Insulin and glucose-lowering agents for treating people with diabetes and chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 30246878
- PMCID: PMC6513625
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011798.pub2
Insulin and glucose-lowering agents for treating people with diabetes and chronic kidney disease
Abstract
Background: Diabetes is the commonest cause of chronic kidney disease (CKD). Both conditions commonly co-exist. Glucometabolic changes and concurrent dialysis in diabetes and CKD make glucose-lowering challenging, increasing the risk of hypoglycaemia. Glucose-lowering agents have been mainly studied in people with near-normal kidney function. It is important to characterise existing knowledge of glucose-lowering agents in CKD to guide treatment.
Objectives: To examine the efficacy and safety of insulin and other pharmacological interventions for lowering glucose levels in people with diabetes and CKD.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Kidney and Transplant Register of Studies up to 12 February 2018 through contact with the Information Specialist using search terms relevant to this review. Studies in the Register are identified through searches of CENTRAL, MEDLINE, and EMBASE, conference proceedings, the International Clinical Trials Register (ICTRP) Search Portal and ClinicalTrials.gov.
Selection criteria: All randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and quasi-RCTs looking at head-to-head comparisons of active regimens of glucose-lowering therapy or active regimen compared with placebo/standard care in people with diabetes and CKD (estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2) were eligible.
Data collection and analysis: Four authors independently assessed study eligibility, risk of bias, and quality of data and performed data extraction. Continuous outcomes were expressed as post-treatment mean differences (MD). Adverse events were expressed as post-treatment absolute risk differences (RD). Dichotomous clinical outcomes were presented as risk ratios (RR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI).
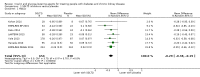
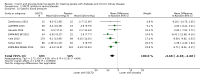
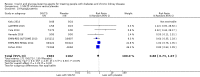
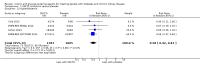
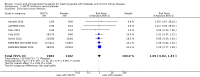
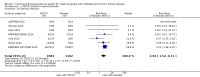
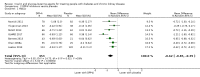
Main results: Forty-four studies (128 records, 13,036 participants) were included. Nine studies compared sodium glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors to placebo; 13 studies compared dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors to placebo; 2 studies compared glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonists to placebo; 8 studies compared glitazones to no glitazone treatment; 1 study compared glinide to no glinide treatment; and 4 studies compared different types, doses or modes of administration of insulin. In addition, 2 studies compared sitagliptin to glipizide; and 1 study compared each of sitagliptin to insulin, glitazars to pioglitazone, vildagliptin to sitagliptin, linagliptin to voglibose, and albiglutide to sitagliptin. Most studies had a high risk of bias due to funding and attrition bias, and an unclear risk of detection bias.Compared to placebo, SGLT2 inhibitors probably reduce HbA1c (7 studies, 1092 participants: MD -0.29%, -0.38 to -0.19 (-3.2 mmol/mol, -4.2 to -2.2); I2 = 0%), fasting blood glucose (FBG) (5 studies, 855 participants: MD -0.48 mmol/L, -0.78 to -0.19; I2 = 0%), systolic blood pressure (BP) (7 studies, 1198 participants: MD -4.68 mmHg, -6.69 to -2.68; I2 = 40%), diastolic BP (6 studies, 1142 participants: MD -1.72 mmHg, -2.77 to -0.66; I2 = 0%), heart failure (3 studies, 2519 participants: RR 0.59, 0.41 to 0.87; I2 = 0%), and hyperkalaemia (4 studies, 2788 participants: RR 0.58, 0.42 to 0.81; I2 = 0%); but probably increase genital infections (7 studies, 3086 participants: RR 2.50, 1.52 to 4.11; I2 = 0%), and creatinine (4 studies, 848 participants: MD 3.82 μmol/L, 1.45 to 6.19; I2 = 16%) (all effects of moderate certainty evidence). SGLT2 inhibitors may reduce weight (5 studies, 1029 participants: MD -1.41 kg, -1.8 to -1.02; I2 = 28%) and albuminuria (MD -8.14 mg/mmol creatinine, -14.51 to -1.77; I2 = 11%; low certainty evidence). SGLT2 inhibitors may have little or no effect on the risk of cardiovascular death, hypoglycaemia, acute kidney injury (AKI), and urinary tract infection (low certainty evidence). It is uncertain whether SGLT2 inhibitors have any effect on death, end-stage kidney disease (ESKD), hypovolaemia, fractures, diabetic ketoacidosis, or discontinuation due to adverse effects (very low certainty evidence).Compared to placebo, DPP-4 inhibitors may reduce HbA1c (7 studies, 867 participants: MD -0.62%, -0.85 to -0.39 (-6.8 mmol/mol, -9.3 to -4.3); I2 = 59%) but may have little or no effect on FBG (low certainty evidence). DPP-4 inhibitors probably have little or no effect on cardiovascular death (2 studies, 5897 participants: RR 0.93, 0.77 to 1.11; I2 = 0%) and weight (2 studies, 210 participants: MD 0.16 kg, -0.58 to 0.90; I2 = 29%; moderate certainty evidence). Compared to placebo, DPP-4 inhibitors may have little or no effect on heart failure, upper respiratory tract infections, and liver impairment (low certainty evidence). Compared to placebo, it is uncertain whether DPP-4 inhibitors have any effect on eGFR, hypoglycaemia, pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, or discontinuation due to adverse effects (very low certainty evidence).Compared to placebo, GLP-1 agonists probably reduce HbA1c (7 studies, 867 participants: MD -0.53%, -1.01 to -0.06 (-5.8 mmol/mol, -11.0 to -0.7); I2 = 41%; moderate certainty evidence) and may reduce weight (low certainty evidence). GLP-1 agonists may have little or no effect on eGFR, hypoglycaemia, or discontinuation due to adverse effects (low certainty evidence). It is uncertain whether GLP-1 agonists reduce FBG, increase gastrointestinal symptoms, or affect the risk of pancreatitis (very low certainty evidence).Compared to placebo, it is uncertain whether glitazones have any effect on HbA1c, FBG, death, weight, and risk of hypoglycaemia (very low certainty evidence).Compared to glipizide, sitagliptin probably reduces hypoglycaemia (2 studies, 551 participants: RR 0.40, 0.23 to 0.69; I2 = 0%; moderate certainty evidence). Compared to glipizide, sitagliptin may have had little or no effect on HbA1c, FBG, weight, and eGFR (low certainty evidence). Compared to glipizide, it is uncertain if sitagliptin has any effect on death or discontinuation due to adverse effects (very low certainty).For types, dosages or modes of administration of insulin and other head-to-head comparisons only individual studies were available so no conclusions could be made.
Authors' conclusions: Evidence concerning the efficacy and safety of glucose-lowering agents in diabetes and CKD is limited. SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 agonists are probably efficacious for glucose-lowering and DPP-4 inhibitors may be efficacious for glucose-lowering. Additionally, SGLT2 inhibitors probably reduce BP, heart failure, and hyperkalaemia but increase genital infections, and slightly increase creatinine. The safety profile for GLP-1 agonists is uncertain. No further conclusions could be made for the other classes of glucose-lowering agents including insulin. More high quality studies are required to help guide therapeutic choice for glucose-lowering in diabetes and CKD.
Conflict of interest statement
Clement Lo: none known
Tadashi Toyoma: none known
Ying Wang: none known
Jin Lin: none known
Yoichiro Hirakawa: none known
Min Jun: none known
Sunil Badve: none known
Helen Pilmore: none known
Carmel Hawley has received fees from Amgen, Shire, Roche, Abbott, Bayer, Fresenius, Baxter, Gambro, Janssen‐Cilag and Genzyme in relation to consultancy, speakers' fees, education, and grants for activities unrelated to this review
Alan Cass: The Menzies School of Health Research has received unconditional research funding from AMGEN, Merck and Novartis for research in chronic kidney disease in Indigenous populations.
Vlado Perkovic: has received support from Boehringer Ingelheim for Advisory Boards, and his employer has received payments from Boehringer Ingelheim and Merck for Advisory activities, and has a contract for the conduct of a clinical study of glucose‐lowering with Janssen
Sophia Zoungas has received fees from Abbvie, Amgen Australia Pty Ltd, AstraZeneca Pty Ltd, Bristol Myers Squibb Australia Pty Ltd, Boehringer Ingleheim, Janssen‐Cilag Pty Ltd, Merck Sharp & Dohme (Australia) Pty Ltd, Novo Nordisk, Novartis Pharmaceuticals Australia, Ogilvy Healthworld, Sanofi, Servier Laboratories, and Takeda Pharmaceuticals Australia Pty Ltd in relation to consultancy, speakers' fees, education, and grants for activities unrelated to this review
Figures






















































































































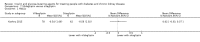




























Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Abe 2007 {published data only}
-
- Abe M, Kikuchi F, Kaizu K, Matsumoto K. Combination therapy of pioglitazone with voglibose improves glycemic control safely and rapidly in Japanese type 2‐diabetic patients on hemodialysis. Clinical Nephrology 2007;68(5):287‐94. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Abe 2008a {published data only}
-
- Abe M, Okada K, Kikuchi F, Matsumoto K. Clinical investigation of the effects of pioglitazone on the improvement of insulin resistance and blood pressure in type 2‐diabetic patients undergoing hemodialysis. Clinical Nephrology 2008;70(3):220‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Abe 2010 {published data only}
-
- Abe M, Okada K, Maruyama T, Maruyama N, Matsumoto K. Combination therapy with mitiglinide and voglibose improves glycemic control in type 2 diabetic patients on hemodialysis. Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy 2010;11(2):169‐76. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Abe 2010a {published data only}
-
- Abe M, Okada K, Maruyama T, Maruyama N, Soma M, Matsumoto K. Clinical effectiveness and safety evaluation of long‐term pioglitazone treatment for erythropoietin responsiveness and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetic patients on hemodialysis. Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy 2010;11(10):1611‐20. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Abe 2016 {published data only}
-
- Abe M, Higuchi T, Moriuchi M, Okamura M, Tei R, Nagura C, et al. Efficacy and safety of saxagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitor, in hemodialysis patients with diabetic nephropathy: A randomized open‐label prospective trial. Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice 2016;116:244‐52. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Abe M, Okada K, Oikawa O, Maruyama N, Furukawa T. Efficacy and safety of dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 (DPP‐4) inhibitor in hemodialysis patients with type 2 diabetes [abstract]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2016;31(Suppl 1):i216. [EMBASE: 72326481]
-
- Abe M, Otsuki T, Maruyama N, Oikawa O, Okada K. Efficacy and safety of saxagliptin, dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitor, in hemodialysis patients with type 2 diabetes [abstract]. Nephrology 2016;21(Suppl 2):65. [EMBASE: 612312682]
AleNephro 2014 {published data only}
-
- Herz M, Ruilope L, Hanefeld M, Lincoff AM, Viberti G, Reigner SM, et al. Effects of aleglitazar on renal function in patients with stage 3 chronic kidney disease and type‐2 diabetes [abstract no: O22]. British Transplantation Society & the Renal Association Joint Congress; 2013 Mar 13‐15; Bournemouth, UK. 2013.
-
- Malmberg K, Hanefeld M, Ruilope L, Lincoff A, Viberti G, Mudie N, et al. Effects of aleglitazar on cardiovascular risk factors in patients with stage 3 chronic kidney disease and type II diabetes [abstract]. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2013;10(Suppl 1):E1173. [EMBASE: 71020536]
-
- Ruilope L, Hanefeld M, Lincoff AM, Viberti G, Meyer‐Reigner S, Mudie N, et al. Effects of the dual peroxisome proliferator‐activated receptor‐alpha/gamma agonist aleglitazar on renal function in patients with stage 3 chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes: a Phase IIb, randomized study. BMC Nephrology 2014;15(1):180. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Arjona Ferreira 2013 {published data only}
-
- Arjona Ferreira JC, Engel SS, Guo H, Golm GT, Johnson‐Levonas AO, Kaufman KD, et al. Consistency of the A1C‐lowering effects of sitagliptin versus glipizide in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic renal insufficiency across a variety of baseline characteristics [abstract]. Diabetes 2012;61:A281. [EMBASE: 70797683]
-
- Arjona Ferreira JC, Engel SS, Guo H, Golm GT, Sisk CM, Kaufman KD, et al. Sitagliptin more effectively achieves a composite endpoint of a1c reduction, no body weight gain, and lack of hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes and renal insufficiency compared to glipizide [abstract]. Diabetes 2012;61:A258. [EMBASE: 70797604]
-
- Arjona Ferreira JC, Marre M, Rabelink TJ, Barzilai N, Bakris GL, Guo H, et al. Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin versus glipizide in patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate to severe chronic renal insufficiency [abstract]. Diabetes, Stoffwechsel und Herz 2011;20(6):419. [EMBASE: 70696902] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arjona Ferreira JCA, Marre M, Bakris GL, Rabelink TJ. Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin vs. glipizide in patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate to severe chronic renal insufficiency [abstract no: LB‐PO3166]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2011;22(Abstracts):8B.
