The Cancer Spliceome: Reprograming of Alternative Splicing in Cancer
- PMID: 30246013
- PMCID: PMC6137424
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2018.00080
The Cancer Spliceome: Reprograming of Alternative Splicing in Cancer
Abstract
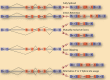
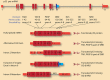
Alternative splicing allows for the expression of multiple RNA and protein isoforms from one gene, making it a major contributor to transcriptome and proteome diversification in eukaryotes. Advances in next generation sequencing technologies and genome-wide analyses have recently underscored the fact that the vast majority of multi-exon genes under normal physiology engage in alternative splicing in tissue-specific and developmental-specific manner. On the other hand, cancer cells exhibit remarkable transcriptome alterations partly by adopting cancer-specific splicing isoforms. These isoforms and their encoded proteins are not insignificant byproducts of the abnormal physiology of cancer cells, but either drivers of cancer progression or small but significant contributors to specific cancer hallmarks. Thus, it is paramount that the pathways that regulate alternative splicing in cancer, including the splicing factors that bind to pre-mRNAs and modulate spliceosome recruitment. In this review, we present a few distinct cases of alternative splicing in cancer, with an emphasis on their regulation as well as their contribution to cancer cell phenotype. Several categories of splicing aberrations are highlighted, including alterations in cancer-related genes that directly affect their pre-mRNA splicing, mutations in genes encoding splicing factors or core spliceosomal subunits, and the seemingly mutation-free disruptions in the balance of the expression of RNA-binding proteins, including components of both the major (U2-dependent) and minor (U12-dependent) spliceosomes. Given that the latter two classes cause global alterations in splicing that affect a wide range of genes, it remains a challenge to identify the ones that contribute to cancer progression. These challenges necessitate a systematic approach to decipher these aberrations and their impact on cancer. Ultimately, a sufficient understanding of splicing deregulation in cancer is predicted to pave the way for novel and innovative RNA-based therapies.
Keywords: alternative splicing; cancer spliceome; exons; introns; splicing.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

