ARAP1 Bridges Actin Dynamics and AP-3-Dependent Membrane Traffic in Bone-Digesting Osteoclasts
- PMID: 30240610
- PMCID: PMC6137390
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2018.07.019
ARAP1 Bridges Actin Dynamics and AP-3-Dependent Membrane Traffic in Bone-Digesting Osteoclasts
Abstract
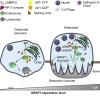
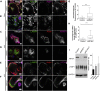
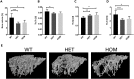
Bone-resorbing osteoclasts play a central role in bone remodeling and its pathology. To digest bone, osteoclasts re-organize both F-actin, to assemble podosomes/sealing zones, and membrane traffic, to form bone-facing ruffled borders enriched in lysosomal membrane proteins. It remains elusive how these processes are coordinated. Here, we show that ARAP1 (ArfGAP with RhoGAP domain, ankyrin repeat and PH domain-containing protein 1) fulfills this function. At podosomes/sealing zones, ARAP1 is part of a protein complex where its RhoGAP domain regulates actin dynamics. At endosomes, ARAP1 interacts with AP-3 adaptor complexes where its Arf-GAP domain regulates the Arf1-dependent AP-3 binding to membranes and, consequently lysosomal membrane protein transport to ruffled borders. Accordingly, ARAP1 or AP-3 depletion in osteoclasts alters their capacity to digest bone in vitro. and AP-3δ-deficient mocha mice, a model of the Hermansky-Pudlak storage pool syndrome, develop osteoporosis. Thus, ARAP1 bridges F-actin and membrane dynamics in osteoclasts for proper bone homeostasis.
Keywords: Cell Biology; Functional Aspects of Cell Biology; Organizational Aspects of Cell Biology.
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Akamine A., Tsukuba T., Kimura R., Maeda K., Tanaka Y., Kato K., Yamamoto K. Increased synthesis and specific localization of a major lysosomal membrane sialoglycoprotein (LGP107) at the ruffled border membrane of active osteoclasts. Histochemistry. 1993;100:101–108. - PubMed
-
- Borinstein S.C., Hyatt M.A., Sykes V.W., Straub R.E., Lipkowitz S., Boulter J., Bogler O. SETA is a multifunctional adapter protein with three SH3 domains that binds Grb2, Cbl, and the novel SB1 proteins. Cell. Signal. 2000;12:769–779. - PubMed
-
- Buccione R., Orth J.D., McNiven M.A. Foot and mouth: podosomes, invadopodia and circular dorsal ruffles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004;5:647–657. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

