Idea and innovation: Secure fixation between dermis and periosteum using perforator flap to prevent recurrence of pilonidal sinus disease
- PMID: 30240147
- PMCID: PMC7949350
- DOI: 10.1111/iwj.12981
Idea and innovation: Secure fixation between dermis and periosteum using perforator flap to prevent recurrence of pilonidal sinus disease
Abstract
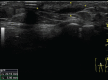
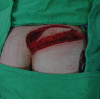
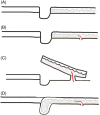
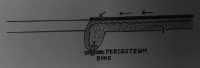
In the past decades, numerous surgical techniques and conservative treatments for pilonidal sinus disease (PSD) had been discussed and published. There is still no consensus yet of the best techniques because of high recurrence rates and prolonged wound healing. In the case of complicated discharging sinus or recurrent PSD resistant to treatment with antibiotics, we recommend radical excision followed by a regional flap, which can obliterate the dead space with well-vascularised tissue. In this article, we presented the technique of snug suture fixation between the dermis and periosteum using a superior gluteal artery perforator (SGAP) flap. The study demonstrates a few key concepts on the prevention of PSD recurrence, an off-midline, well-perfused flap that allows flattened natal cleft and obliteration of gluteal cleft and eventually showed good aesthetic results. We aim to demonstrate a reliable surgical technique for wound closure of recurrent pilonidal sinus after radical excision followed by reconstruction with an SGAP flap. The history, surgery, and images are described, and the literature is reviewed. The pitfalls of disease recurrence will be discussed in this literature. Keys to successful treatment will be elaborated. An 18-year-old female with recurrent pilonidal sinus disease over right medial gluteal region presented with sacral pain and infection. She developed progressive swelling and burst of abscess from several sinus tracts and did not respond to the treatment with antibiotics alone. After radical excision of the entire pilonidal sinus and adjacent fibrotic tissue, a deep and large defect was measured. A superior gluteal perforator flap was designed based on three perforators from the superior gluteal artery. A medial 3 cm of the SGAP flap was de-epithelised to provide soft tissue bulk to obliterate the deep cavity. Strong sutures were applied to secure the flap to the periosteum. There was no recurrence at 3 years of follow up. The patient stood the operation well and had prompt recovery.
© 2018 Medicalhelplines.com Inc and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A useful alternative surgical technique to reconstructing large defects following excision of recurrent pilonidal sinus disease in the intergluteal region: An operative approach for the transverse lumbar artery perforator flap.Int Wound J. 2018 Aug;15(4):534-537. doi: 10.1111/iwj.12894. Epub 2018 May 21. Int Wound J. 2018. PMID: 29781208 Free PMC article.
-
Superior gluteal artery perforator flap in the reconstruction of pilonidal sinus.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2010 Jan;63(1):133-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2008.07.017. Epub 2008 Nov 14. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2010. PMID: 19010110
-
[Effectiveness of fascial tissue flaps and skin flaps with layered sutures for repair of wounds after excision of sacrococcygeal pilonidal sinus].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023 Apr 15;37(4):478-481. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202301035. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37070318 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Contralateral Limberg flap reconstruction for pilonidal disease recurrence.Asian J Surg. 2019 Aug;42(8):787-791. doi: 10.1016/j.asjsur.2018.12.008. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Asian J Surg. 2019. PMID: 30711442 Review.
-
A comparison of flap reconstruction vs the laying open technique or excision and direct suture for pilonidal sinus disease: A meta-analysis of randomised studies.Int Wound J. 2019 Oct;16(5):1119-1135. doi: 10.1111/iwj.13163. Epub 2019 Jun 23. Int Wound J. 2019. PMID: 31230414 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Corman ML. Classic articles in colonic and rectal surgery, pilonidal sinus. Dis Colon Rectum. 1981;24:324‐326. - PubMed
-
- Shabbir J, Chaudhary BN, Britton DC. Management of sacrococcygeal pilonidal sinus disease: a snapshot of current practice. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2011;26:1619‐1620. - PubMed
-
- Doll D, Friederichs J, Dettmann H, Boulesteix A‐L, Duesel W, Petersen S. Time and rate of sinus formation in pilonidal sinus disease. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2008;23:359‐364. - PubMed
-
- Doll D, Matevossian E, Wietelmann K, Evers T, Kriner M, Petersen S. Family history of pilonidal sinus predisposes to earlier onset of disease and a 50% long‐term recurrence rate. Dis Colon Rectum. 2009;52:1610‐1615. - PubMed
-
- de Parades V, Bouchard D, Janier M, Berger A. Pilonidal sinus disease. J Visc Surg. 2013;150:237‐247. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

