Smartphone-based pathogen diagnosis in urinary sepsis patients
- PMID: 30245056
- PMCID: PMC6197494
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.09.001
Smartphone-based pathogen diagnosis in urinary sepsis patients
Abstract
Background: There is an urgent need for rapid, sensitive, and affordable diagnostics for microbial infections at the point-of-care. Although a number of innovative systems have been reported that transform mobile phones into potential diagnostic tools, the translational challenge to clinical diagnostics remains a significant hurdle to overcome.
Methods: A smartphone-based real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification (smaRT-LAMP) system was developed for pathogen ID in urinary sepsis patients. The free, custom-built mobile phone app allows the phone to serve as a stand-alone device for quantitative diagnostics, allowing the determination of genome copy-number of bacterial pathogens in real time.
Findings: A head-to-head comparative bacterial analysis of urine from sepsis patients revealed that the performance of smaRT-LAMP matched that of clinical diagnostics at the admitting hospital in a fraction of the time (~1 h vs. 18-28 h). Among patients with bacteremic complications of their urinary sepsis, pathogen ID from the urine matched that from the blood - potentially allowing pathogen diagnosis shortly after hospital admission. Additionally, smaRT-LAMP did not exhibit false positives in sepsis patients with clinically negative urine cultures.
Interpretation: The smaRT-LAMP system is effective against diverse Gram-negative and -positive pathogens and biological specimens, costs less than $100 US to fabricate (in addition to the smartphone), and is configurable for the simultaneous detection of multiple pathogens. SmaRT-LAMP thus offers the potential to deliver rapid diagnosis and treatment of urinary tract infections and urinary sepsis with a simple test that can be performed at low cost at the point-of-care. FUND: National Institutes of Health, Chan-Zuckerberg Biohub, Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation.
Keywords: Smartphone-based pathogen diagnosis; Urinary diagnostic test; Urinary sepsis; Urinary tract infection.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

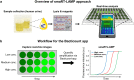


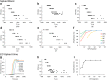

Comment in
-
Calling in the test: Smartphone-based urinary sepsis diagnostics.EBioMedicine. 2018 Nov;37:11-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.10.047. Epub 2018 Oct 25. EBioMedicine. 2018. PMID: 30482724 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization . 2015. Worldwide Country Situation Analysis: Response to Antimicrobial Resistance.
-
- Opota O., Jaton K., Greub G. Microbial diagnosis of bloodstream infection: towards molecular diagnosis directly from blood. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2015;21(4):323–331. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

