Extensive evaluation of the generalized relevance network approach to inferring gene regulatory networks
- PMID: 30239704
- PMCID: PMC6420648
- DOI: 10.1093/gigascience/giy118
Extensive evaluation of the generalized relevance network approach to inferring gene regulatory networks
Abstract
Background: The generalized relevance network approach to network inference reconstructs network links based on the strength of associations between data in individual network nodes. It can reconstruct undirected networks, i.e., relevance networks, sensu stricto, as well as directed networks, referred to as causal relevance networks. The generalized approach allows the use of an arbitrary measure of pairwise association between nodes, an arbitrary scoring scheme that transforms the associations into weights of the network links, and a method for inferring the directions of the links. While this makes the approach powerful and flexible, it introduces the challenge of finding a combination of components that would perform well on a given inference task.
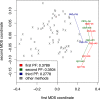
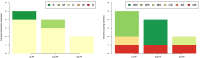
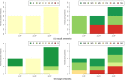
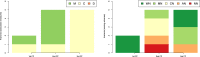
Results: We address this challenge by performing an extensive empirical analysis of the performance of 114 variants of the generalized relevance network approach on 47 tasks of gene network inference from time-series data and 39 tasks of gene network inference from steady-state data. We compare the different variants in a multi-objective manner, considering their ranking in terms of different performance metrics. The results suggest a set of recommendations that provide guidance for selecting an appropriate variant of the approach in different data settings.
Conclusions: The association measures based on correlation, combined with a particular scoring scheme of asymmetric weighting, lead to optimal performance of the relevance network approach in the general case. In the two special cases of inference tasks involving short time-series data and/or large networks, association measures based on identifying qualitative trends in the time series are more appropriate.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

