Sarcolab pilot study into skeletal muscle's adaptation to long-term spaceflight
- PMID: 30246141
- PMCID: PMC6141586
- DOI: 10.1038/s41526-018-0052-1
Sarcolab pilot study into skeletal muscle's adaptation to long-term spaceflight
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Author Correction: Sarcolab pilot study into skeletal muscle's adaptation to longterm spaceflight.NPJ Microgravity. 2018 Oct 24;4:23. doi: 10.1038/s41526-018-0058-8. eCollection 2018. NPJ Microgravity. 2018. PMID: 30374455 Free PMC article.
Abstract
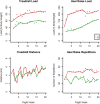
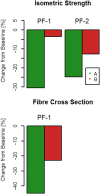
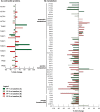
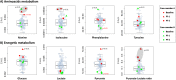
Spaceflight causes muscle wasting. The Sarcolab pilot study investigated two astronauts with regards to plantar flexor muscle size, architecture, and function, and to the underlying molecular adaptations in order to further the understanding of muscular responses to spaceflight and exercise countermeasures. Two crew members (A and B) spent 6 months in space. Crew member A trained less vigorously than B. Postflight, A showed substantial decrements in plantar flexor volume, muscle architecture, in strength and in fiber contractility, which was strongly mitigated in B. The difference between these crew members closely reflected FAK-Y397 abundance, a molecular marker of muscle's loading history. Moreover, crew member A showed downregulation of contractile proteins and enzymes of anaerobic metabolism, as well as of systemic markers of energy and protein metabolism. However, both crew members exhibited decrements in muscular aerobic metabolism and phosphate high energy transfer. We conclude that countermeasures can be effective, particularly when resistive forces are of sufficient magnitude. However, to fully prevent space-related muscular deterioration, intersubject variability must be understood, and intensive exercise countermeasures programs seem mandatory. Finally, proteomic and metabolomic analyses suggest that exercise benefits in space may go beyond mere maintenance of muscle mass, but rather extend to the level of organismic metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
Martin Flück reports personal fees and others from Resortho Foundation, grants and personal fees from Swiss National Science Foundation, grants and personal fees from Balgrist Foundation, outside the submitted work. In addition, Dr. Flück has a patent on Regulation of muscle repair (ÐS 20090280103 A1 pending to Martin Flück). All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Crew-Friendly Countermeasures Against Musculoskeletal Injuries in Aviation and Spaceflight.Front Physiol. 2020 Jul 10;11:837. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00837. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32754055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recovery from 6-month spaceflight at the International Space Station: muscle-related stress into a proinflammatory setting.FASEB J. 2019 Apr;33(4):5168-5180. doi: 10.1096/fj.201801625R. Epub 2019 Jan 8. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 30620616 Free PMC article.
-
Erratum: Author Correction: Sarcolab pilot study into skeletal muscle's adaptation to longterm spaceflight.NPJ Microgravity. 2018 Oct 24;4:23. doi: 10.1038/s41526-018-0058-8. eCollection 2018. NPJ Microgravity. 2018. PMID: 30374455 Free PMC article.
-
NK cell function is impaired during long-duration spaceflight.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019 Apr 1;126(4):842-853. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00761.2018. Epub 2018 Nov 1. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019. PMID: 30382809
-
The Astronaut-Athlete: Optimizing Human Performance in Space.J Strength Cond Res. 2015 Dec;29(12):3531-45. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000001191. J Strength Cond Res. 2015. PMID: 26595138 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel computational framework for the estimation of internal musculoskeletal loading and muscle adaptation in hypogravity.Front Physiol. 2024 Feb 7;15:1329765. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1329765. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38384800 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Ontology (GO)-Driven Inference of Candidate Proteomic Markers Associated with Muscle Atrophy Conditions.Molecules. 2022 Aug 27;27(17):5514. doi: 10.3390/molecules27175514. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36080280 Free PMC article.
-
Improving Obesity and Insulin Resistance by Targeting Skeletal Muscle MKP-1.J Cell Signal. 2020;1(4):160-168. J Cell Signal. 2020. PMID: 33179019 Free PMC article.
-
Space omics research in Europe: Contributions, geographical distribution and ESA member state funding schemes.iScience. 2022 Feb 15;25(3):103920. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.103920. eCollection 2022 Mar 18. iScience. 2022. PMID: 35265808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Five Padua days on muscle and mobility medicine (2024Pdm3) 27 February - 2 March, 2024 at Hotel Petrarca, Thermae of Euganean Hills, Padua, and San Luca Hall, Prato della Valle, Padua, Italy.Eur J Transl Myol. 2023 Dec 18;33(4):12161. doi: 10.4081/ejtm.2023.12161. Eur J Transl Myol. 2023. PMID: 38112609 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