Arjona Ferreira 2013a {published data only}
-
- Arjona Ferreira JC, Corry D, Mogensen CE, Sloan L, Xu L, Golm GT, et al. Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes and ESRD receiving dialysis: a 54‐week randomized trial. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2013;61(4):579‐87. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Arjona Ferreira JC, Corry D, Mogensen CE, Slone L, Xii L, Gonzalez EJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin vs. glipizide in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and end‐stage renal disease on dialysis: A 54‐week randomised trial [abstract]. Diabetes, Stoffwechsel und Herz 2011;20(6):430. [EMBASE: 70696927]
-
- Arjona Ferreira JC, Corry DB, Mogensen CE. Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin vs. glipizide in patients with type 2 diabetes and end‐stage renal disease on dialysis [abstract no: LB‐PO3167]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2011;22(Abstracts):8B.
Baldwin 2012 {published data only}
-
- Zander J, Raghu P, Lee H, Molitch M, Glossop V, Smallwood K, et al. Initial insulin doses should be decreased in hospitalized patients with renal insufficiency and type 2 diabetes [abstract]. Diabetes 2011;60:A297. [EMBASE: 70628849]
Barnett 2013 {published data only}
-
- Barnett AH, Huisman H, Jones R. Efficacy and safety of linagliptin in elderly patients (.70 years) with type 2 diabetes mellitus [abstract no: OCS‐05‐3]. Journal of Diabetes Investigation 2012;3(Suppl 1):102.
-
- Barnett AH, Huisman H, Jones R, Eynatten M, Patel S, Woerle HJ. Linagliptin for patients aged 70 years or older with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with common antidiabetes treatments: a randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Lancet 2013;382(9902):1413‐23. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- McGill JB, Barnett AH, Lewin AJ, Patel S, Neubacher D, Eynatten M, et al. Linagliptin added to sulphonylurea in uncontrolled type 2 diabetes patients with moderate‐to‐severe renal impairment. Diabetes & Vascular Disease Research 2014;11(1):34‐40. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bellante 2016 {published data only}
-
- Bellante R, Lucchesi D, Giusti L, Garofolo M, Sancho‐Bornez V, Caprioli R, et al. Sitagliptin increases circulating endothelial progenitor cells in patients with type 2 diabetes and advanced chronic kidney disease [abstract]. Diabetologia 2016;59(1 Suppl 1):S360‐1. [EMBASE: 612313307]
Chan 2008a {published data only}
-
- Chan JC, Scott R, Arjona Ferreira JC, Sheng D, Gonzalez E, Davies MJ, et al. Safety and efficacy of sitagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic renal insufficiency. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2008;10(7):545‐55. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Diez 1987 {published data only}
-
- Diez JJ, Alvaro F, Munoz J, Miguelez C, P‐Diaz V, Jabari NS, et al. Comparative randomized study of insulin administration through two different routes in CAPD diabetic patients [abstract]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 1987;2(5):452‐3.
-
- Diez JJ, Alvaro F, Munoz J, Miguelez C, P‐Diaz V, Jabari NS, et al. Comparative randomized study of insulin administration through two different routes in CAPD diabetic patients. [abstract]. Kidney International 1988;34(2):296.
EMPA‐REG BP 2015 {published data only}
-
- Cherney D, Cooper M, Tikkanen I, Crowe S, Johansen OE, Lund SS, et al. Contrasting influences of renal function on blood pressure and HbA1c reductions with empagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension [abstract no: 16709]. Circulation 2014;130(Suppl 1):n/a.
-
- Cherney D, Cooper M, Tikkanen I, Crowe S, Johansen OE, Lund SS, et al. Contrasting influences of renal function on blood pressure and hba1c reductions with empagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension [abstract no: 4B.01]. Journal of Hypertension 2015;33(Suppl 1):e53. [MEDLINE: ]
-
- Mancia G, Cannon CP, Tikkanen I, Zeller C, Ley L, Woerle HJ, et al. Impact of empagliflozin on blood pressure in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension by background antihypertensive medication. Hypertension 2016;68(6):1355‐64. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Tikkanen I, Narko K, Zeller C, Green A, Salsali A, Broedl UC, et al. Empagliflozin reduces blood pressure in patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension. Diabetes Care 2015;38(3):420‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
EMPA‐REG OUTCOME 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Cherney DZI, Zinman B, Inzucchi SE, Koitka‐Weber A, Mattheus M, von EM, et al. Effects of empagliflozin on the urinary albumin‐to‐creatinine ratio in patients with type 2 diabetes and established cardiovascular disease: an exploratory analysis from the EMPA‐REG OUTCOME randomised, placebo‐controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology 2017;5(8):610‐21. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- D'Emden M, Bergenstal R, Maldonado Lutomirsky M, Wanner C. Effect of empagliflozin on nephropathy in subgroups by age: Results from EMPA‐REG OUTCOME [abstract]. Nephrology 2016;21(Suppl 2):59. [EMBASE: 612313031]
-
- Daacke I, Kandaswamy P, Tebboth A, Kansal A, Reifsnider O. Impact of empagliflozin (jardiance) to the NHS: Estimation of budget and event impact based on EMPA‐REG OUTCOME data [abstract]. Value in Health 2016;19(7):A668. [EMBASE: 613236982]
-
- Inzucchi SE, Zinman B, Lachin JM, Wanner C, Ferrari R, Bluhmki E, et al. Design of the empagliflozin cardiovascular outcome event trial in type 2 diabetes mellitus [abstract]. Diabetologia 2013;56(Suppl 1):S378. [EMBASE: 71439366]
-
- Langslet G, Zinman B, Wanner C, Hantel S, Espadero R, Johansen O, et al. Cardiovascular (CV) outcomes according to LDL cholesterol (LDLC) levels in EMPA‐REG OUTCOME [abstract]. Diabetologia 2016;59(1 Suppl 1):S537. [EMBASE: 612313836]
EMPA‐REG RENAL 2014 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Barnett AH, Mithal A, Manassie J, Jones R, Rattunde H, Woerle HJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of empagliflozin added to existing antidiabetes treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease: a randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology 2014;2(5):369‐84. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
GUARD 2017 {published data only}
-
- Yoon S, Han B, Kim S, Han S, Jo Y, Jeong K, et al. Efficacy and safety of gemigliptin in type 2 diabetes patients with moderate to severe renal impairment [abstract no:804]. Diabetologia 2015;58(1 Suppl 1):S387. [EMBASE: 72031048]
-
- Yoon S, Han B, Kim S, Han S, Jo YI, Jeong K, et al. Efficacy and safety of gemigliptin in type 2 diabetes patients with moderate to severe renal impairment (GUARD study) [abstract no: 760]. Diabetologia 2016;59(1 Suppl 1):S361. [EMBASE: 612313344]
-
- Yoon SA, Han BG, Kim SG, Han SY, Jo YI, Jeong KH, et al. Efficacy, safety and albuminuria‐reducing effect of gemigliptin in Korean type 2 diabetes patients with moderate to severe renal impairment: A 12‐week, double‐blind randomized study (the GUARD Study). Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2017;19(4):590‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Haneda 2016 {published data only}
-
- Haneda M, Seino Y, Inagaki N, Kaku K, Sasaki T, Fukatsu A, et al. Influence of renal function on the 52‐week efficacy and safety of the sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor luseogliflozin in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clinical Therapeutics 2016;38(1):66‐88. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Idorn 2013 {published data only}
-
- Idorn T, Knop FK, Jorgensen M, Jensen T, Resuli M, Hansen PM, et al. Safety and efficacy of liraglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes and end‐stage renal disease: protocol for an investigator‐initiated prospective, randomised, placebo‐controlled, double‐blinded, parallel intervention study. BMJ Open 2013;3(4):1. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Idorn T, Knop FK, Jorgensen MB, Jensen T, Resuli M, Hansen PM, et al. Safety and efficacy of liraglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes and end‐stage renal disease: An investigator‐initiated, randomised, placebo controlled trial [abstract]. Diabetologia 2014;57(1 Suppl):S370‐1. [EMBASE: 71595559]
-
- Idorn T, Knop FK, Jorgensen MB, Jensen T, Resuli M, Hansen PM, et al. Safety and efficacy of liraglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes and end‐stage renal disease: an investigator‐initiated, placebo‐controlled, double‐blind, parallel‐group, randomized trial. Diabetes Care 2016;39(2):206‐13. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ito 2011a {published data only}
-
- Ito M, Abe M, Okada K, Sasaki H, Maruyama N, Tsuchida M, et al. The dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 (DPP‐4) inhibitor vildagliptin improves glycemic control in type 2 diabetic patients undergoing hemodialysis. Endocrine Journal 2011;58(11):979‐87. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jin 2007 {published data only}
-
- Jin HM, Pan Y. Angiotensin type‐1 receptor blockade with losartan increases insulin sensitivity and improves glucose homeostasis in subjects with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2007;22(7):1943‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Jin HM, Pan Y. Renoprotection provided by losartan in combination with pioglitazone is superior to renoprotection provided by losartan alone in patients with type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Kidney & Blood Pressure Research 2007;30(4):203‐11. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kaku 2014 {published data only}
-
- Kaku K, Kiyosue A, Inoue S, Ueda N, Tokudome T, Yang J, et al. Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin monotherapy in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled by diet and exercise. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism 2014;16(11):1102‐1110. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kohan 2014 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Kohan DE, Firescu C, List JF, Tang W. Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate renal impairment [abstract no:TH‐PO524]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2011;22(Abstracts):232A‐3A.
Kothny 2015 {published data only}
Laakso 2015 {published data only}
-
- Groop P, Perkovic V, Cooper M, Crowe S, Lee J, Patel S, et al. Long‐term efficacy and safety of linagliptin in type 2 diabetes patients with moderate to severe renal disease. Diabetes 2014;63(Suppl 1):A264. [EMBASE: 71559411]
-
- Groop PH, Laakso M, Rosenstock J, Hehnke U, Tamminen I, Patel S, et al. Linagliptin versus placebo followed by glimepiride in type 2 diabetes patients with moderate to severe renal impairment [abstract no:P13‐11527]. Diabetologia 2016;56(Suppl 1):S364‐5.
