Dietary Antioxidants, Circulating Antioxidant Concentrations, Total Antioxidant Capacity, and Risk of All-Cause Mortality: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Observational Studies
- PMID: 30239557
- PMCID: PMC6247336
- DOI: 10.1093/advances/nmy040
Dietary Antioxidants, Circulating Antioxidant Concentrations, Total Antioxidant Capacity, and Risk of All-Cause Mortality: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Observational Studies
Abstract
The associations of various dietary or circulating antioxidants with the risk of all-cause mortality in the general population have not been established yet. A systematic search was performed in PubMed and Scopus, from their inception up to October 2017. Prospective observational studies reporting risk estimates of all-cause mortality in relation to dietary intake and/or circulating concentrations of antioxidants were included. Random-effects meta-analyses were conducted. Forty-one prospective observational studies (total n = 507,251) involving 73,965 cases of all-cause mortality were included. The RRs of all-cause mortality for the highest compared with the lowest category of circulating antioxidant concentrations were as follows: total carotenes, 0.60 (95% CI: 0.46, 0.74); vitamin C, 0.61 (95% CI: 0.53, 0.69); selenium, 0.62 (95% CI: 0.45, 0.79); β-carotene, 0.63 (95% CI: 0.57, 0.70); α-carotene, 0.68 (95% CI: 0.58, 0.78); total carotenoids, 0.68 (95% CI: 0.56, 0.80); lycopene, 0.75 (95% CI: 0.54, 0.97); and α-tocopherol, 0.84 (95% CI: 0.77, 0.91). The RRs for dietary intakes were: total carotenoids, 0.76 (95% CI: 0.66, 0.85); total antioxidant capacity, 0.77 (95% CI: 0.73, 0.81); selenium, 0.79 (95% CI: 0.73, 0.85); α-carotene, 0.79 (95% CI: 0.63, 0.94); β-carotene, 0.82 (95% CI: 0.77, 0.86); vitamin C, 0.88 (95% CI: 0.83, 0.94); and total carotenes, 0.89 (95% CI: 0.81, 0.97). A nonsignificant inverse association was found for dietary zinc, zeaxanthin, lutein, and vitamin E. The nonlinear dose-response meta-analyses demonstrated a linear inverse association in the analyses of dietary β-carotene and total antioxidant capacity, as well as in the analyses of circulating α-carotene, β-carotene, selenium, vitamin C, and total carotenoids. The association appeared to be U-shaped in the analyses of serum lycopene and dietary vitamin C. The present study indicates that adherence to a diet with high antioxidant properties may reduce the risk of all-cause mortality. Our results confirm current recommendations that promote higher intake of antioxidant-rich foods such as fruit and vegetables.
Figures
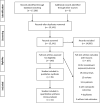
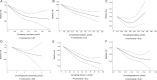
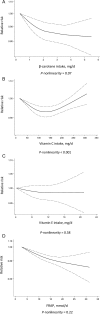
References
-
- Beaglehole R, Bonita R, Horton R, Adams C, Alleyne G, Asaria P, Baugh V, Bekedam H, Billo N, Casswell S. Priority actions for the non-communicable disease crisis. Lancet North Am Ed 2011;377(9775):1438–47. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Global status report on noncommunicable diseases 2014. Geneva: WHO; 2014. - PubMed
-
- Sies H. Oxidative stress: oxidants and antioxidants. Exp Physiol 1997;82(2):291–5. - PubMed
-
- Siti HN, Kamisah Y, Kamsiah J. The role of oxidative stress, antioxidants and vascular inflammation in cardiovascular disease (a review). Vascul Pharmacol 2015;71:40–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

