Mechanistic insights into histone deposition and nucleosome assembly by the chromatin assembly factor-1
- PMID: 30239791
- PMCID: PMC6212844
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gky823
Mechanistic insights into histone deposition and nucleosome assembly by the chromatin assembly factor-1
Abstract
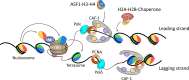
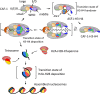
Eukaryotic chromatin is a highly dynamic structure with essential roles in virtually all DNA-dependent cellular processes. Nucleosomes are a barrier to DNA access, and during DNA replication, they are disassembled ahead of the replication machinery (the replisome) and reassembled following its passage. The Histone chaperone Chromatin Assembly Factor-1 (CAF-1) interacts with the replisome and deposits H3-H4 directly onto newly synthesized DNA. Therefore, CAF-1 is important for the establishment and propagation of chromatin structure. The molecular mechanism by which CAF-1 mediates H3-H4 deposition has remained unclear. However, recent studies have revealed new insights into the architecture and stoichiometry of the trimeric CAF-1 complex and how it interacts with and deposits H3-H4 onto substrate DNA. The CAF-1 trimer binds to a single H3-H4 dimer, which induces a conformational rearrangement in CAF-1 promoting its interaction with substrate DNA. Two CAF-1•H3-H4 complexes co-associate on nucleosome-free DNA depositing (H3-H4)2 tetramers in the first step of nucleosome assembly. Here, we review the progress made in our understanding of CAF-1 structure, mechanism of action, and how CAF-1 contributes to chromatin dynamics during DNA replication.
Figures

References
-
- Luger K., Mäder A.W., Richmond R.K., Sargent D.F., Richmond T.J.. Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 2.8 A resolution. Nature. 1997; 389:251–260. - PubMed
-
- Kornberg R.D. Chromatin structure: a repeating unit of histones and DNA. Science. 1974; 184:868–871. - PubMed
-
- Alabert C., Groth A.. Chromatin replication and epigenome maintenance. Nat. Rev MCB. 2012; 13:153–167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