-
- Laakso M, Rosenstock J, Groop P, Hehnke U, Tamminen I, Patel S, et al. Linagliptin vs. placebo followed by glimepiride in type 2 diabetes patients with moderate to severe renal impairment. Diabetes 2013;62(Suppl 1):A281‐A2. [EMBASE: 71287521] - PubMed
-
- Laakso M, Rosenstock J, Groop PH, Barnett AH, Gallwitz B, Hehnke U, et al. Treatment with the dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitor linagliptin or placebo followed by glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes with moderate to severe renal impairment: a 52‐week, randomized, double‐blind clinical trial. Diabetes Care 2015;38(2):e15‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
LANTERN 2015 {published data only}
-
- Kashiwagi A, Takahashi H, Ishikawa H, Yoshida S, Kazuta K, Utsuno A, et al. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study on long‐term efficacy and safety of ipragliflozin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and renal impairment: results of the long‐term ASP1941 safety evaluation in patients with type 2 diabetes with renal impairment (LANTERN) study. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism 2015;17(2):152‐60. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Leiter 2014 {published data only}
-
- Leiter LA, Carr MC, Stewart M, Jones‐Leone A, Scott R, Yang F, et al. Efficacy and safety of the once‐weekly GLP‐1 receptor agonist albiglutide versus sitagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes and renal impairment: a randomized phase III study. Diabetes Care 2014;37(10):2723‐30. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lewin 2012 {published data only}
-
- Lewin AJ, Arvay L, Liu D, Patel S, Eynatten M, Woerle HJ. Efficacy and tolerability of linagliptin added to a sulfonylurea regimen in patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus: an 18‐week, multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Clinical Therapeutics 2012;34(9):1909‐19. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- McGill JB, Barnett AH, Lewin AJ, Patel S, Neubacher D, Eynatten M, et al. Linagliptin added to sulphonylurea in uncontrolled type 2 diabetes patients with moderate‐to‐severe renal impairment. Diabetes & Vascular Disease Research 2014;11(1):34‐40. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
LIRA‐RENAL 2016 {published data only}
-
- Davies MJ, Bain SC, Atkin SL, Rossing P, Scott D, Shamkhalova MS, et al. Efficacy and safety of liraglutide versus placebo as add‐on to glucose‐lowering therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate renal impairment (LIRA‐RENAL): a randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Care 2016;39(2):222‐30. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Mathieu C, Umpierrez G, Atkin S, Bain S, Rossing P, Scott D, et al. Efficacy and safety of liraglutide versus placebo in subjects with type 2 diabetes and moderate renal impairment (LIRA‐RENAL): a randomised trial [abstract no: OP60]. Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice 2014;106(Suppl 1):S31. [EMBASE: 71824748]
-
- Ngo P, Davies M, Atkin S, Bain S, Rossing P, Scott D, et al. Efficacy and safety of liraglutide vs. placebo as add‐on to existing diabetes medication in subjects with type 2 diabetes and moderate renal impairment (LIRA‐RENAL) [abstract no: 18]. Canadian Journal of Diabetes 2014;38(5 Suppl):S9‐S10. [EMBASE: 72003971]
-
- Umpierrez G, Atkin S, Bain S, Rossing P, Scott D, Shamkhalova M, et al. Efficacy and safety of liraglutide versus placebo in subjects with type 2 diabetes and moderate renal impairment (LIRA‐RENAL): a randomised trial [abstract]. Diabetologia 2014;57(Suppl 1):S84. [EMBASE: 71594832] - PubMed
Lukashevich 2011 {published data only}
-
- Kothny W, Schweizer A, Naik R, Groop P, Shao Q, Lukashevich V. Comparison of vildagliptin with placebo in a 24‐week study of 221 patients with type 2 diabetes and severe renal impairment (eGFR<30) [abstract]. Diabetologia 2011;54:S332. [EMBASE: 70562964]
-
- Kothny W, Shao Q, Groop PH, Lukashevich V. One‐year safety, tolerability and efficacy of vildagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate or severe renal impairment. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2012;14(11):1032‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Kothny W, Wang M, Shao Q, Groop P, Lukashevich V. One‐year safety, tolerability and efficacy of vildagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and moderate or severe renal insufficiency [abstract]. Diabetes 2012;61:A253. [EMBASE: 70797589] - PubMed
-
- Lukashevich V, Schweizer A, Foley J, Shao Q, Groop P, Kothny W. Efficacy of vildagliptin therapy in combination with insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes and severe renal impairment [abstract]. Diabetologia 2011;54:S332‐3. [EMBASE: 70562965]
McGill 2013 {published data only}
-
- McGill JB, Barnett AH, Lewin AJ, Patel S, Neubacher D, Eynatten M, et al. Linagliptin added to sulphonylurea in uncontrolled type 2 diabetes patients with moderate‐to‐severe renal impairment. Diabetes & Vascular Disease Research 2014;11(1):34‐40. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- McGill JB, Yki‐Jarvinen H, Crowe S, Woerle HJ, Eynatten M. Combination of the dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitor linagliptin with insulin‐based regimens in type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Diabetes & Vascular Disease Research 2015;12(4):249‐57. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mohideen 2005 {published data only}
-
- Mohideen P, Bornemann M, Sugihara J, Genadio V, Sugihara V, Arakaki R. The metabolic effects of troglitazone in patients with diabetes and end‐stage renal disease. Endocrine 2005;28(2):181‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mori 2016 {published data only}
Nakamura 2001 {published data only}
-
- Nakamura T, Ushiyama C, Osada S, Shimada N, Ebihara I, Koide H. Effect of pioglitazone on dyslipidemia in hemodialysis patients with type 2 diabetes. Renal Failure 2001;23(6):863‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Nowicki 2011 {published data only}
-
- Nowicki M, Rychlik I, Haller H, Warren M, Suchower L, Gause‐Nilsson I, et al. Long‐term treatment with the dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitor saxagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and renal impairment: a randomised controlled 52‐week efficacy and safety study. International Journal of Clinical Practice 2011;65(12):1230‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Nowicki M, Rychlik I, Haller H, Warren ML, Suchower L, Gause‐Nilsson I, et al. Saxagliptin improves glycaemic control and is well tolerated in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and renal impairment. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2011;13(6):523‐32. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Pfutzner 2011 {published data only}
-
- Pfutzner AH, Schondorf T, Dikta G, Krajewski V, Fuchs W, Forst T, et al. Use of pioglitazone vs. placebo in addition to standard insulin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus requiring hemodialysis treatment [abstract]. Diabetes 2011;60(Suppl 1):A315‐6. [EMBASE: 70628912]
Ruggenenti 2003a {published data only}
-
- Ruggenenti P, Flores C, Aros C, Ene‐Iordache B, Trevisan R, Ottomano C, et al. Renal and metabolic effects of insulin lispro in type 2 diabetic subjects with overt nephropathy. Diabetes Care 2003;26(2):502‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
SAVOR‐TIMI 53 2011 {published data only}
-
- Cahn A, Raz I, Mosenzon O, Leibowitz G, Yanuv I, Rozenberg A, et al. Predisposing factors for any and major hypoglycemia with saxagliptin versus placebo and overall: analysis from the SAVOR‐TIMI 53 trial. Diabetes care 2016;39(8):1329‐37. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Kalra S, Gupta Y, Baruah MP, Gupta A. Comment on Udell et al. Saxagliptin and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate or severe renal impairment: observations from the SAVOR‐TIMI 53 Trial. Diabetes Care 2015;38:696‐705. Diabetes Care 2015;38(6):e88‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Krempf M. Study on the risk reduction of cardiovascular events with saxagliptin in type 2 diabetic patients (SAVOR‐TIMI 53): Study and patients description. Medecine des Maladies Metaboliques 2013;7(4):354‐9. [EMBASE: 2014082407]
-
- Leiter LA, Teoh H, Mosenzon O, Cahn A, Hirshberg B, Stahre CA, et al. Frequency of cancer events with saxagliptin in the SAVOR‐TIMI 53 trial. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2016;18(2):186‐90. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Mosenzon O, Leibowitz G, Bhatt DL, Cahn A, Hirshberg B, Wei C, et al. Effect of saxagliptin on renal outcomes in the SAVOR‐TIMI 53 trial. Diabetes care 2017;40(1):69‐76. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Scarpioni 1994 {published data only}
-
- Scarpioni L, Ballocchi S, Castelli A, Scarpioni R. Insulin therapy in uremic diabetic patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis; comparison of intraperitoneal and subcutaneous administration. Peritoneal Dialysis International 1994;14(2):127‐31. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
TECOS 2013 {published data only}
-
- Bethel MA, Engel SS, Green JB, Huang Z, Josse RG, Kaufman KD, et al. Assessing the safety of sitagliptin in older participants in the trial evaluating cardiovascular outcomes with sitagliptin (TECOS). Diabetes Care 2017;40(4):494‐501. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Cornel JH, Bakris GL, Stevens SR, Alvarsson M, Bax WA, Chuang LM, et al. Effect of sitagliptin on kidney function and respective cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes: outcomes from TECOS. Diabetes care 2017;39(12):2304‐10. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Engel SS, Suryawanshi S, Josse RG, Peterson ED, Holman RR. Assessing the safety of sitagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease in the Trial Evaluating Cardiovascular Outcomes with Sitagliptin (TECOS) [abstract]. Diabetologia 2016;59(1 Suppl 1):S361. [EMBASE: 612313326]
-
- Green JB, Bethel MA, Armstrong PW, Buse JB, Engel SS, Garg J, et al. Effect of sitagliptin on cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes.[Erratum appears in N Engl J Med. 2015 Aug 6;373(6):586; PMID: 26182233]. New England Journal of Medicine 2015;373(3):232‐42. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wong 2005 {published data only}
-
- Wong TY, Szeto CC, Chow KM, Leung CB, Lam CW, Li PK. Rosiglitazone reduces insulin requirement and C‐reactive protein levels in type 2 diabetic patients receiving peritoneal dialysis. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2005;46(4):713‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Yale 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Bakris G, Yale JF, Wajs E, Li X, Usiskin K, Meininger G. Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin (CANA) in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus (t2dm) and moderate renal impairment [abstract no:TH‐PO536]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2012;23(Abstracts):220A.
-
- Nieto Iglesias J, Yale JF, Bakris G, Cariou B, Wajs E, Figueroa K, et al. Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease over 52 weeks [abstract no: 951]. Diabetologia 2013;56(Suppl 1):S381.
-
- Yale J, Bakris G, Cariou B, Iglesias JN, Wajs E, Figueroa K, et al. Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin (CANA) in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and chronic kidney disease (CKD) over 52 weeks [abstract]. Diabetes 2013;62(Suppl 1):A277‐8. [EMBASE: 71287507]
-
- Yale JF, Bakris G, Cariou B, Nieto Iglesias J, Wajs E, Figueroa K, et al. Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin (CANA) in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus T2DM) and chronic kidney disease (CKD) over 52 weeks [abstract no: 71]. Canadian Journal of Diabetes 2015;37(Suppl 4):S27.
-
- Yale JF, Bakris G, Cariou B, Nieto J, David‐Neto E, Yue D, et al. Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin over 52 weeks in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2014;16(10):1016‐27. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Yki‐Järvinen 2013 {published data only}
-
- Sheu WH, Park SW, Gong Y, Pinnetti S, Bhattacharya S, Patel S, et al. Linagliptin improves glycemic control after 1 year as add‐on therapy to basal insulin in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Current Medical Research & Opinion 2015;31(3):503‐12. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Zambrowicz 2015 {published data only}
-
- Zambrowicz B, Lapuerta P, Strumph P, Banks P, Wilson A, Ogbaa I, et al. LX4211 therapy reduces postprandial glucose levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and renal impairment despite low urinary glucose excretion. Clinical Therapeutics 2015;37(1):71‐82. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
ACCORD 2007 {published data only}
-
- ACCORD Study Group, ACCORD Eye Study Group, Chew EY, Ambrosius WT, Davis MD, Danis RP, et al. Effects of medical therapies on retinopathy progression in type 2 diabetes.[Erratum appears in N Engl J Med. 2011 Jan 13;364(2):190], [Erratum appears in N Engl J Med. 2012 Dec 20;367(25):2458]. New England Journal of Medicine 2010;363(3):233‐44. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- ACCORD Study Group, Buse JB, Bigger JT, Byington RP, Cooper LS, Cushman WC, et al. Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes (ACCORD) trial: design and methods. American Journal of Cardiology 2007;99(12A):21i‐33i. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
ADOPT 2011 {published data only}
-
- Kahn SE, Haffner SM, Heise MA, Herman WH, Holman RR, Jones NP, et al. Glycemic durability of rosiglitazone, metformin, or glyburide monotherapy.[erratum appears in N Engl J Med. 2007 Mar 29;356(13):1387‐8]. New England Journal of Medicine 2006;355(23):2427‐43. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Kahn SE, Zinman B, Haffner SM, O'Neill MC, Kravitz BG, Yu D, et al. Obesity is a major determinant of the association of C‐reactive protein levels and the metabolic syndrome in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2006;55(8):2357‐64. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Zinman B, Kahn SE, Haffner SM, O'Neill MC, Heise MA, Freed MI, et al. Phenotypic characteristics of GAD antibody‐positive recently diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes in North America and Europe. Diabetes 2004;53(12):3193‐200. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
ADVANCE 2001 {published data only}
-
- Rationale and design of the ADVANCE study: a randomised trial of blood pressure lowering and intensive glucose control in high‐risk individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Action in Diabetes and Vascular Disease: PreterAx and DiamicroN Modified‐Release Controlled Evaluation. Journal of Hypertension ‐ Supplement 2001;19(4):S21‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Study rationale and design of ADVANCE: action in diabetes and vascular disease‐‐preterax and diamicron MR controlled evaluation. Diabetologia 2001;44(9):1118‐20. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- ADVANCE Collaborative Group. ADVANCE‐‐Action in Diabetes and Vascular Disease: patient recruitment and characteristics of the study population at baseline. Diabetic Medicine 2005;22(7):882‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- ADVANCE Collaborative Group, Patel A, MacMahon S, Chalmers J, Neal B, Billot L, et al. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine 2008;358(24):2560‐72. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Chalmers J. [ADVANCE study: objectives, design and current status]. [French]. Drugs 2003;63(Spec No 1):39‐44. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Agarwal 2005 {published data only}
-
- Agarwal R. Anti‐inflammatory effects of short‐term pioglitazone therapy in men with advanced diabetic nephropathy. American Journal of Physiology ‐ Renal Physiology 2006;290(3):F600‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Agarwal R, Saha C, Battiwala M, Vasavada N, Curley T, Chase SD, et al. A pilot randomized controlled trial of renal protection with pioglitazone in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney International 2005;68(1):285‐92. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Aljabri 2004 {published data only}
-
- Aljabri K, Kozak SE, Thompson DM. Addition of pioglitazone or bedtime insulin to maximal doses of sulfonylurea and metformin in type 2 diabetes patients with poor glucose control: a prospective, randomized trial. American Journal of Medicine 2004;116(4):230‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Amador‐Licona 2000 {published data only}
-
- Amador‐Licona N, Guizar‐Mendoza J, Vargas E, Sanchez‐Camargo G, Zamora‐Mata L. The short‐term effect of a switch from glibenclamide to metformin on blood pressure and microalbuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Archives of Medical Research 2000;31(6):571‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Aoki 1995 {published data only}
-
- Aoki TT, Grecu EO, Prendergast JJ, Arcangeli MA, Meisenheimer R. Effect of chronic intermittent intravenous insulin therapy on antihypertensive medication requirements in IDDM subjects with hypertension and nephropathy. Diabetes Care 1995;18(9):1260‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
APRIME 2011 {published data only}
-
- Morikawa A, Ishizeki K, Iwashima Y, Yokoyama H, Muto E, Oshima E, et al. Pioglitazone reduces urinary albumin excretion in renin‐angiotensin system inhibitor‐treated type 2 diabetic patients with hypertension and microalbuminuria: the APRIME study. Clinical & Experimental Nephrology 2011;15(6):848‐53. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bakris 2006 {published data only}
-
- Bakris GL, Ruilope LM, McMorn SO, Weston WM, Heise MA, Freed MI, et al. Rosiglitazone reduces microalbuminuria and blood pressure independently of glycemia in type 2 diabetes patients with microalbuminuria. Journal of Hypertension 2006;24(10):2047‐55. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bangstad 1992 {published data only}
-
- Bangstad HJ. Early glomerulopathy is present in young, type 1 (insulin‐dependent) diabetic patients with microalbuminuria. Diabetologia 1993;36(6):523‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Bangstad HJ, Kofoed‐Enevoldsen A, Dahl‐Jorgensen K, Hanssen KF. Glomerular charge selectivity and the influence of improved blood glucose control in type 1 (insulin‐dependent) diabetic patients with microalbuminuria. Diabetologia 1992;35(12):1165‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Bangstad HJ, Osterby R, Dahl‐Jorgensen K, Berg KJ, Hartmann A, Hanssen KF. Improvement of blood glucose control in IDDM patients retards the progression of morphological changes in early diabetic nephropathy. Diabetologia 1994;37(5):483‐90. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Berg TJ, Nourooz‐Zadeh J, Wolff SP, Tritschler HJ, Bangstad HJ, Hanssen KF. Hydroperoxides in plasma are reduced by intensified insulin treatment. A randomized controlled study of IDDM patients with microalbuminuria. Diabetes Care 1998;21(8):1295‐300. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Hartmann A, Bangstad HJ, Holdass H, Fauchald P, Hanssen KF, Dahl‐Jorgensen K, et al. Effects of glucose control on renal tubular and glomerular functions in incipient IDDM nephropathy [abstract]. Nephrology 1997;3(Suppl 1):S378. [CENTRAL: CN‐00460903]
BARI 2D 2011 {published data only}
-
- Albu JB, Lu J, Mooradian AD, Krone RJ, Nesto RW, Porter MH, et al. Relationships of obesity and fat distribution with atherothrombotic risk factors: baseline results from the Bypass Angioplasty Revascularization Investigation 2 Diabetes (BARI 2D) trial. Obesity 2010;18(5):1046‐54. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Althouse AD, Abbott JD, Sutton‐Tyrrell K, Forker AD, Lombardero MS, Buitron LV, et al. Favorable effects of insulin sensitizers pertinent to peripheral arterial disease in type 2 diabetes: results from the Bypass Angioplasty Revascularization Investigation 2 Diabetes (BARI 2D) trial. Diabetes Care 2013;36(10):3269‐75. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- August P, Hardison RM, Hage FG, Marroquin OC, McGill JB, Rosenberg Y, et al. Change in albuminuria and eGFR following insulin sensitization therapy versus insulin provision therapy in the BARI 2D study. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology: CJASN 2014;9(1):64‐71. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Barnett 1984 {published data only}
-
- Barnett AH, Wakelin K, Leatherdale BA, Britton JR, Polak A, Bennett J, et al. Specific thromboxane synthetase inhibition and albumin excretion rate in insulin‐dependent diabetes. Lancet 1984;1(8390):1322‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
CANTATA‐SU 2016 {published data only}
-
- Cefalu WT, Leiter LA, Yoon KH, Arias P, Niskanen L, Xie J, et al. Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin versus glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin (CANTATA‐SU): 52 week results from a randomised, double‐blind, phase 3 non‐inferiority trial. Lancet 2013;382(9896):941‐50. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Heerspink HJL, Desai M, Jardine M, Meininger G, Perkovic V. Canagliflozin slows progression of renal function decline independent of glycaemic effects [abstract]. Diabetologia 2016;59(1 Suppl 1):S28. [EMBASE: 612313272]
Cao 2005 {published data only}
-
- Cao WH, Lan CH, Wang XL, Sun JH. The effects of pioglitazone on urinary albumin in excretion rate of early diabetic nephropathy. Chinese General Practice 2005;8(18):1484‐5.
