Field evaluation of two commercial RT-rtPCR assays for porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus detection using sera from ill and healthy pigs, China
- PMID: 30239308
- PMCID: PMC6505843
- DOI: 10.1177/1040638718800357
Field evaluation of two commercial RT-rtPCR assays for porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus detection using sera from ill and healthy pigs, China
Abstract
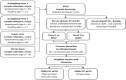
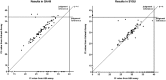
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) is a highly contagious respiratory virus causing severe morbidity in pigs worldwide. Control strategies for PRRSV often rely on detecting PRRSV, culling or isolating sick pigs, disinfecting pig barns, vaccination, and monitoring for virus spread. Given the high economic impact of PRRSV on pig farms, there is a great need for rapid and reliable PRRSV detection assays. We compared the performance of 2 commercial reverse-transcription real-time PCR (RT-rtPCR) assays, the VetMAX PRRSV NA and EU reagents (ABI assay) and the PRRSV general RT-rtPCR kit (Anheal assay), for the molecular detection of PRRSV in sera collected from pigs in China. Between June and September 2015, sera were collected from 219 healthy and 104 suspected PRRSV-infected pigs on 4 farms in China. Employing blinding, the 2 assays were run by 2 laboratories (Guangzhou Animal Health Inspection Institute [GAHII] and Sun Yat-sen University [SYSU] laboratories) and compared. Although both assays detected PRRSV with 100% specificity at both laboratories, the sensitivity (95% vs. 78% at GAHII; 94% vs. 72% at SYSU Laboratory) and the reproducibility (kappa value 0.933 vs. 0.931) were slightly better for the ABI assay compared to the Anheal assay.
Keywords: China; detection; porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome; test evaluation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Callahan JD, et al. Use of a portable real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction assay for rapid detection of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Am Vet Med Assoc 2002;220:1636–1642. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

