Excision release of 5?hydroxycytosine oxidatively induced DNA base lesions from the lung genome by cat dander extract challenge stimulates allergic airway inflammation
- PMID: 30244512
- PMCID: PMC6588164
- DOI: 10.1111/cea.13284
Excision release of 5?hydroxycytosine oxidatively induced DNA base lesions from the lung genome by cat dander extract challenge stimulates allergic airway inflammation
Abstract
Background: Ragweed pollen extract (RWPE) induces TLR4-NFκB-CXCL-dependent recruitment of ROS-generating neutrophils to the airway and OGG1 DNA glycosylase-dependent excision of oxidatively induced 8-OH-Gua DNA base lesions from the airway epithelial cell genome. Administration of free 8-OH-Gua base stimulates RWPE-induced allergic lung inflammation. These studies suggest that stimulation of innate receptors and their adaptor by allergenic extracts initiates excision of a set of DNA base lesions that facilitate innate/allergic lung inflammation.
Objective: To test the hypothesis that stimulation of a conserved innate receptor/adaptor pathway by allergenic extracts induces excision of a set of pro-inflammatory oxidatively induced DNA base lesions from the lung genome that stimulate allergic airway inflammation.
Methods: Wild-type (WT), Tlr4KO, Tlr2KO, Myd88KO, and TrifKO mice were intranasally challenged once or repeatedly with cat dander extract (CDE), and innate or allergic inflammation and gene expression were quantified. We utilized GC-MS/MS to quantify a set of oxidatively induced DNA base lesions after challenge of naïve mice with CDE.
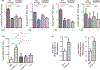
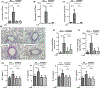
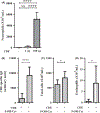
Results: A single CDE challenge stimulated innate neutrophil recruitment that was partially dependent on TLR4 and TLR2, and completely on Myd88, but not TRIF. A single CDE challenge stimulated MyD88-dependent excision of DNA base lesions 5-OH-Cyt, FapyAde, and FapyGua from the lung genome. A single challenge of naïve WT mice with 5-OH-Cyt stimulated neutrophilic lung inflammation. Multiple CDE instillations stimulated MyD88-dependent allergic airway inflammation. Multiple administrations of 5-OH-Cyt with CDE stimulated allergic sensitization and allergic airway inflammation.
Conclusions and clinical relevance: We show for the first time that CDE challenge stimulates MyD88-dependent excision of DNA base lesions. Our data suggest that the resultant-free base(s) contribute to CDE-induced innate/allergic lung inflammation. We suggest that blocking the MyD88 pathway in the airways with specific inhibitors may be a novel targeted strategy of inhibiting amplification of innate and adaptive immune inflammation in allergic diseases by oxidatively induced DNA base lesions.
© 2018 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
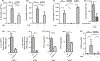


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

