Characterization of a strong and constitutive promoter from the Arabidopsis serine carboxypeptidase-like gene AtSCPL30 as a potential tool for crop transgenic breeding
- PMID: 30241468
- PMCID: PMC6151023
- DOI: 10.1186/s12896-018-0470-x
Characterization of a strong and constitutive promoter from the Arabidopsis serine carboxypeptidase-like gene AtSCPL30 as a potential tool for crop transgenic breeding
Abstract
Background: Transgenic technology has become an important technique for crop genetic improvement. The application of well-characterized promoters is essential for developing a vector system for efficient genetic transformation. Therefore, isolation and functional validation of more alternative constitutive promoters to the CaMV35S promoter is highly desirable.
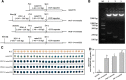
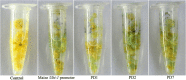
Results: In this study, a 2093-bp sequence upstream of the translation initiation codon ATG of AtSCPL30 was isolated as the full-length promoter (PD1). To characterize the AtSCPL30 promoter (PD1) and eight 5' deleted fragments (PD2-PD9) of different lengths were fused with GUS to produce the promoter::GUS plasmids and were translocated into Nicotiana benthamiana. PD1-PD9 could confer strong and constitutive expression of transgenes in almost all tissues and development stages in Nicotiana benthamiana transgenic plants. Additionally, PD2-PD7 drove transgene expression consistently over twofold higher than the well-used CaMV35S promoter under normal and stress conditions. Among them, PD7 was only 456 bp in length, and its transcriptional activity was comparable to that of PD2-PD6. Moreover, GUS transient assay in the leaves of Nicotiana benthamiana revealed that the 162-bp (- 456~ - 295 bp) and 111-bp (- 294~ - 184 bp) fragments from the AtSCPL30 promoter could increase the transcriptional activity of mini35S up to 16- and 18-fold, respectively.
Conclusions: As a small constitutive strong promoter of plant origin, PD7 has the advantage of biosafety and reduces the probability of transgene silencing compared to the virus-derived CaMV35S promoter. PD7 would also be an alternative constitutive promoter to the CaMV35S promoter when multigene transformation was performed in the same vector, thereby avoiding the overuse of the CaMV35S promoter and allowing for the successful application of transgenic technology. And, the 162- and 111-bp fragments will also be very useful for synthetic promoter design based on their high enhancer activities.
Keywords: AtSCPL30; CaMV35S; Constitutive promoter; GUS analysis; Nicotiana benthamiana; Stress treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A Synthetic Strong and Constitutive Promoter Derived from the Stellaria media pro-SmAMP1 and pro-SmAMP2 Promoters for Effective Transgene Expression in Plants.Genes (Basel). 2020 Nov 26;11(12):1407. doi: 10.3390/genes11121407. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33256091 Free PMC article.
-
Development of an intra-molecularly shuffled efficient chimeric plant promoter from plant infecting Mirabilis mosaic virus promoter sequence.J Biotechnol. 2014 Jan;169:103-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2013.08.022. Epub 2013 Sep 20. J Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24060830
-
Development of useful recombinant promoter and its expression analysis in different plant cells using confocal laser scanning microscopy.PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24627. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024627. Epub 2011 Sep 9. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21931783 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional and post-transcriptional controls for tuning gene expression in plants.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2023 Feb;71:102315. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2022.102315. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2023. PMID: 36462457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intron-Mediated Enhancement: A Tool for Heterologous Gene Expression in Plants?Front Plant Sci. 2017 Jan 6;7:1977. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01977. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28111580 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Overview of Repressive miRNA Regulation by Short Tandem Target Mimic (STTM): Applications and Impact on Plant Biology.Plants (Basel). 2023 Feb 3;12(3):669. doi: 10.3390/plants12030669. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36771753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arabidopsis as a model for translational research.Plant Cell. 2025 May 9;37(5):koae065. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koae065. Plant Cell. 2025. PMID: 38411602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An endogenous promoter LpSUT2 discovered in duckweed: a promising transgenic tool for plants.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Apr 3;15:1368284. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1368284. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38638348 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and analysis of the promoter region of monodehydroascorbate reductase 4 (CpMDAR4) in papaya.Plant Reprod. 2022 Dec;35(4):233-264. doi: 10.1007/s00497-022-00447-2. Epub 2022 Aug 3. Plant Reprod. 2022. PMID: 35920937
-
Ectopic Expression of the Rice Grain-Size-Affecting Gene GS5 in Maize Affects Kernel Size by Regulating Endosperm Starch Synthesis.Genes (Basel). 2022 Aug 26;13(9):1542. doi: 10.3390/genes13091542. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36140710 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Potenza C, Aleman L, Sengupta-Gopalan C. Targeting transgene expression in research, agricultural, and environmental applications: promoters used in plant transformation. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 2004;40:1–22. doi: 10.1079/IVP2003477. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

