Cell Volume Control in Healthy Brain and Neuropathologies
- PMID: 30243438
- PMCID: PMC6416787
- DOI: 10.1016/bs.ctm.2018.07.006
Cell Volume Control in Healthy Brain and Neuropathologies
Abstract
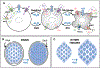
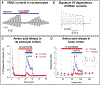
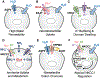
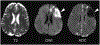
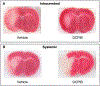
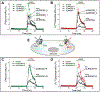
Regulation of cellular volume is a critical homeostatic process that is intimately linked to ionic and osmotic balance in the brain tissue. Because the brain is encased in the rigid skull and has a very complex cellular architecture, even minute changes in the volume of extracellular and intracellular compartments have a very strong impact on tissue excitability and function. The failure of cell volume control is a major feature of several neuropathologies, such as hyponatremia, stroke, epilepsy, hyperammonemia, and others. There is strong evidence that such dysregulation, especially uncontrolled cell swelling, plays a major role in adverse pathological outcomes. To protect themselves, brain cells utilize a variety of mechanisms to maintain their optimal volume, primarily by releasing or taking in ions and small organic molecules through diverse volume-sensitive ion channels and transporters. In principle, the mechanisms of cell volume regulation are not unique to the brain and share many commonalities with other tissues. However, because ions and some organic osmolytes (e.g., major amino acid neurotransmitters) have a strong impact on neuronal excitability, cell volume regulation in the brain is a surprisingly treacherous process, which may cause more harm than good. This topical review covers the established and emerging information in this rapidly developing area of physiology.
Keywords: Brain; Cell swelling; Cell volume regulation; Central nervous system; Epilepsy; Excitotoxicity; Glutamate release; Hyponatremia; Hyrerammonemia; Stroke; Volume-regulated anion channel.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Adrogue HJ & Madias NE (2000). Hyponatremia. N.Engl.J.Med, 342, 1581–1589. - PubMed
-
- Aitken PG, Borgdorff AJ, Juta AJ, Kiehart DP, Somjen GG, & Wadman WJ (1998). Volume changes induced by osmotic stress in freshly isolated rat hippocampal neurons. Pflugers Arch., 436, 991–998. - PubMed
-
- Aitken PG, Fayuk D, Somjen GG, & Turner DA (1999). Use of intrinsic optical signals to monitor physiological changes in brain tissue slices. Methods, 18, 91–103. - PubMed
-
- Akita T, Fedorovich SV, & Okada Y (2011). Ca2+ nanodomain-mediated component of swelling-induced volume-sensitive outwardly rectifying anion current triggered by autocrine action of ATP in mouse astrocytes. Cell Physiol Biochem., 28, 1181–1190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

