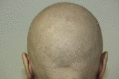
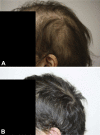
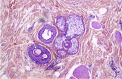
Nivolumab-induced alopecia areata: A reversible factor of good prognosis?
- PMID: 30246120
- PMCID: PMC6141643
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2018.05.022
Nivolumab-induced alopecia areata: A reversible factor of good prognosis?
Keywords: AA, alopecia areata; CTLA-4, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte–associated antigen-4; ICI, immune checkpoint inhibitors; PD-1, programmed cell death protein-1; PD-L1, programmed death ligand-1; alopecia areata; anti–programmed cell death protein-1; drug adverse event; immune related; lung cancer; melanoma; nivolumab.
Figures



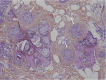
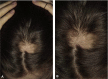
References
-
- Azoury S.C., Straughan D.M., Shukla V. Immune checkpoint inhibitors for cancer therapy: clinical efficacy and safety. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2015;15:452–462. - PubMed
-
- Tsirigotis P., Savani B.N., Nagler A. Programmed death-1 immune checkpoint blockade in the treatment of hematological malignancies. Ann Med. 2016;48:428–439. - PubMed
-
- Sibaud V. Dermatologic reactions to immune checkpoint inhibitors: skin toxicities and immunotherapy. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:345–361. - PubMed
-
- Weber J.S., Hodi F.S., Wolchok J.D. Safety profile of nivolumab monotherapy: a pooled analysis of patients with advanced melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:785–792. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
