiatry Publishing; 10.1176/appi.books.9780890425596.744053 - DOI
-
- Bentall, R. P. , & Slade, P. D. (1985). Reality testing and auditory hallucinations: A signal detection analysis. The British Journal of Clinical Psychology/the British Psychological Society, 24(Pt 3), 159–169. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4052663 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

