Vascular Leaking, a Pivotal and Early Pathogenetic Event in Systemic Sclerosis: Should the Door Be Closed?
- PMID: 30245695
- PMCID: PMC6137210
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02045
Vascular Leaking, a Pivotal and Early Pathogenetic Event in Systemic Sclerosis: Should the Door Be Closed?
Abstract
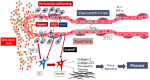
The early phase of systemic sclerosis (SSc) presents edema as one of the main features: this is clinically evident in the digital swelling (puffy fingers) as well as in the edematous skin infiltration of the early active diffuse subset. Other organs could be affected by this same disease process, such as the lung (with the appearance of ground glass opacities) and the heart (with edematous changes on cardiac magnetic resonance imaging). The genesis of tissue edema is tightly linked to pathological changes in the endothelium: various reports demonstrated the effect of transforming growth factor β, vascular endothelial growth factor and hypoxia-reperfusion damage with reactive oxygen species generation in altering vascular permeability and extravasation, in particular in SSc. This condition has an alteration in the glycocalyx thickness, reducing the protection of the vessel wall and causing non-fibrotic interstitial edema, a marker of vascular leak. Moreover, changes in the junctional adhesion molecule family and other adhesion molecules, such as ICAM and VCAM, are associated with an increased myeloid cells' extravasation in the skin and increased myofibroblasts transformation with further vascular leak and cellular migration. This mini-review examines current knowledge on determinants of vascular leak in SSc, shedding light on the role of vascular protection. This could enhance further studies in the light of drug development for early treatment, suggesting that the control of vascular leakage should be considered in the same way that vasodilation and inflammation reduction, as potential therapeutic targets.
Keywords: capillary leak; edema; endothelial dysfunction; extravasation; permeability; systemic sclerosis; vasculopathy.
Figures

References
-
- Varga J, Trojanowska M, Kuwana M. Pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis: recent insights of molecular and cellular mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. J Scleroderma Relat Disord. (2017) 2:137–52. 10.5301/jsrd.5000249 - DOI
-
- Seymour LW. Passive tumor targeting of soluble macromolecules and drug conjugates. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. (1992) 9:135–87. - PubMed
-
- Schoefl GI. Electron microscopic observations on the regeneration of blood vessels after injury. Ann N Y Acad Sci. (1964) 116:789–802. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