Chacra 2009 {published data only}
-
- Chacra AR, Tan GH, Apanovitch A, Ravichandran S, List J, Chen R, et al. Saxagliptin added to a submaximal dose of sulphonylurea improves glycaemic control compared with uptitration of sulphonylurea in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomised controlled trial.[Erratum appears in Int J Clin Pract. 2010 Jan;64(2):277]. International Journal of Clinical Practice 2009;63(9):1395‐406. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Chen 2004b {published data only}
-
- Chen WK. Clinical observation of pioglitazone in diabetic nephropathy. International Medical Healthcare Guiding Journal 2004;10(1):50‐1.
Chen 2006h {published data only}
-
- Chen H, Song QH, Wang ZS, Tan LL. Observation on the therapeutic effect of rosiglitazone combined with metformin on diabetic nephropathy. China Tropical Medicine 2006;6(7):1194‐5.
Christensen 1986 {published data only}
-
- Christensen CK, Christiansen JS, Christensen T, Hermansen K, Mogensen CE. The effect of six months continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion on kidney function and size in insulin‐dependent diabetics. Diabetic Medicine 1986 Jan;3(1):29‐32. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Christensen 2001c {published data only}
-
- Christensen PK, Lund S, Parving HH. The impact of glycaemic control on autoregulation of glomerular filtration rate in patients with non‐insulin dependent diabetes. Scandinavian Journal of Clinical & Laboratory Investigation 2001 Feb;61(1):43‐50. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Chu 2006 {published data only}
-
- Chu P, Chiu Y, Lin J, Chen S, Wu K. The effect of low‐flux and high‐flux dialysers on endothelial dysfunction, oxidative stress and insulin resistance [abstract no: SA‐PO774]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2006;17(Abstracts):738A.
-
- Chu PL, Chiu YL, Lin JW, Chen SI, Wu KD. Effects of low‐ and high‐flux dialyzers on oxidative stress and insulin resistance. Blood Purification 2008;26(2):213‐20. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ciavarella 1985 {published data only}
-
- Ciavarella A, Vannini P, Flammini M, Bacci L, Forlani G, Borgnino LC. Effect of long‐term near‐normoglycemia on the progression of diabetic nephropathy. Diabete et Metabolisme 1985 Feb;11(1):3‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Dailey 2000 {published data only}
-
- Dailey GE, Boden GH, Creech RH, Johnson DG, Gleason RE, Kennedy FP, et al. Effects of pulsatile intravenous insulin therapy on the progression of diabetic nephropathy. Metabolism ‐ Clinical & Experimental 2000;49(11):1491‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Weinrauch LA, Bayliss G, Gleason RE, Lee AT, D'Elia JA. A pilot study to assess utility of changes in elements of the Diabetes Impact Management Scale in evaluating diabetic patients for progressive nephropathy. Metabolism ‐ Clinical & Experimental 2009;58(4):492‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Weinrauch LA, Bayliss G, Gleason RE, Lee AT, D'Elia JA. Utilization of an abbreviated diabetes impact management scale to assess change in subjective disability during a trial of pulsatile insulin delivery demonstrates benefit. Metabolism ‐ Clinical & Experimental 2009;58(4):488‐91. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Weinrauch LA, Burger AJ, Aepfelbacher F, Lee AT, Gleason RE, D'Elia JA. A pilot study to test the effect of pulsatile insulin infusion on cardiovascular mechanisms that might contribute to attenuation of renal compromise in type 1 diabetes mellitus patients with proteinuria. Metabolism ‐ Clinical & Experimental 2007 Nov;56(11):1453‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Davidson 2007 {published data only}
-
- Davidson JA, McMorn SO, Waterhouse BR, Cobitz AR. A 24‐week, multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, parallel‐group study of the efficacy and tolerability of combination therapy with rosiglitazone and sulfonylurea in African American and Hispanic American patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with sulfonylurea monotherapy. Clinical Therapeutics 2007 Sep;29(9):1900‐14. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
DCCT 1986 {published data only}
-
- Al‐Kateb H, Boright AP, Mirea L, Xie X, Sutradhar R, Mowjoodi A, et al. Multiple superoxide dismutase 1/splicing factor serine alanine 15 variants are associated with the development and progression of diabetic nephropathy: the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications Genetics study. Diabetes 2008;57(1):218‐28. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anonymous. Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT). Update. DCCT Research Group. Diabetes Care 1990;13(4):427‐33. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Anonymous. Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT): results of feasibility study. The DCCT Research Group. Diabetes Care 1987;10(1):1‐19. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Anonymous. Effect of intensive diabetes treatment on the development and progression of long‐term complications in adolescents with insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus: Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. Journal of Pediatrics 1994;125(2):177‐88. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Anonymous. Effect of intensive therapy on the development and progression of diabetic nephropathy in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. The Diabetes Control and Complications (DCCT) Research Group. Kidney International 1995;47(6):1703‐20. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
de Boer 2013 {published data only}
DeFronzo 2009 {published data only}
Derosa 2004 {published data only}
-
- Derosa G, Franzetti I, Gadaleta G, Ciccarelli L, Fogari R. Metabolic variations with oral antidiabetic drugs in patients with Type 2 diabetes: comparison between glimepiride and metformin. Diabetes, Nutrition & Metabolism ‐ Clinical & Experimental 2004;17(3):143‐50. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Didjurgeit 2002 {published data only}
-
- Didjurgeit U, Kruse J, Schmitz N, Stuckenschneider P, Sawicki PT. A time‐limited, problem‐orientated psychotherapeutic intervention in Type 1 diabetic patients with complications: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetic Medicine 2002;19(10):814‐21. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Di Mauro 2001 {published data only}
-
- Mauro M, Papalia G, Moli R, Nativo B, Nicoletti F, Lunetta M. Effect of octreotide on insulin requirement, hepatic glucose production, growth hormone, glucagon and c‐peptide levels in type 2 diabetic patients with chronic renal failure or normal renal function. Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice 2001;51(1):45‐50. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
DNETT Japan 2010 {published data only}
-
- Shikata K, Haneda M, Koya D, Suzuki Y, Tomino Y, Yamada K, et al. Diabetic Nephropathy Remission and Regression Team Trial in Japan (DNETT‐Japan): rationale and study design. Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice 2010;87(2):228‐32. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Einhorn 2000 {published data only}
-
- Einhorn D, Rendell M, Rosenzweig J, Egan JW, Mathisen AL, Schneider RL. Pioglitazone hydrochloride in combination with metformin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, placebo‐controlled study. The Pioglitazone 027 Study Group. Clinical Therapeutics 2000;22(12):1395‐409. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Fadini 2016 {published data only}
-
- Fadini GP, Bonora BM, Cappellari R, Menegazzo L, Vedovato M, Iori E, et al. Acute effects of linagliptin on progenitor cells, monocyte phenotypes, and soluble mediators in type 2 diabetes. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 2016;101(2):748‐56. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Fang 2007 {published data only}
-
- Fang YJ. Observation of treatment effect of pioglitazone in diabetic kidney disease. Modern Practical Medicine 2007;19(7):555‐6. [CENTRAL: CN‐00783737]
Feldt‐Rasmussen 1986 {published data only}
-
- Feldt‐Rasmussen B, Mathiesen ER, Deckert T. Effect of two years of strict metabolic control on progression of incipient nephropathy in insulin‐dependent diabetes. Lancet 1986;2(8519):1300‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Feldt‐Rasmussen B, Mathiesen ER, Hegedus L, Deckert T. Kidney function during 12 months of strict metabolic control in insulin‐dependent diabetic patients with incipient nephropathy. New England Journal of Medicine 1986;314(11):665‐70. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Frederich 2012 {published data only}
Gadallah 2000b {published data only}
-
- Gadallah M, Andrews G, Hanna D, Patel A, Po S, Wooldridge T. Role of metformin in treatment of hypertension in patients with insulin resistance mediated hypertension [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2000;11(Sept):347A. [CENTRAL: CN‐00583336]
Gan 2007 {published data only}
-
- Gan JX, Tang FR. Observation of therapeutic effects of rosiglitazone in type2 diabetic nephropathy. Chinese Medical Journal of Metallurgical Industry 2007;24(1):45‐6. [CENTRAL: CN‐00783735]
Gao 2006a {published data only}
-
- Gao XH, HP X. Short‐term improvement effects of pioglitazone combined prostaglandin E1 in diabetic nephropathy. Clinical Focus 2006;21(20):1497‐8. [CENTRAL: CN‐00784213]
Gao 2007a {published data only}
-
- Gao L, Yu DM. Effects of rosiglitazone on urinary albumin excretion in patients with early diabetic nephropathy. Zhong Guo Man Xing Bing Yu Fang Yu Kong Zhi [Chinese Journal of Prevention and Control of Chronic Non‐communicable Diseases] 2007;15(2):126‐8. [CENTRAL: CN‐00783105]
Gao 2007b {published data only}
-
- Gao MS, Zheng CH, Ke SH. Pioglitazone combined fosinopril in treating 52 patients with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria. Journal of New Medicine 2007;17(3):176‐7. [CENTRAL: CN‐00783869]
GEMINI 2005 {published data only}
-
- Bakris GL, Bell DS, Fonseca V, Katholi R, McGill J, Phillips R, et al. The rationale and design of the Glycemic Effects in Diabetes Mellitus Carvedilol‐Metoprolol Comparison in Hypertensives (GEMINI) trial. Journal of Diabetes & its Complications 2005;19(2):74‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Bakris GL, Fonseca V, Katholi RE, McGill JB, Messerli F, Phillips RA, et al. Differential effects of beta‐blockers on albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes. Hypertension 2005;46(6):1309‐15. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Goicolea 2002 {published data only}
-
- Goicolea I, Fernandez Gonzalez R, Pinies J, Garrido J, Martinez JM, Armenteros S, et al. Effect of antihypertensive combinations on arterial pressure, albuminuria, and glycemic control in patients with type II diabetic nephropathy: a randomized study [Efecto de dos combinaciones antihipertensivas sobre la presion arterial, albuminuria y control glucemico en pacientes con nefropatia diabetica tipo 2: un estudio aleatorizado]. Nefrologia 2002;22(2):170‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
He 2004 {published data only}
-
- He JP, Zhao Q, Yuan WS, Zeng WX. Observation of therapeutic effects of pioglitazone in early diabetic nephropathy. Journal of Practical Medicine 2004;20(6):704‐5. [CENTRAL: CN‐00783733]
Hollander 2009 {published data only}
-
- Hollander P, Li J, Allen E, Chen R, CV181‐013 Investigators. Saxagliptin added to a thiazolidinedione improves glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes and inadequate control on thiazolidinedione alone. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 2009;94(12):4810‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Holman 1983 {published data only}
