A Novel Natural Antimicrobial Can Reduce the in vitro and in vivo Pathogenicity of T6SS Positive Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli Chicken Isolates
- PMID: 30245680
- PMCID: PMC6137164
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02139
A Novel Natural Antimicrobial Can Reduce the in vitro and in vivo Pathogenicity of T6SS Positive Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli Chicken Isolates
Abstract
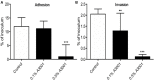
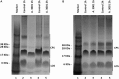
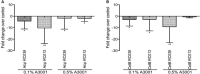
Human campylobacteriosis is considered one of the most common foodborne diseases worldwide with poultry identified as the main source of infection accounting for 50-80% of human cases. Highly virulent Campylobacter spp., positive for the Type VI secretion system (T6SS), which have an increased ability to adhere to and invade the host gastrointestinal epithelium are highly prevalent in poultry. Multidrug resistant strains of bacteria are rapidly evolving and therefore, new antimicrobials to supplement animal feed that are able to control Campylobacter species, are in great need. The work presented herein indicates that a novel phenolic antimicrobial, Auranta 3001, is able to reduce the adhesion and invasion of human intestinal epithelial cells (HCT-8) by two T6SS positive chicken isolates, C. jejuni RC039 (p < 0.05) and C. coli RC013 (p < 0.001). Exposure of C. jejuni RC039 and C. coli RC013 to Auranta 3001 downregulated the expression of hcp and cetB genes, known to be important in the functionality of T6SS. Furthermore, the reduced adhesion and invasion is associated with a significant decrease in bacterial motility of both isolates (p < 0.05-p < 0.001) in vitro. Most importantly our in vivo results show that Auranta 3001 is able to reduce cecum colonization levels from log 8 CFU/ml to log 2 CFU/ml for C. jejuni RC039 and from log 7 CFU/ml to log 2 CFU/ml for C. coli RC013. In conclusion, this novel antimicrobial is able to reduce the pathogenic properties of T6SS campylobacters in vitro and also to decrease colonization in vivo.
Keywords: Campylobacter coli; Campylobacter jejuni; HCT-8; attachment; gene expression; invasion.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Virulence characteristics of hcp (+) Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli isolates from retail chicken.Gut Pathog. 2015 Jul 24;7:20. doi: 10.1186/s13099-015-0067-z. eCollection 2015. Gut Pathog. 2015. PMID: 26207145 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of natural antimicrobials on the Campylobacter coli T6SS+/- during in vitro infection assays and on their ability to adhere to chicken skin and carcasses.Int J Food Microbiol. 2021 Jan 2;338:108998. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2020.108998. Epub 2020 Nov 27. Int J Food Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33279789
-
The Campylobacter jejuni Type VI Secretion System Enhances the Oxidative Stress Response and Host Colonization.Front Microbiol. 2019 Dec 17;10:2864. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02864. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31921044 Free PMC article.
-
Campylobacter jejuni type VI secretion system: roles in adaptation to deoxycholic acid, host cell adherence, invasion, and in vivo colonization.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e42842. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042842. Epub 2012 Aug 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22952616 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical impact of the type VI secretion system on virulence of Campylobacter species during infection.BMC Infect Dis. 2019 Mar 7;19(1):237. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-3858-x. BMC Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 30845966 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Attenuation of Vibrio parahaemolyticus Virulence Factors by a Mixture of Natural Antimicrobials.Microorganisms. 2019 Dec 11;7(12):679. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7120679. Microorganisms. 2019. PMID: 31835728 Free PMC article.
-
Phenolic-Rich Plant Extracts With Antimicrobial Activity: An Alternative to Food Preservatives and Biocides?Front Microbiol. 2022 Jan 4;12:753518. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.753518. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35058892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined application of bacteriophages with a competitive exclusion culture and carvacrol with organic acids can reduce Campylobacter in primary broiler production.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 22;14(1):9218. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-59563-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38649444 Free PMC article.
-
Virulence of a T6SS Campylobacter jejuni chicken isolate from North Romania.BMC Res Notes. 2019 Mar 28;12(1):180. doi: 10.1186/s13104-019-4201-8. BMC Res Notes. 2019. PMID: 30922352 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral activity of a novel mixture of natural antimicrobials, in vitro, and in a chicken infection model in vivo.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 6;10(1):16631. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73916-1. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33024252 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burt S. A., Adolfse S. J., Ahad D. S., Tersteeg-Zijderveld M. H., Jongerius-Gortemaker B. G., Post J. A., et al. (2016). Cinnamaldehyde, carvacrol and organic acids affect gene expression of selected oxidative stress and inflammation markers in IPEC-J2 cells exposed to Salmonella typhimurium. Phytother. Res. 30 1988–2000. 10.1002/ptr.5705 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

