The effect of low-magnitude, high-frequency vibration on poly(ethylene glycol)-microencapsulated mesenchymal stem cells
- PMID: 30245801
- PMCID: PMC6146326
- DOI: 10.1177/2041731418800101
The effect of low-magnitude, high-frequency vibration on poly(ethylene glycol)-microencapsulated mesenchymal stem cells
Abstract
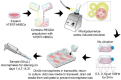
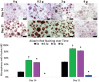
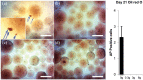
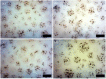
Low-magnitude, high-frequency vibration has stimulated osteogenesis in mesenchymal stem cells when these cells were cultured in certain types of three-dimensional environments. However, results of osteogenesis are conflicting with some reports showing no effect of vibration at all. A large number of vibration studies using three-dimensional scaffolds employ scaffolds derived from natural sources. Since these natural sources potentially have inherent biochemical and microarchitectural cues, we explored the effect of low-magnitude, high-frequency vibration at low, medium, and high accelerations when mesenchymal stem cells were encapsulated in poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate microspheres. Low and medium accelerations enhanced osteogenesis in mesenchymal stem cells while high accelerations inhibited it. These studies demonstrate that the isolated effect of vibration alone induces osteogenesis.
Keywords: Cell microencapsulation; differentiation; high-frequency vibration; low-magnitude; mesenchymal stem cells; osteogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures



References
-
- Xie L, Jacobson JM, Choi ES, et al. Low-level mechanical vibrations can influence bone resorption and bone formation in the growing skeleton. Bone 2006; 39: 1059–1066. - PubMed
-
- Judex S, Lei X, Han D, et al. Low-magnitude mechanical signals that stimulate bone formation in the ovariectomized rat are dependent on the applied frequency but not on the strain magnitude. J Biomech 2007; 40: 1333–1339. - PubMed
-
- Xie L, Rubin C, Judex S. Enhancement of the adolescent murine musculoskeletal system using low-level mechanical vibrations. J Appl Physiol 2008; 104: 1056–1062. - PubMed
-
- Shi H-F, Cheung W-H, Qin L, et al. Low-magnitude high-frequency vibration treatment augments fracture healing in ovariectomy-induced osteoporotic bone. Bone 2010; 46: 1299–1305. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