-
- Holman RR, Dornan TL, Mayon‐White V, Howard‐Williams J, Orde‐Peckar C, Jenkins L, et al. Prevention of deterioration of renal and sensory‐nerve function by more intensive management of insulin‐dependent diabetic patients. A two‐year randomised prospective study. Lancet 1983;1(8318):204‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hu 2007 {published data only}
-
- Hu ZY, Zhao JW. Effect of rosiglitazone on serum CRP and plasma PAI‐1 in patients with early type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Central Plains Medical Journal 2007;34(20):27‐8. [CENTRAL: CN‐00783022]
Hu 2010 {published data only}
-
- Hu YY, Ye SD, Zhao LL, Zheng M, Chen Y. Hydrochloride pioglitazone decreases urinary TGF‐beta1 excretion in type 2 diabetics. European Journal of Clinical Investigation 2010;40(7):571‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Hu YY, Ye SD, Zhao LL, Zheng M, Wu FZ, Chen Y. Hydrochloride pioglitazone decreases urinary cytokines excretion in type 2 diabetes. Clinical Endocrinology 2010;73(6):739‐43. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Huang 2004 {published data only}
-
- Huang H, Liu PY. Observation of therapeutic effects of rosiglitazone in diabetic nephropathy. Acta Medicinae Sinica 2004;17(3):324‐5. [CENTRAL: CN‐00783734]
Huang 2006 {published data only}
-
- Huang XX, Zhang JE, Li XF, Li T. Effect of rosiglitazone on urinary monocyte chemoattractant protein‐1 in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Journal of Yunyang Medical College 2006;25(4):211‐3. [CENTRAL: CN‐00783023]
Huang 2007 {published data only}
-
- Huang YY, Liu JH. Effects of pioglitazone on changes of haemorrheology and insulin resistance in patients with early diabetic nephropathy. IMHGN ‐ International Medicine & Health Guidance News 2007;13(7):51‐4. [CENTRAL: CN‐00783093]
Imano 1998 {published data only}
-
- Imano E, Kanda T, Nakatani Y, Nishida T, Arai K, Motomura M, et al. Effect of troglitazone on microalbuminuria in patients with incipient diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Care 1998;21(12):2135‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Inagaki 2014 {published data only}
Jerums 1987 {published data only}
-
- Jerums G, Murray RM, Seeman E, Cooper ME, Edgley S, Marwick K, et al. Lack of effect of gliclazide on early diabetic nephropathy and retinopathy: a two‐year controlled study. Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice 1987;3(2):71‐80. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kadhim 2006 {published data only}
-
- Kadhim HM, Ismail SH, Hussein KI, Bakir IH, Sahib AS, Khalaf BH, et al. Effects of melatonin and zinc on lipid profile and renal function in type 2 diabetic patients poorly controlled with metformin. Journal of Pineal Research 2006;41(2):189‐93. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kadowaki 2014 {published data only}
-
- Kadowaki T, Haneda M, Inagaki N, Terauchi Y, Taniguchi A, Koiwai K, et al. Empagliflozin monotherapy in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, 12‐week, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, phase II trial. Advances in Therapy 2014;31(6):621‐38. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Karalliedde 2006 {published data only}
-
- Karalliedde J, Buckingham R, Starkie M, Lorand D, Stewart M, Viberti G, et al. Effect of various diuretic treatments on rosiglitazone‐induced fluid retention. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2006;17(12):3482‐90. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Katavetin 2006 {published data only}
-
- Katavetin P, Eiam‐Ong S, Suwanwalaikorn S. Pioglitazone reduces urinary protein and urinary transforming growth factor‐beta excretion in patients with type 2 diabetes and overt nephropathy. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand 2006;89(2):170‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kim 2003 {published data only}
-
- Do J, Cho K, Park J, Yoon K, Cho D, Kim Y. Local and systemic effects of neutral pH, low GDP dialysate in CAPD patients [abstract no: SA‐FC202]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2002;13(September, Program & Abstracts):41A. [CENTRAL: CN‐00445121]
-
- Park J, Do J, Kim Y, Kim T, Yoon K, Park S. The effect of low GDPs solution on peritoneal fibrosis markers [abstract no: SA‐PO333]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2004;15(Oct):374A. [CENTRAL: CN‐00583515]
Kirk 1999 {published data only}
-
- Kirk JK, Pearce KA, Michielutte R, Summerson JH. Troglitazone or metformin in combination with sulfonylureas for patients with type 2 diabetes?. Journal of Family Practice 1999;48(11):879‐82. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
KUMAMOTO 1995 {published data only}
-
- Ohkubo Y, Kishikawa H, Araki E, Miyata T, Isami S, Motoyoshi S, et al. Intensive insulin therapy prevents the progression of diabetic microvascular complications in Japanese patients with non‐insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus: a randomized prospective 6‐year study. Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice 1995;28(2):103‐17. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Shichiri M, Kishikawa H, Ohkubo Y, Wake N. Long‐term results of the Kumamoto Study on optimal diabetes control in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2000;23 Suppl 2:B21‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Wake N, Hisashige A, Katayama T, Kishikawa H, Ohkubo Y, Sakai M, et al. Cost‐effectiveness of intensive insulin therapy for type 2 diabetes: a 10‐year follow‐up of the Kumamoto study. Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice 2000;48(3):201‐10. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lebovitz 2001 {published data only}
-
- Lebovitz HE, Dole JF, Patwardhan R, Rappaport EB, Freed MI, Rosiglitazone Clinical Trials Study Group. Rosiglitazone monotherapy is effective in patients with type 2 diabetes.[Erratum appears in J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002 Feb;2(1):iv.], [Erratum appears in J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001 Apr;86(4):1659]. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 2001;86(1):280‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Leslie 2008 {published data only}
-
- Leslie B, Tang W, Tang W, List JF. Renal effects of the sodium‐glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor dapagliflozin (BMS‐512148) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) [abstract no: TH‐PO1022]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2008;19(Abstracts Issue):341A.
Li 2004a {published data only}
-
- Li X, Duan BH, Wang YW, Feng K, Yang YZ. Observation of effect of rosiglitazone in type 2 diabetes with trace urinary protein. Zhong Guo Wu Zhen Xue Za Zhi [Chinese Journal of Misdiagnostics] 2004;4(9):1432. [CENTRAL: CN‐00783727]
Li 2006e {published data only}
-
- Li ZL. Effects of pioglitazone on microalbuminuria of early diabetic nephropathy. Journal of Medical Forum 2006;27(9):31‐3. [CENTRAL: CN‐00783094]
Li 2008f {published data only}
-
- Li B, Ba HJ, Yun L, Wang SG, Zhao SZ, Yue ZW. Therapeutic effect of captopril combined with rosiglitazone on early diabetic nephropathy. Chinese Journal of Difficult & Complicated Cases 2008;7(2):80‐2. [CENTRAL: CN‐00784501]
Li 2008g {published data only}
-
- Li YL, Wang SJ, Li JZ. Rosiglitazone affect type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Zhong Guo Chang Kuang Yi Xue [Chinese Medicine of Factory and Mine] 2008;21(1):58‐9. [CENTRAL: CN‐00784162]
Lu 2010 {published data only}
-
- Lu WH, Shi BY, Zhang XT, Wei DG, Liu WD, Duan PZ. Significance of intensive glycemic control on early diabetic nephropathy patients with microalbuminuria. Academic Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University 2010;22(2):135‐8. [EMBASE: 2010319798]
Matthews 2005 {published data only}
-
- Charbonnel B, Schernthaner G, Brunetti P, Matthews DR, Urquhart R, Tan MH, et al. Long‐term efficacy and tolerability of add‐on pioglitazone therapy to failing monotherapy compared with addition of gliclazide or metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2005;48(6):1093‐104. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Matthews DR, Charbonnel BH, Hanefeld M, Brunetti P, Schernthaner G. Long‐term therapy with addition of pioglitazone to metformin compared with the addition of gliclazide to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, comparative study. Diabetes/Metabolism Research Reviews 2005;21(2):167‐74. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
MEMO 2011 {published data only}
-
- Crasto W, Jarvis J, Khunti K, Skinner TC, Gray LJ, Brela J, et al. Multifactorial intervention in individuals with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria: the Microalbuminuria Education and Medication Optimisation (MEMO) study. Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice 2011;93(3):328‐36. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Crasto W, Khunti K, Jarvis Kay J, Skinner TC, Gray LJ, Brela J, et al. Impact of intensive multi‐factorial intervention on novel markers of inflammation and vascular stiffness [abstract no: P446]. Diabetic Medicine 2011;28(Suppl 1):166. [EMBASE: 70631246]
-
- Crasto WA, Jarvis J, Brela J, Daly H, Gray LJ, Troughton J, et al. Interim analysis of the effects of a multifactorial intervention in people with Type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria after twelve months [abstract no: P410]. Diabetic Medicine 2009;26(Suppl 1):160. [EMBASE: 70342536]
Miyazaki 2007 {published data only}
-
- Miyazaki Y, Cersosimo E, Triplitt C, DeFronzo RA. Rosiglitazone decreases albuminuria in type 2 diabetic patients. Kidney International 2007;72(11):1367‐73. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Nakamura 2000b {published data only}
-
- Nakamura T, Ushiyama C, Shimada N, Hayashi K, Ebihara I, Koide H. Comparative effects of pioglitazone, glibenclamide, and voglibose on urinary endothelin‐1 and albumin excretion in diabetes patients. Journal of Diabetes & its Complications 2000;14(5):250‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Nakamura 2001b {published data only}
-
- Nakamura T, Ushiyama C, Suzuki S, Shimada N, Sekizuka K, Ebihara L, et al. Effect of troglitazone on urinary albumin excretion and serum type IV collagen concentrations in Type 2 diabetic patients with microalbuminuria or macroalbuminuria. Diabetic Medicine 2001;18(4):308‐13. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Nakamura 2004 {published data only}
-
- Nakamura T, Matsuda T, Kawagoe Y, Ogawa H, Takahashi Y, Sekizuka K, et al. Effect of pioglitazone on carotid intima‐media thickness and arterial stiffness in type 2 diabetic nephropathy patients. Metabolism: Clinical & Experimental 2004;53(10):1382‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Nakamura 2006a {published data only}
-
- Nakamura T, Sugaya T, Kawagoe Y, Ueda Y, Koide H. Effect of pioglitazone on urinary liver‐type fatty acid‐binding protein concentrations in diabetes patients with microalbuminuria. Diabetes/Metabolism Research Reviews 2006;22(5):385‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
NCT00708981 {published data only}
-
- Fogelfeld L, Stroger JH. Combined diabetes‐renal multifactorial intervention in patients with advanced diabetic nephropathy (ADN). www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00708981 (first received 3 July 2008).
NCT01245166 {published data only}
-
- NCT01245166. A phase III randomized, double‐blind, parallel‐group study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of acarmet (metformin HCl 500 mg plus acarbose 50 mg tablets) versus acarbose alone in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01245166 (first received 22 November 2010).
