Sensitivity to S-Cone Stimuli and the Development of Myopia
- PMID: 30242363
- PMCID: PMC6138264
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.18-24113
Sensitivity to S-Cone Stimuli and the Development of Myopia
Abstract
Purpose: Longitudinal chromatic aberration (LCA) is a color signal available to the emmetropization process that causes greater myopic defocus of short wavelengths than long wavelengths. We measured individual differences in chromatic sensitivity to explore the role LCA may play in the development of refractive error.
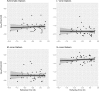
Methods: Forty-four observers were tested psychophysically after passing color screening tests and a questionnaire for visual defects. Refraction was measured and only subjects with myopia or hyperopia without severe astigmatism participated. Psychophysical detection thresholds for 3 cyc/deg achromatic, L-, M-, and S-cone-isolating Gabor patches and low-frequency S-cone increment (S+) and decrement (S-) blobs were measured. Parametric Pearson correlations for refractive error versus threshold were calculated and nonparametric bootstrap 95% percentage confidence intervals (BCIs) for r were computed.
Results: S-cone Gabor detection thresholds were higher than achromatic, L-, and M-cone Gabors. S-cone Gabor thresholds were higher than either S+ or S- blobs. These results are consistent with studies using smaller samples of practiced observers. None of the thresholds for the Gabor stimuli were correlated with refractive error (RE). A negative correlation with RE was observed for both S+ (r = -0.28; P = 0.06; BCI: r = -0.5, -0.04) and S- (r = -0.23; P = 0.13; BCI = -0.46, 0.01) blobs, although this relationship did not reach conventional statistical significance.
Conclusions: Thresholds for S+ and S- stimuli were negatively related to RE, indicating that myopes may have reduced sensitivity to low spatial frequency S-cone stimuli. This reduced S-cone sensitivity might have played a role in their failure to emmetropize normally.
Figures



References
-
- Flitcroft D. The complex interactions of retinal, optical and environmental factors in myopia aetiology. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2012;31:622–660. - PubMed
-
- Vitale S, Cotch MF, Sperduto R, Ellwein L. Costs of refractive correction of distance vision impairment in the United States, 1999–2002. Ophthalmology. 2006;113:2163–2170. - PubMed
-
- Rein DB, Zhang P, Wirth KE, et al. The economic burden of major adult visual disorders in the United States. Arch Ophthalmol. 2006;124:1754–1760. - PubMed
-
- Wallman J, Winawer J. Homeostasis of eye growth and the question of myopia. Neuron. 2004;43:447–468. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

