Label-free 3D-CLEM Using Endogenous Tissue Landmarks
- PMID: 30240628
- PMCID: PMC6137285
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2018.07.012
Label-free 3D-CLEM Using Endogenous Tissue Landmarks
Abstract
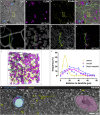
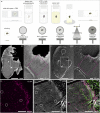
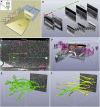
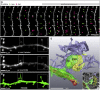
Emerging 3D correlative light and electron microscopy approaches enable studying neuronal structure-function relations at unprecedented depth and precision. However, established protocols for the correlation of light and electron micrographs rely on the introduction of artificial fiducial markers, such as polymer beads or near-infrared brandings, which might obscure or even damage the structure under investigation. Here, we report a general applicable "flat embedding" preparation, enabling high-precision overlay of light and scanning electron micrographs, using exclusively endogenous landmarks in the brain: blood vessels, nuclei, and myelinated axons. Furthermore, we demonstrate feasibility of the workflow by combining in vivo 2-photon microscopy and focused ion beam scanning electron microscopy to dissect the role of astrocytic coverage in the persistence of dendritic spines.
Keywords: Biological Sciences Research Methodologies; Biological Sciences Tools; Neuroscience; Techniques in Neuroscience.
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Araque A., Parpura V., Sanzgiri R.P., Haydon P.G. Tripartite synapses: glia, the unacknowledged partner. Trends Neurosci. 1999;22:208–215. - PubMed
-
- Belu A., Schnitker J., Bertazzo S., Neumann E., Mayer D., Offenhäusser A., Santoro F. Ultra-thin resin embedding method for scanning electron microscopy of individual cells on high and low aspect ratio 3D nanostructures. J. Microsc. 2016;263:78–86. - PubMed
-
- Bishop D., Nikić I., Brinkoetter M., Knecht S., Potz S., Kerschensteiner M., Misgeld T. Near-infrared branding efficiently correlates light and electron microscopy. Nat. Methods. 2011;8:568–570. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