Nishimura 2015 {published data only}
-
- Jinnouchi H, Nozaki K, Watase H, Omiya H, Sakai S, Samukawa Y. Impact of reduced renal function on the glucose‐lowering effects of luseogliflozin, a selective SGLT2 inhibitor, assessed by continuous glucose monitoring in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Advances in Therapy 2016;33(3):460‐79. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nishimura R, Osonoi T, Kanada S, Jinnouchi H, Sugio K, Omiya H, et al. Effects of luseogliflozin, a sodium‐glucose co‐transporter 2 inhibitor, on 24‐h glucose variability assessed by continuous glucose monitoring in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, crossover study. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2015;17(8):800‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
OSLO 1986 {published data only}
-
- Dahl‐Jorgensen K, Brinchmann‐Hansen O, Hanssen KF, Ganes T, Kierulf P, Smeland E, et al. Effect of near normoglycaemia for two years on progression of early diabetic retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy: the Oslo study. British Medical Journal Clinical Research Ed 1986;293(6556):1195‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dahl‐Jorgensen K, Hanssen KF, Kierulf P, Bjoro T, Sandvik L, Aagenaes O. Reduction of urinary albumin excretion after 4 years of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus. The Oslo Study. Acta Endocrinologica 1988;117(1):19‐25. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ostman 1998 {published data only}
-
- Ostman J, Asplund K, Bystedt T, Dahlof B, Jern S, Kjellstrom T, et al. Comparison of effects of quinapril and metoprolol on glycaemic control, serum lipids, blood pressure, albuminuria and quality of life in non‐insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus patients with hypertension. Swedish Quinapril Group. Journal of Internal Medicine 1998;244(2):95‐107. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Pan 2012 {published data only}
-
- Pan CY, Yang W, Tou C, Gause‐Nilsson I, Zhao J. Efficacy and safety of saxagliptin in drug‐naive Asian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes/Metabolism Research Reviews 2012;28(3):268‐75. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Petrica 2009 {published data only}
-
- Petrica L, Petrica M, Vlad A, Dragos Jianu C, Gluhovschi G, Ianculescu C, et al. Nephro‐ and neuroprotective effects of rosiglitazone versus glimepiride in normoalbuminuric patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial. Wiener Klinische Wochenschrift 2009;121(23‐24):765‐75. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Pistrosch 2004 {published data only}
-
- Pistrosch F, Passauer J, Fischer S, Fuecker K, Hanefeld M, Gross P. In type 2 diabetes, rosiglitazone therapy for insulin resistance ameliorates endothelial dysfunction independent of glucose control. Diabetes Care 2004;27(2):484‐90. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Pistrosch 2005 {published data only}
-
- Pistrosch F, Herbrig K, Kindel B, Passauer J, Fischer S, Gross P. Rosiglitazone improves glomerular hyperfiltration, renal endothelial dysfunction, and microalbuminuria of incipient diabetic nephropathy in patients. Diabetes 2005;54(7):2206‐11. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Pistrosch 2012 {published data only}
-
- Pistrosch F, Passauer J, Herbrig K, Schwanebeck U, Gross P, Bornstein SR. Effect of thiazolidinedione treatment on proteinuria and renal hemodynamic in type 2 diabetic patients with overt nephropathy. Hormone & Metabolic Research 2012;44(12):914‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
PIVIT 2010 {published data only}
-
- Weinrauch LA, Sun J, Gleason RE, Boden GH, Creech RH, Dailey G, et al. Pulsatile intermittent intravenous insulin therapy for attenuation of retinopathy and nephropathy in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism: Clinical & Experimental 2010;59(10):1429‐34. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Pomerleau 1993 {published data only}
-
- Pomerleau J, Verdy M, Garrel DR, Nadeau MH. Effect of protein intake on glycaemic control and renal function in type 2 (non‐insulin‐dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 1993;36(9):829‐34. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
QUARTET 2004 {published data only}
-
- Charbonnel B, Schernthaner G, Brunetti P, Matthews DR, Urquhart R, Tan MH, et al. Long‐term efficacy and tolerability of add‐on pioglitazone therapy to failing monotherapy compared with addition of gliclazide or metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2005;48(6):1093‐104. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Charbonnel BH, Matthews DR, Schernthaner G, Hanefeld M, Brunetti P, QUARTET Study Group. A long‐term comparison of pioglitazone and gliclazide in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, double‐blind, parallel‐group comparison trial. Diabetic Medicine 2005;22(4):399‐405. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Hanefeld M, Brunetti P, Schernthaner GH, Matthews DR, Charbonnel BH, QUARTET Study Group. One‐year glycemic control with a sulfonylurea plus pioglitazone versus a sulfonylurea plus metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004;27(1):141‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Schernthaner G, Matthews DR, Charbonnel B, Hanefeld M, Brunetti P, Quartet [corrected] Study Group. Efficacy and safety of pioglitazone versus metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a double‐blind, randomized trial.[Erratum appears in J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005 Feb;90(2):746]. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 2004;89(12):6068‐76. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Reinhard 2013 {published data only}
Rosenstock 2009 {published data only}
-
- Rosenstock J, Aguilar‐Salinas C, Klein E, Nepal S, List J, Chen R, et al. Effect of saxagliptin monotherapy in treatment‐naive patients with type 2 diabetes. Current Medical Research & Opinion 2009;25(10):2401‐11. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
SDIS 1988 {published data only}
-
- Jensen‐Urstad K, Reichard P, Jensen‐Urstad M. Decreased heart rate variability in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus is related to arterial wall stiffness. Journal of Internal Medicine 1999;245(1):57‐61. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Johansson J, Reichard P, Jensen‐Urstad K, Rosfors S, Jensen‐Urstad M. Influence of glucose control, lipoproteins, and haemostasis function on brachial endothelial reactivity and carotid intima‐media area, stiffness and diameter in Type 1 diabetes mellitus patients. European Journal of Clinical Investigation 2003;33(6):472‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Rathsman B, Jensen‐Urstad K, Nystrom T. Intensified insulin treatment is associated with improvement in skin microcirculation and ischaemic foot ulcer in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus: a long‐term follow‐up study. Diabetologia 2014;57(8):1703‐10. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Reichard P. Risk factors for progression of microvascular complications in the Stockholm Diabetes Intervention Study (SDIS). Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice 1992;16(2):151‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Reichard P, Berglund B, Britz A, Cars I, Nilsson BY, Rosenqvist U. Intensified conventional insulin treatment retards the microvascular complications of insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM): the Stockholm Diabetes Intervention Study (SDIS) after 5 years. Journal of Internal Medicine 1991;230(2):101‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Seino 2015 {published data only}
SESTA R 2011 {published data only}
-
- Herz M, Gaspari F, Perico N, Viberti G, Urbanowska T, Rabbia M, et al. Effects of high dose aleglitazar on renal function in patients with type 2 diabetes. International Journal of Cardiology 2011;151(2):136‐42. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Shata'er 2007 {published data only}
-
- Shata'er R. Rosiglitazone in urinary protein of diabetic nephropathy. Chinese Medicine Clinical Research ‐ Chinese Magazine of Clinical Medicinal Professional Research 2007;13(15):2162‐3. [CENTRAL: CN‐00784163]
SPEAD‐A 2013 {published data only}
-
- Katakami N, Mita T, Yoshii H, Onuma T, Kaneto H, Osonoi T, et al. Rationale, design, and baseline characteristics of a trial for the prevention of diabetic atherosclerosis using a DPP‐4 inhibitor: the Study of Preventive Effects of Alogliptin on Diabetic Atherosclerosis (SPEAD‐A). Journal of Atherosclerosis & Thrombosis 2013;20(12):893‐902. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Stein 2014 {published data only}
-
- Stein P, Berg JK, Morrow L, Polidori D, Artis E, Rusch S, et al. Canagliflozin, a sodium glucose co‐transporter 2 inhibitor, reduces post‐meal glucose excursion in patients with type 2 diabetes by a non‐renal mechanism: results of a randomized trial. Metabolism: Clinical & Experimental 2014;63(10):1296‐303. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
STENO‐2 1999 {published data only}
-
- Gaede P, Lund‐Andersen H, Parving HH, Pedersen O. Effect of a multifactorial intervention on mortality in type 2 diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine 2008;358(6):580‐91. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Gaede P, Parving H, Pedersen O. Multifactorial intervention in patients with type 2 diabetes: long‐term effects on mortality and vascular complications [abstract no: SA‐FC042]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2007;18(Abstracts):43A. [CENTRAL: CN‐00740461]
-
- Gaede P, Vedel P, Larsen N, Jensen G, Parving HH, Pedersen O. The STENO‐2 study: intensified multifactorial intervention reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria [abstract no: F‐FC031]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2002;13(September, Program & Abstracts):72A. [CENTRAL: CN‐00445410]
-
- Gaede P, Vedel P, Larsen N, Jensen G, Parving HH, Pedersen O. The Steno‐2 study: intensified multifactorial intervention reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with Type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria [abstract no: 181]. 38th Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD); 2002 Sep 1‐5; Budapest, Hungary. 2002.
Strojek 2011 {published data only}
-
- Strojek K, Yoon KH, Hruba V, Elze M, Langkilde AM, Parikh S. Effect of dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes who have inadequate glycaemic control with glimepiride: a randomized, 24‐week, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2011;13(10):928‐38. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Su 2006 {published data only}
-
- Su RT, Hang XJ. Pioglitazone affects the urinary protein extracting rate in early diabetic nephropathy. Youjiang Medical Journal 2006;34(6):593‐4. [CENTRAL: CN‐00783868]
Sun 2006 {published data only}
-
- Sun Z, Ren X, Jin H, Gong Y, Li l, Zhang L. Effect of pioglitazone on serum advanced glycosylation end product peptide and monocyte chemoattractant protein‐1 in type 2 diabetic patients. Jiangsu Medical Journal 2006;32(2):101‐3. [CENTRAL: CN‐00783008]
Tan 2006 {published data only}
-
- Tan YH, Zheng W. Observation of therapeutic effect of rosiglitazone in type 2 diabetes with nephropathy. Journal of Modern Clinical Medical Bioengineering 2006;12(2):176‐8. [CENTRAL: CN‐00783732]
Tang 2007 {published data only}
-
- Tang GJ, Zhu GD, Xie NR. Treatment effect of rosiglitazone in type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Clinical Medicine 2007;27(7):47‐8. [CENTRAL: CN‐00784585]
Thrasher 2012 {published data only}
-
- Thrasher J, Daniels K, Patel S, Whetteckey J. Black/African American patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: study design and baseline patient characteristics from a randomized clinical trial of linagliptin. Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy 2012;13(17):2443‐52. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
UKPDS 1991 {published data only}
-
- Turner R, Cull C, Holman R. United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study 17: a 9‐year update of a randomized, controlled trial on the effect of improved metabolic control on complications in non‐insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus. Annals of Internal Medicine 1996;124(1 Pt 2):136‐45. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
UKPDS‐HD 1998 {published data only}
VA‐CSDM 1992 {published data only}
-
- Abraira C, Colwell J, Nuttall F, Sawin CT, Henderson W, Comstock JP, et al. Cardiovascular events and correlates in the Veterans Affairs Diabetes Feasibility Trial. Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study on Glycemic Control and Complications in Type II Diabetes. Archives of Internal Medicine 1997;157(2):181‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Abraira C, Colwell JA, Nuttall FQ, Sawin CT, Nagel NJ, Comstock JP, et al. Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study on glycemic control and complications in type II diabetes (VA CSDM). Results of the feasibility trial. Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study in Type II Diabetes. Diabetes Care 1995;18(8):1113‐23. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Abraira C, Emanuele N, Colwell J, Henderson W, Comstock J, Levin S, et al. Glycemic control and complications in type II diabetes. Design of a feasibility trial. VA CS Group (CSDM). Diabetes Care 1992;15(11):1560‐71. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Abraira C, Henderson WG, Colwell JA, Nuttall FQ, Comstock JP, Emanuele NV, et al. Response to intensive therapy steps and to glipizide dose in combination with insulin in type 2 diabetes. VA feasibility study on glycemic control and complications (VA CSDM). Diabetes Care 1998;21(4):574‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Abraira C, McGuire DK. Intensive insulin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes: implications of the Veterans affairs (VA CSDM) feasibility trial. American Heart Journal 1999;138(5 Pt 1):S360‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Viswanathan 1990 {published data only}
-
- Viswanathan M, Snehalatha C, Mohan V, Ramachandran A, Mohan R. Comparative study of monocomponent insulins and conventional insulins on the course of diabetic nephropathy. A follow‐up study. Journal of the Association of Physicians of India 1990;38(11):833‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Vos 2011 {published data only}
-
- Vos FE, Manning PJ, Sutherland WH, Schollum JB, Walker RJ. Anti‐inflammatory effect of an insulin infusion in patients on maintenance haemodialysis: a randomized controlled pilot study. Nephrology 2011;16(1):68‐75. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Vos FE, Manning PJ, Sutherland WHF, Schollum J, Walker RJ. Does insulin have an anti‐inflammatory effect in patients with end‐stage renal disease on haemodialysis?. Nephrology 2009;14(Suppl 1):A4.
Wang 2004 {published data only}
-
- Wang L. Renal protecting effects of pioglitazone in diabetic nephropathy. Clinical Medicine 2004;24(6):13‐4. [CENTRAL: CN‐00784118]
Wang 2005b {published data only}
-
- Wang XQ, Chen JY, Wang YH, Chen JF, Wu G, Jin Y. Rosiglitazone affects albuminuria in type 2 diabetes. Journal of Postgraduates of Medicine 2005;28(11A):36‐7. [CENTRAL: CN‐00784160]
Wang 2005c {published data only}
-
- Wang YW, Duan BH, Feng K, Zhang XL. Effects of rosiglitazone in type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Clinical Medicine of China 2005;21(8):711‐2. [CENTRAL: CN‐00783103]
-
- Wang YW, Duan BH, Feng K, Zhang XL. Rosiglitazone affects urinary protein excretory rate and C‐reactive protein in diabetic nephropathy. Zhong Guo Wu Zhen Xue Za Zhi [Chinese Journal of Misdiagnostics] 2005;5(4):692‐4. [CENTRAL: CN‐00784161]
Wang 2006 {published data only}
-
- Wang JG. Twenty‐two cases diagnosed with diabetic nephropathy treated with pioglitazone combined prostaglandin. Zheng Zhou Da Xue Xue Bao (Yi Xue Ban) [Journal of Zhengzhou University (Medical Science)] 2006;41(4):808‐9.
