Preclinical Efficacy and Characterization of Candidate Vaccines for Treatment of Opioid Use Disorders Using Clinically Viable Carrier Proteins
- PMID: 30240216
- PMCID: PMC6361123
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b00592
Preclinical Efficacy and Characterization of Candidate Vaccines for Treatment of Opioid Use Disorders Using Clinically Viable Carrier Proteins
Abstract
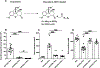
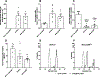
Vaccines may offer a new treatment strategy for opioid use disorders and opioid-related overdoses. To speed translation, this study evaluates opioid conjugate vaccines containing components suitable for pharmaceutical manufacturing and compares analytical assays for conjugate characterization. Three oxycodone-based haptens (OXY) containing either PEGylated or tetraglycine [(Gly)4] linkers were conjugated to a keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH) carrier protein via carbodiimide (EDAC) or maleimide chemistry. The EDAC-conjugated OXY(Gly)4-KLH was most effective in reducing oxycodone distribution to the brain in mice. Vaccine efficacy was T cell-dependent. The lead OXY hapten was conjugated to the KLH, tetanus toxoid, diphtheria cross-reactive material (CRM), as well as the E. coli-expressed CRM (EcoCRM) and nontoxic tetanus toxin heavy chain fragment C (rTTHc) carrier proteins. All vaccines induced early hapten-specific B cell expansion and showed equivalent efficacy against oxycodone in mice. However, some hapten-protein conjugates were easier to characterize for molecular weight and size. Finally, heroin vaccines formulated with either EcoCRM or KLH were equally effective in reducing heroin-induced antinociception and distribution to the brain of heroin and its metabolites in mice. This study identifies vaccine candidates and vaccine components for further development.
Keywords: carrier protein; conjugate vaccine; hapten; heroin; linkers; oxycodone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): M.P. is the inventor of Cytokine Signaling Immunomodulators and Methods. Provisional Patent Application No. 62/334, 167 filed on May 10, 2016 and International Application No. PCT/US2017/031907 filed on May 10, 2017. A.L. is the Scientific Director at Fina BioSolutions, LLC. and owner. The other authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- World Drug Report. 2018 https://www.unodc.org/wdr2018/index.html.
-
- Butler DC; Shanks K; Behonick GS; Smith D; Presnell SE; Tormos LM Three Cases of Fatal Acrylfentanyl Toxicity in the United States and a Review of Literature. J. Anal. Toxicol 2018, 42 (1), e6–e11. - PubMed
-
- Helander A; Backberg M; Signell P; Beck O Intoxications involving acrylfentanyl and other novel designer fentanyls - results from the Swedish STRIDA project. Clin. Toxicol 2017, 55 (6), 589–599. - PubMed
-
- Key substance use and mental health indicators in the United States: Results from the 2016 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (HHS Publication No. SMA 17–5044, NSDUH Series H-52); Center for Behavioral Health Statistics and Quality, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration: Rockville, 2017.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

