Catheter Ablation of Ventricular Tachycardia in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia/Cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 30238706
- PMCID: PMC6158456
- DOI: 10.4070/kcj.2018.0268
Catheter Ablation of Ventricular Tachycardia in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia/Cardiomyopathy
Abstract
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia/cardiomyopathy (ARVD/C) is predominantly an inherited cardiomyopathy with typical histopathological characteristics of fibro-fatty infiltration mainly involving the right ventricular (RV) inflow tract, RV outflow tract, and RV apex in the majority of patients. The above pathologic evolution frequently brings patients with ARVD/C to medical attention owing to the manifestation of syncope, sudden cardiac death (SCD), ventricular arrhythmogenesis, or heart failure. To prevent future or recurrent SCD, an implantable cardiac defibrillator (ICD) is highly desirable in patients with ARVD/C who had experienced unexplained syncope, hemodynamically intolerable ventricular tachycardia (VT), ventricular fibrillation, and/or aborted SCD. Notably, the management of frequent ventricular tachyarrhythmias in ARVD/C is challenging, and the use of antiarrhythmic drugs could be unsatisfactory or limited by the unfavorable side effects. Therefore, radiofrequency catheter ablation (RFCA) has been implemented to treat the drug-refractory VT in ARVD/C for decades. However, the initial understanding of the link between fibro-fatty pathogenesis and ventricular arrhythmogenesis in ARVD/C is scarce, the efficacy and prognosis of endocardial RFCA alone were limited and disappointing. The electrophysiologists had broken through this frontier after better illustration of epicardial substrates and broadly application of epicardial approaches in ARVD/C. In recent works of literature, the application of epicardial ablation also successfully results in higher procedural success and decreases VT recurrences in patients with ARVD/C who are refractory to the endocardial approach during long-term follow-up. In this article, we review the important evolution on the delineation of arrhythmogenic substrates, ablation strategies, and ablation outcome of VT in patients with ARVD/C.
Keywords: Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia-cardiomyopathy; Catheter ablation; Percutaneous epicardial mapping; Ventricular tachycardia.
Copyright © 2018. The Korean Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
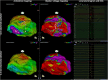
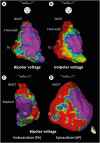
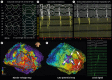
References
-
- Dalla Volta S, Fameli O, Maschio G. The clinical and hemodynamic syndrome of auricularisation of the right ventricle. (Apropos of 4 personal cases) Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 1965;58:1129–1143. - PubMed
-
- Basso C, Thiene G, Corrado D, et al. Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. Dysplasia, dystrophy, or myocarditis? Circulation. 1996;94:983–991. - PubMed
-
- Marcus FI, Fontaine GH, Guiraudon G, et al. Right ventricular dysplasia: a report of 24 adult cases. Circulation. 1982;65:384–398. - PubMed
-
- Hulot JS, Jouven X, Empana JP, et al. Natural history and risk stratification of arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia/cardiomyopathy. Circulation. 2004;110:1879–1884. - PubMed
-
- Dalal D, Nasir K, Bomma C, et al. Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia: a United States experience. Circulation. 2005;112:3823–3832. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- MOST 106-2314-B-075-006-MY3/Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan
- MOST 106-2314-B-010-046-MY3/Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan
- MOST 106-2314-B-075-073-MY3/Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan
- MOST 104-2314-B-010-063-MY2/Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan
- MOST 104-2314-B-075-089-MY3/Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan
- VGHUST105-G7-9-1/Research Foundation of Cardiovascular Medicine
- VGHUST105-G7-4-1/Research Foundation of Cardiovascular Medicine
- VGHUST104-G7-3-1/Research Foundation of Cardiovascular Medicine
- V104B-018/Szu-Yuan Research Foundation of Internal Medicine and Taipei Veterans General Hospital
- V104E7-001/Szu-Yuan Research Foundation of Internal Medicine and Taipei Veterans General Hospital
- V104C-121/Szu-Yuan Research Foundation of Internal Medicine and Taipei Veterans General Hospital
- V104C-109/Szu-Yuan Research Foundation of Internal Medicine and Taipei Veterans General Hospital
- V105B-014/Szu-Yuan Research Foundation of Internal Medicine and Taipei Veterans General Hospital
- V105C-122/Szu-Yuan Research Foundation of Internal Medicine and Taipei Veterans General Hospital
- V105C-116/Szu-Yuan Research Foundation of Internal Medicine and Taipei Veterans General Hospital
- V106C-158/Szu-Yuan Research Foundation of Internal Medicine and Taipei Veterans General Hospital
- V106B-010/Szu-Yuan Research Foundation of Internal Medicine and Taipei Veterans General Hospital
- V106C-104/Szu-Yuan Research Foundation of Internal Medicine and Taipei Veterans General Hospital
- V107B-014/Szu-Yuan Research Foundation of Internal Medicine and Taipei Veterans General Hospital
- V107C-060/Szu-Yuan Research Foundation of Internal Medicine and Taipei Veterans General Hospital
- V107C-054/Szu-Yuan Research Foundation of Internal Medicine and Taipei Veterans General Hospital
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