Wang 2008e {published data only}
-
- Wang XH. Effect of rosiglitazone in early stage of diabetic nephropathy. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine 2008;7(2):95‐6. [CENTRAL: CN‐00783020]
Wiseman 1985 {published data only}
-
- Wiseman MJ, Saunders AJ, Keen H, Viberti G. Effect of blood glucose control on increased glomerular filtration rate and kidney size in insulin‐dependent diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine 1985;312(10):617‐21. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Xu 2005 {published data only}
-
- Xu FJ, Yu FL, Yu FQ, Gu QX, Li Q. Observation of trace urinary protein and C‐reactive protein level of pioglitazone treating early diabetic nephropathy. Chongqin Medicine Journal 2005;34(1):56‐7. [CENTRAL: CN‐00783736]
Yang 2011a {published data only}
-
- Yang W, Pan CY, Tou C, Zhao J, Gause‐Nilsson I. Efficacy and safety of saxagliptin added to metformin in Asian people with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice 2011;94(2):217‐24. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Yokoyama 2009 {published data only}
-
- Yokoyama H, Inoue T, Node K. Effect of insulin‐unstimulated diabetic therapy with miglitol on serum cystatin C level and its clinical significance. Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice 2009;83(1):77‐82. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Zhang 2007c {published data only}
-
- Zhang JD. Clinical observation of treatment effect of enalapril combined rosiglitazone in early stage diabetic nephropathy. Zhong Guo Yi Yuan Yao Xue Za Zhi [Chinese Journal of Hospital Pharmacy] 2007;27(10):1432‐4. [CENTRAL: CN‐00782589]
Zhang 2012a {published data only}
-
- Zhang H, Zhang X, Hu C, Lu W. Exenatide reduces urinary transforming growth factor‐beta1 and type IV collagen excretion in patients with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria. Kidney & Blood Pressure Research 2012;35(6):483‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Zhao 2007 {published data only}
-
- Zhao ZG, Liu J, Hou YL. Effect of rosiglitazone in microalbuminuria in type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Clinical Focus 2007;22(14):1037‐8. [CENTRAL: CN‐00783021]
Zheng 2006 {published data only}
-
- Zheng W. The clinical observation of benazepril combined with rosiglitazone in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Academic Journal of GuangZhou Medical College 2006;34(6):36‐8. [CENTRAL: CN‐00784331]
Zhou 2003 {published data only}
-
- Zhou GY, Su XS, Liu Y, Li DT. Renal protection effects of rosiglitazone in diabetic nephropathy. Liaoning Pharmacy and Clinical Remedies 2003;6(2):72‐3. [CENTRAL: CN‐00784119]
Zhou 2007 {published data only}
-
- Zhou DY, Sheng CQ. Observation of treatment effect of rosiglitazone combined irbesartan. Zhong Guo Man Xing Bing Yu Fang Yu Kong Zhi [Chinese Journal of Prevention and Control of Chronic Non‐communicable Diseases] 2007;15(5):480‐1. [CENTRAL: CN‐00783738]
Zhu 2007 {published data only}
-
- Zhu K, Yang BY, Jin Y, Liu W. Metformin treatment of early diabetic nephropathy. JiLin Medical Journal 2007;28(17):1845‐6. [CENTRAL: CN‐00783630]
Zou 2005 {published data only}
-
- Zou XB, Zhou YH. Observation of curative effect of rosiglitazone on delaying progression of type 2 diabetic nephropathy. China Pharmacy 2005;16(12):931‐3. [CENTRAL: CN‐00783726]
References to studies awaiting assessment
AWARD‐7 2017 {published data only}
-
- Tuttle KR, Lakshmanan MC, Gross JL, Rayner B, Busch RS, Woodward DB, et al. Comparable glycaemic control with once weekly dulaglutide versus insulin glargine, both combined with lispro, in type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease (AWARD‐7) [abstract]. Diabetologia 2017;60(1 Suppl 1):S3. [EMBASE: 618051873]
Chacra 2017 {published data only}
-
- Chacra A, Gantz I, Mendizabal G, Durlach L, O'Neill EA, Zimmer Z, et al. A randomised, double‐blind, trial of the safety and efficacy of omarigliptin (a once‐weekly DPP‐4 inhibitor) in subjects with type 2 diabetes and renal impairment. International Journal of Clinical Practice 2017;71(6):1. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Chan 2011 {published data only}
-
- Chan D, Watts G, Irish A, Dogra G. Effect of rosiglitazone on arterial function and stiffness in patients with stage 3 to 4 chronic kidney disease [abstract no: 127]. Nephrology 2008;13(Suppl 3):A133.
-
- Chan D, Watts G, Irish A, Dogra G. Rosiglitazone improves inflammation and in vivo marker of endothelial function but not arterial function and stiffness in patients with stage 3 ‐ 4 chronic kidney disease [abstract no: SA181]. World Congress of Nephrology; 2009 May 22‐26; Milan, Italy. 2009.
-
- Chan D, Watts G, Irish A, Dogra G. Rosiglitazone lowers insulin resistance, inflammation and von Willebrand factor in patients with stage 1‐4 chronic kidney disease [abstract no: 126]. Nephrology 2008;13(Suppl 3):A132‐3.
-
- Chan D, Watts G, Irish A, Dogra G. Safety and tolerability of rosiglitazone in stage 3‐4 chronic kidney disease [abstract no: 125]. Nephrology 2008;13(Suppl 3):A132.
-
- Chan D, Watts G, Irish A, Lim E, Dogra G. Impact of rosiglitazone on markers of bone metabolism in chronic kidney disease [abstract no: 060]. Nephrology 2010;15(Suppl 4):42. [EMBASE: 70467064]
DEVOTE 2017 {published data only}
-
- Marso SP, McGuire DK, Zinman B, Poulter NR, Emerson SS, Pieber TR, et al. Design of DEVOTE (Trial Comparing Cardiovascular Safety of Insulin Degludec vs Insulin Glargine in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes at High Risk of Cardiovascular Events) ‐ DEVOTE 1. American Heart Journal 2016;179:175‐83. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
EXAMINE 2011 {published data only}
-
- Cavender MA, White WB, Jarolim P, Bakris GL, Cushman WC, Kupfer S, et al. Serial measurement of high‐sensitivity troponin i and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in the EXAMINE Trial (Examination of Cardiovascular Outcomes With Alogliptin Versus Standard of Care). Circulation 2017;135(20):1911‐21. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- White WB, Bakris GL, Bergenstal RM, Cannon CP, Cushman WC, Fleck P, et al. EXamination of cArdiovascular outcoMes with alogliptIN versus standard of carE in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and acute coronary syndrome (EXAMINE): a cardiovascular safety study of the dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor alogliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes with acute coronary syndrome. American Heart Journal 2011;162(4):620‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- White WB, Cannon CP, Heller SR, Nissen SE, Bergenstal RM, Bakris GL, et al. Alogliptin after acute coronary syndrome in patients with type 2 diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine 2013;369(14):1327‐35. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- White WB, Kupfer S, Zannad F, Mehta CR, Wilson CA, Lei L, et al. Cardiovascular mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes and recent acute coronary syndromes from the EXAMINE trial. Diabetes Care 2016;39(7):1267‐73. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Zannad F, Cannon CP, Cushman WC, Bakris GL, Menon V, Perez AT, et al. Heart failure and mortality outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes taking alogliptin versus placebo in EXAMINE: a multicentre, randomised, double‐blind trial. Lancet 2015;385(9982):2067‐76. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
LEADER 2017 {published data only}
-
- Daniels GH, Hegedus L, Marso SP, Nauck MA, Zinman B, Bergenstal RM, et al. LEADER 2: baseline calcitonin in 9340 people with type 2 diabetes enrolled in the Liraglutide Effect and Action in Diabetes: Evaluation of cardiovascular outcome Results (LEADER) trial: preliminary observations. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2015;17(5):477‐86. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mann J, Nauck M, Jacob S, Ludemann J, Brown‐Frandsen K, Rieck M, et al. Liraglutide and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: Results of the LEADER trial [abstract]. Internist 2017;58(Suppl 1):S8. [EMBASE: 615632528]
-
- Mann JF, Frandsen KB, Daniels G, Kristensen P, Nauck M, Nissen S, et al. Liraglutide and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: results of the LEADER trial [abstract no: HI‐OR01]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2016;27(Abstract Suppl):1B.
-
- Mann JF, Orsted DD, Brown‐Frandsen K, Marso SP, Poulter NR, Rasmussen S, et al. Liraglutide and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine 2017;377(9):839‐48. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Li 2012b {published data only}
-
- Li Y, Xie QH, You HZ, Tian J, Hao CM, Lin SY, et al. Twelve weeks of pioglitazone therapy significantly attenuates dysmetabolism and reduces inflammation in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients‐‐a randomized crossover trial. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2012;32(5):507‐15. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
MARLINA‐T2D 2015 {published data only}
-
- Groop PH, Cooper ME, Perkovic V, Hocher B, Kanasaki K, Haneda M, et al. Linagliptin and its effects on hyperglycaemia and albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes and renal dysfunction: the randomized MARLINA‐T2D trial. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2017;19(11):1610‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Groop PH, Cooper ME, Perkovic V, Sharma K, Schernthaner G, Haneda M, et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibition with linagliptin and effects on hyperglycaemia and albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes and renal dysfunction: Rationale and design of the MARLINA‐T2DTM trial. Diabetes & Vascular Disease Research 2015;12(6):455‐62. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Schernthaner G, Groop P, Cooper ME, Perkovic V, Hocher B, Kanasaki K, et al. Effects of linagliptin on glycaemic control and albuminuria in type 2 diabetes: The MARLINA‐T2DTM trial [abstract]. Diabetologia 2016;59(1 Suppl 1):S360. [EMBASE: 612313287]
-
- Schernthaner G, Groop P‐H, Cooper ME, Perkovic V, Hocher B, Kanasaki K, et al. Effects of linagliptin on glycaemic control and albuminuria in type 2 diabetes‐the MARLINA‐T2DTM trial [abstract]. Nephrology 2016;21(Suppl 2):60. [EMBASE: 612313048]
NCT00846716 {published data only}
-
- Kashiwagi A, Maegawa H. Exploratory study to investigate the suppressive effect of oral anti‐diabetic drug (tzd) on progression of diabetic nephropathy on Japanese type 2 diabetic patients. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00846716 (first received 19 February 2009).
Neff 2016 {published data only}
-
- Neff KJ, Tobin LM, Hogan AE, Docherty NG, Roux CW, O'Shea D. The effect of low dose liraglutide on renal inflammation in type 2 diabetic kidney disease: a randomised controlled study [abstract]. Diabetic Medicine 2016;33(Suppl 1):64. [EMBASE: 72230717]
Ott 2016 {published data only}
-
- Ott C, Kistner I, Keller M, Friedrich S, Willam C, Bramlage P, et al. Effects of linagliptin on renal endothelial function in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomised clinical trial. Diabetologia 2016;59(12):2579‐87. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Schmieder RE, Friedrich S, Kistner I, Ott C. Effects of linagliptin on early alterations of renal endothelial function in patients with type‐2 diabetes [abstract]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2015;30(Suppl 3):iii11. [EMBASE: 72206303]
SUSTAIN‐6 2016 {published data only}
-
- Consoli A, Bain SC, Davies M, Lingvay I, Bergan EQ, Hansen O, et al. Semaglutide provides sustained reductions in body weight over 2 years in subjects with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 6) [abstract]. Diabetologia 2017;60(1 Suppl 1):S4. [EMBASE: 618051943]
-
- Marso SP, Bain SC, Consoli A, Eliaschewitz FG, Jodar E, Leiter LA, et al. Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine 2016;375(19):1834‐44. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Sanyal AJ, Hansen M, Linder M, Newsome PN. Effect of semaglutide on alanine aminotransferase in subjects with type 2 diabetes and high cardiovascular risk [abstract]. Hepatology 2017;66(Suppl 1):1175A. [EMBASE: 618937026]
von Scholten 2017 {published data only}
-
- Scholten BJ, Persson F, Rosenlund S, Hovind P, Faber J, Hansen TW, et al. The effect of liraglutide on renal function: a randomized clinical trial. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2017;19(2):239‐47. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Xie 2006 {published data only}
-
- Xie XR, Jiang HY. Rosiglitazone's effect to trace urinary protein and C‐reactive protein in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Chinese Journal of Postgraduate Medicine 2006;29(11A):55‐6. [CENTRAL: CN‐00784164]
References to ongoing studies
CARMELINA 2017 {published data only}
-
- Perkovic V, Rosenstock J, MacGuire DK. CARMELINA trial baseline characteristics: A cardiovascular and renal microvascular outcome trial with linagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes at high vascular risk [abstract]. Diabetologia 2017;60(1 Suppl 1):S357. [EMBASE: 618052704]
-
- Rosenstock J, Perkovic V, Alexander JH, Cooper ME, Kahn SE, Marx N, et al. CARMELINA trial baseline characteristics: A cardiovascular and renal microvascular outcome trial with linagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes at high vascular risk [abstract]. Diabetes 2017;66(Suppl 1):A344. [EMBASE: 616960820]
NCT02547935 {published data only}
-
- NCT02547935. A study to evaluate the effect of dapagliflozin with and without saxagliptin on albuminuria, and to investigate the effect of dapagliflozin and saxagliptin on hba1c in patients with type 2 diabetes and CKD3. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02547935 (first received 14 September 2015).
NCT02608177 {published data only}
-
- Boer I. Continuous glucose monitoring to assess glycemia in chronic kidney disease ‐ changing glucose management (CANDY‐CANE). www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02608177 (first received 18 November 2015).
Additional references
ADA 2017
-
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes‐‐2017. Diabetes Care 2017;40(Suppl 1):S1‐135. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
ADVANCE Group 2008
-
- ADVANCE Collaborative Group, Patel A, MacMahon S, Chalmers J, Neal B, Billot L, et al. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine 2008;358(24):2560‐72. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
ALECARDIO 2013
-
- Nainggolan L. ALECARDIO trial halted for safety. Medscape: News and Perspective: www.medscape.com/viewarticle/793304 July 10, 2013.
Andrianesis 2016
ANZDATA 2008
-
- McDonald S, Excell L, Dent H. ANZDATA 32nd Annual Report. 2009 Report: Data to 2008. Chapter 2: New patients commencing treatment in 2008. www.anzdata.org.au/anzdata/AnzdataReport/32ndReport/Ch02.pdf (accessed 9 August 2018).
