Randomized Controlled Trial of a Mobile Health Intervention to Promote Retention and Adherence to Preexposure Prophylaxis Among Young People at Risk for Human Immunodeficiency Virus: The EPIC Study
- PMID: 30239620
- PMCID: PMC6541706
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciy810
Randomized Controlled Trial of a Mobile Health Intervention to Promote Retention and Adherence to Preexposure Prophylaxis Among Young People at Risk for Human Immunodeficiency Virus: The EPIC Study
Abstract
Background: Young men who have sex with men are among the most vulnerable to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. Although preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) has demonstrated effectiveness, adherence and retention have been low among youth.
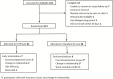
Methods: We conducted a randomized controlled trial to evaluate the impact of a youth-tailored, bidirectional text-messaging intervention (PrEPmate) on study retention and PrEP adherence. Young individuals at risk for HIV initiating PrEP within Chicago's safety-net system were randomized 2:1 to receive PrEPmate or standard of care (SoC) for 36 weeks. The primary retention outcome was study-visit completion, and the primary adherence outcome was tenofovir diphosphate (TFV-DP) concentrations ≥700 fmol/punch (consistent with ≥4 doses/week) assessed at 4, 12, 24, and 36 weeks. The impact of PrEPmate on retention and adherence was evaluated using generalized estimating equation logistic models with robust standard errors.
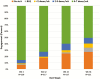
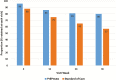
Results: From April 2015 to March 2016, 121 participants enrolled (mean age 24; 27% black, 36% Latino). Participants who received PrEPmate were more likely to attend study visits (86% PrEPmate vs. 71% SoC, odds ratio [OR] = 2.62, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.24-5.54) and have TFV-DP levels consistent with ≥4 doses/week (72% PrEPmate vs. 57% SoC, OR = 2.05, 95% CI 1.06-3.94). PrEPmate efficacy did not differ significantly by age, race/ethnicity, education, or insurance. Overall, 88% reported PrEPmate to be very/somewhat helpful, and 92% would recommend PrEPmate to others.
Conclusions: An interactive text-messaging intervention had high acceptability and significantly increased study-visit retention and PrEP adherence among young individuals at risk for HIV acquisition.
Clinical trials registration: NCT02371525.
Keywords: adherence; men who have sex with men (MSM); preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP); retention; text-messaging.
© The Author(s) 2018. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures

References
-
- Thigpen MC, Kebaabetswe PM, Paxton LA, et al. ; TDF2 Study Group. Antiretroviral preexposure prophylaxis for heterosexual HIV transmission in Botswana. N Engl J Med 2012; 367:423–34. - PubMed
-
- Choopanya K, Martin M, Suntharasamai P, et al. ; Bangkok Tenofovir Study Group. Antiretroviral prophylaxis for HIV infection in injecting drug users in Bangkok, Thailand (the Bangkok Tenofovir Study): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2013; 381:2083–90. - PubMed
-
- Molina JM, Capitant C, Spire B, et al. ; ANRS IPERGAY Study Group. On-demand preexposure prophylaxis in men at high risk for HIV-1 infection. N Engl J Med 2015; 373:2237–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

