Meiotic Double-Strand Break Proteins Influence Repair Pathway Utilization
- PMID: 30242011
- PMCID: PMC6218235
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.118.301402
Meiotic Double-Strand Break Proteins Influence Repair Pathway Utilization
Abstract
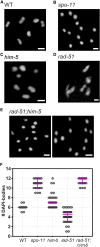
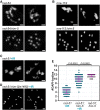
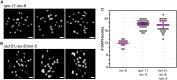
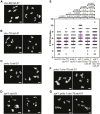
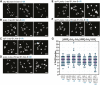
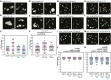
Double-strand breaks (DSBs) are among the most deleterious lesions DNA can endure. Yet, DSBs are programmed at the onset of meiosis, and are required to facilitate appropriate reduction of ploidy in daughter cells. Repair of these breaks is tightly controlled to favor homologous recombination (HR)-the only repair pathway that can form crossovers. However, little is known about how the activities of alternative repair pathways are regulated at these stages. We discovered an unexpected synthetic interaction between the DSB machinery and strand-exchange proteins. Depleting the Caenorhabditis elegans DSB-promoting factors HIM-5 and DSB-2 suppresses the formation of chromosome fusions that arise in the absence of RAD-51 or other strand-exchange mediators. Our investigations reveal that nonhomologous and theta-mediated end joining (c-NHEJ and TMEJ, respectively) and single strand annealing (SSA) function redundantly to repair DSBs when HR is compromised, and that HIM-5 influences the utilization of TMEJ and SSA.
Keywords: C. elegans; DNA repair; WormBase; double-strand break; meiosis; pathway choice.
Copyright © 2018 by the Genetics Society of America.
Figures

References
-
- Agostinho A., Meier B., Sonneville R., Jagut M., Woglar A., et al. , 2013. Combinatorial regulation of meiotic Holliday junction resolution in C. elegans by HIM-6 (BLM) helicase, SLX-4, and the SLX-1, MUS-81 and XPF-1 nucleases. PLoS Genet. 9: e1003591 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003591 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y., Krieger A. M., Yekutieli D., 2006. Adaptive linear step-up procedures that control the false discovery rate. Biometrika 93: 491–507. 10.1093/biomet/93.3.491 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