Bennett 1983
-
- Bennett WM, Aronoff GR, Morrison G, Golper TA, Pulliam J, Wolfson M, et al. Drug prescribing in renal failure: dosing guidelines for adults. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 1983;3(3):155‐93. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Chadban 2003
-
- Chadban SJ, Briganti EM, Kerr PG, Dunstan DW, Welborn, TA, et al. Prevalence of kidney damage in Australian adults: the AusDiab kidney study. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2003;14(7 Suppl 2):S131‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Chadban 2010
-
- Chadban S, Howell M, Twigg S, Thomas M, Jerums G, Cass A, et al. The CARI Guidelines. Prevention and management of chronic kidney disease in type 2 diabetes. Nephrology 2010;15 Suppl 1:S162‐94. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Charpentier 2000
-
- Charpentier G, Riveline JP, Varroud‐Vial M. Management of drugs affecting blood glucose in diabetic patients with renal failure. Diabetes & Metabolism 2000;26 Suppl 4:73‐85. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Cheng 2014
-
- Cheng D, Fei Y, Liu Y, Li J, Chen Y, Wang X, et al. Efficacy and safety of dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with moderate to severe renal impairment: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. PLoS ONE (Electronic Resource] 2014;9(10):e111543. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Collins 2007
-
- Collins AJ, Kasiske B, Herzog C, Chavers B, Foley R, Gilbertson D, et al. Excerpts from the United States Renal Data System 2006 Annual Data Report. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2007;49(1 Suppl 1):A6‐7, S6‐296. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Collins 2008
-
- Collins AJ, Foley R, Herzog C, Chavers B, Gilbertson D, Ishani A, et al. Excerpts from the United States Renal Data System 2007 Annual Data Report. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2008;51(1 Suppl 1):S1‐320. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
CONTROL Group 2009
-
- Control Group, Turnbull FM, Abraira C, Anderson RJ, Byington RP, Chalmers JP, et al. Intensive glucose control and macrovascular outcomes in type 2diabetes.[Erratum appears in Diabetologia. 2009 Nov;52(1):2470 Note: Control Group [added]]. Diabetologia 2009;52(11):2288‐98. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Coresh 2003
-
- Coresh J, Astor BC, Greene T, Eknoyan G, Levey AS. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease and decreased kidney function in the adult US population: Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2003;41(1):1‐12. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
DCCT Group 1993
-
- Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group, Nathan DM, Genuth S, Lachin J, Cleary P, Crofford O, et al. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long‐term complications in insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus. New England Journal of Medicine 1993;329(14):977‐86. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
DCCT Group 1995
-
- Anonymous. Effect of intensive therapy on the development and progression of diabetic nephropathy in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. The Diabetes Control and Complications (DCCT) Research Group. Kidney International 1995;47(6):1703‐20. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Duckworth 2009
-
- Duckworth W, Abraira C, Moritz T, Reda D, Emanuele N, Reaven PD, et al. Glucose control and vascular complications in veterans with type 2 diabetes.[Erratum appears in N Engl J Med. 2009 Sep 3;361(10):1028], [Erratum appears in N Engl J Med. 2009 Sep 3;361(10):1024‐5; PMID: 19726779]. New England Journal of Medicine 2009;360(2):129‐39. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Elashoff 2011
ERBP 2015
-
- Guideline Development Group. Clinical Practice Guideline on management of patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease stage 3b or higher (eGFR <45 mL/min). Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2015;30 Suppl 2:ii1‐11142. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
FDA 2000
-
- US Food, Drug Administration. Rezulin from the market. www.nfb.org/Images/nfb/Publications/vod/vsum0003.htm 21 March 2000.
Feldt‐Rasmussen 2006
-
- Feldt‐Rasmussen B. Is there a need to optimize glycemic control in hemodialyzed diabetic patients?. Kidney International 2006;70(8):1392‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
GRADE 2008
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JP, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Holman 2008
-
- Holman R, Paul SK, Bethel A, Matthews DR, Neil HA. 10‐year follow‐up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine 2008;359(15):1577‐89. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Howse 2016
-
- Howse PM, Chibrikova LN, Twells LK, Barrett BJ, Gamble JM. Safety and efficacy of incretin‐based therapies in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and CKD: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2016;68(5):733‐42. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
IDF 2013
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas. 6th edition. 2013. www.idf.org/component/attachments/attachments.html?id=813&task=download (accessed 9 August 2018).
Inzucchi 2012
-
- Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, Diamant M, Ferrannini E, Nauck M, et al. Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes: a patient‐centered approach. Position statement of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD).[Erratum appears in Diabetologia. 2013 Mar;56(3):680]. Diabetologia 2012;55(6):1577‐96. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ismail‐Beigi 2010
-
- Ismail‐Beigi F, Craven T, Banerji MA, Basile J, Calles J, Cohen RM, et al. Effect of intensive treatment of hyperglycaemia on microvascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes: an analysis of the ACCORD randomised trial.[Erratum appears in Lancet. 2010 Oct 30;376(9751):1466]. Lancet 2010;376(9739):419‐30. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Jackson 2000
-
- Jackson MA, Holland MR, Nicholas J, Lodwick R, Forster D, Macdonald IA. Hemodialysis‐induced hypoglycemia in diabetic patients. Clinical Nephrology 2000;54(1):30‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jun 2012
-
- Jun M, Lo C, Badve SV, Pilmore H, White SL, Hawley C, et al. Glucose lowering therapies for chronic kidney disease and kidney transplantation. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012, Issue 8. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009966] - DOI
KDIGO 2011
-
- Levey AS, Jong PE, Coresh J, Nahas M, Astor BC, Matsushita K, et al. The definition, classification, and prognosis of chronic kidney disease: a KDIGO Controversies Conference report.[Erratum appears in Kidney Int. 2011 Nov;80(9):1000], [Erratum appears in Kidney Int. 2011 Nov 1;80(9):1000; PMID: 30036909]. Kidney International 2011;80(1):17‐28. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
KDOQI 2002
-
- National Kidney Foundation. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2002;39(2 Suppl 1):S1‐266. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
KDOQI 2012
-
- National Kidney Foundation. KDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes and CKD: 2012 Update.[Erratum appears in Am J Kidney Dis. 2013 Jun;61(6):1049]. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2012;60(5):850‐86. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kobayashi 2000
-
- Kobayashi S, Maejima S, Ikeda T, Nagase M. Impact of dialysis therapy on insulin resistance in end‐stage renal disease: comparison of haemodialysis and continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2000;15(1):65‐70. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Levin 2000
-
- Levin SR, Coburn JW, Abraira C, Henderson WG, Colwell JA, Emanuele NV, et al. Effect of intensive glycemic control on microalbuminuria in type 2 diabetes. Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study on Glycemic Control and Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Feasibility Trial Investigators. Diabetes Care 2000;23(10):1478‐85. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lo 2017
Loipl 2005
-
- Loipl J, Schmekal B, Biesenbach G. Long‐term impact of chronic hemodialysis on glycemic control and serum lipids in insulin‐treated type 2 diabetic patients. Renal Failure 2005;27(3):305‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Moen 2009
Morioka 2001
-
- Morioka T, Emoto M, Tabata T, Shoji T, Tahara H, Kishimoto H, et al. Glycemic control is a predictor of survival for diabetic patients on hemodialysis. Diabetes Care 2001;24(5):909‐13. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Nathan 2005
Ohkubo 1995
-
- Ohkubo Y, Kishikawa H, Araki E, Miyata T, Isami S, Motoyoshi S, et al. Intensive insulin therapy prevents the progression of diabetic microvascular complications in Japanese patients with non‐insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus: a randomized prospective 6‐year study. Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice 1995;28(2):103‐17. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Oomichi 2006
-
- Oomichi T, Emoto M, Tabata T, Morioka T, Tsujimoto Y, Tahara H, et al. Impact of glycemic control on survival of diabetic patients on chronic regular hemodialysis: a 7‐year observational study. Diabetes Care 2006;29(7):1496‐500. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Orme 2017
-
- Orme ME, Nguyen H, Lu JY, Thomas SA. Comparative effectiveness of glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with GLP‐1 receptor agonists: a network meta‐analysis of placebo‐controlled and active‐comparator trials. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome & Obesity Targets & Therapy 2017;10:111‐22. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Patel 2016
-
- Patel S, Gohel K, Patel BG. A systematic review on effect of canagliflozin in special population. Current Diabetes Reviews 2016; Vol. 12, issue 3:211‐22. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Perkovic 2007
-
- Perkovic V, Ninomiya T, Arima H, Gallagher M, Jardine M, Cass A, et al. Chronic kidney disease, cardiovascular events, and the effects of perindopril‐based blood pressure lowering: Data from the PROGRESS Study. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2007;18(10):2766‐72. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Perkovic 2013
-
- Perkovic V, Heerspink HL, Chalmers J, Woodward M, Jun M, Li Q, et al. Intensive glucose control improves kidney outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. Kidney International 2013;83(3):517‐23. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Radbill 2008
-
- Radbill B, Murphy B, LeRoith D. Rationale and strategies for early detection and management of diabetic kidney disease. Mayo Clinic Proceedings 2008;83(12):1373‐81. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Rave 2001
-
- Rave K, Heise T, Pfutzner A, Heinemann L, Sawicki PT. Impact of diabetic nephropathy on pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties of insulin in type 1 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2001;24(5):886‐90. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Rehman 2017
-
- Rehman MB, Tudrej BV, Soustre J, Buisson M, Archambault P, Pouchain D, et al. Efficacy and safety of DPP‐4 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes: Meta‐analysis of placebo‐controlled randomized clinical trials. Diabetes & Metabolism 2017;43(1):48‐58. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ruanpeng 2016
-
- Ruanpeng D, Ungprasert P, Sangtian J, Harindhanavudhi T. Sodium glucose co‐transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors and fracture risk in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systemic review and meta‐analysis [abstract]. Diabetes 2016;65(Suppl 1):A288. [EMBASE: 620237755] - PubMed
Scheen 2015
-
- Scheen AJ. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and clinical use of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 2015; Vol. 54, issue 7:691‐708. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Schünemann 2011a
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JP, Vist GE, Glasziou P, Guyatt GH. Chapter 11: Presenting results and 'Summary of findings' tables. In: Higgins JP, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Schünemann 2011b
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JP, Deeks JJ, Glasziou P, Guyatt GH. Chapter 12: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In: Higgins JP, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Shurraw 2010
-
- Shurraw S, Majumdar SR, Thadhani R, Wiebe N, Tonelli M, Alberta Kidney Disease Network. Glycemic control and the risk of death in 1,484 patients receiving maintenance hemodialysis. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2010;55(5):875‐84. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Shurraw 2011
-
- Shurraw S, Hemmelgarn B, Lin M, Majumdar SR, Klarenbach S, Manns B, et al. Association between glycemic control and adverse outcomes in people with diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease: a population‐based cohort study. Archives of Internal Medicine 2011;171(21):1920‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Shyangdan 2016
Singh‐Franco 2016
-
- Singh‐Franco D, Harrington C, Tellez‐Corrales E. An updated systematic review and meta‐analysis on the efficacy and tolerability of dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes with moderate to severe chronic kidney disease. SAGE Open Medicine 2016;4:2050312116659090. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Storgaard 2016
-
- Storgaard H, Gluud LL, Bennett C, Grondahl MF, Christensen MB, Knop FK, et al. Benefits and harms of sodium‐glucose co‐transporter 2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. PLoS ONE (Electronic Resource] 2016; Vol. 11, issue 11:e0166125. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Tuttle 2014
-
- Tuttle KR, Bakris GL, Bilous RW, Chiang JL, Boer IH, Goldstein‐Fuchs J, et al. Diabetic kidney disease: a report from an ADA Consensus Conference. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2014;64(4):510‐33. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
UKPDS 33 1998
-
- Anonynous. Intensive blood‐glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group.[Erratum appears in Lancet 1999 Aug 14;354(9178):602]. Lancet 1998;352(9131):857‐53. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
UKPDS 34 1998
-
- Anonymous. Effect of intensive blood‐glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 34). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group.[Erratum appears in Lancet 1998 Nov 7;352(9139):1558]. Lancet 1998;352(9131):854‐65. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Vallon 2007
Walker 2017
-
- Walker SR, Komenda P, Khojah S, Al‐Tuwaijri W, MacDonald K, Hiebert B, et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitors in chronic kidney disease: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials. Nephron 2017;136(2):85‐94. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Williams 2006
-
- Williams ME, Lacson EJ Jr, Teng M, Ofsthun N, Lazarus JM. Hemodialyzed type I and type II diabetic patients in the US: characteristics, glycemic control, and survival. Kidney International 2006;70(8):1503‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wu 1997
-
- Wu MS, Yu CC, Yang CW, Wu CH, Haung JY, Hong JJ, et al. Poor pre‐dialysis glycaemic control is a predictor of mortality in type II diabetic patients on maintenance haemodialysis. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 1997;12(10):2105‐10. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wu 2016
-
- Wu JH, Foote C, Blomster J, Toyama T, Perkovic V, Sundstrom J, et al. Effects of sodium‐glucose cotransporter‐2 inhibitors on cardiovascular events, death, and major safety outcomes in adults with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta‐analysis.[Erratum appears in Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016 Sep;4(9):e9; PMID: 27174817]. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology 2016; Vol. 4, issue 5:411‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Xu 2017
-
- Xu S, Zhang X, Tang L, Zhang F, Tong N. Cardiovascular effects of dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitor in diabetic patients with and without established cardiovascular disease: a meta‐analysis and systematic review. Postgraduate Medicine 2017;129(2):205‐15. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Zaccardi 2016
-
- Zaccardi F, Webb DR, Htike ZZ, Youssef D, Khunti K, Davies MJ. Efficacy and safety of sodium‐glucose co‐transporter‐2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and network meta‐analysis. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2016; Vol. 18, issue 8:783‐94. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Zanoli 2015
Zoungas 2017
-
- Zoungas S, Arima H, Gerstein HC, Holman RR, Woodward M, Reaven P, et al. Effects of intensive glucose control on microvascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta‐analysis of individual participant data from randomised controlled trials. The Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology 2017;5(6):431‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

