Microwave-mediated synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles: a therapeutic approach against Malassezia species
- PMID: 30247128
- PMCID: PMC8676232
- DOI: 10.1049/iet-nbt.2018.0007
Microwave-mediated synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles: a therapeutic approach against Malassezia species
Abstract
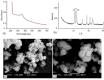
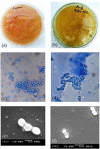
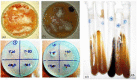
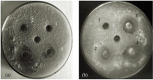
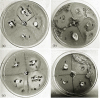
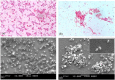
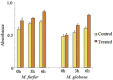
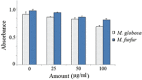
A successful protocol was developed to aid in the reduction in dandruff-causing fungi, namely Malassezia globasa and Malassezia furfur. Both the species were isolated from volunteers aged between 20 and 22 suffering from dandruff, cultured ex vivo, and tested against the presence of synthesised zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnNP). Direct microscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and biochemical assays specific to Malassezia species were conducted to identify dandruff-causing fungal species. Microwave-mediated synthesis of ZnNP was performed and characterised by UV-vis, X-ray diffraction, and SEM. The nanoparticles were tested against both Malassezia species and proved highly effective in inhibiting these fungi, although M. furfur was more susceptible than M. globosa. An optimum amount of 100 ppm was found to be sufficient to work as an antifungal agent. Synergistic effects of ZnNP with commercial shampoos were tested, and the result showed enhanced antifungal effects. To mimic the natural biofilm formed by these species on human skin, the formation of fungal biofilm was allowed on polystyrene coverslips. ZnNP was effective in eradication biofilm. Since zinc is an essential mineral for all living organism and is considered as biocompatible, the synthesised nanomaterials can be used in the formulation of antidandruff shampoos.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel anti-dandruff shampoo incorporated with ketoconazole-coated zinc oxide nanoparticles using green tea extract.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2024 Feb;23(2):563-575. doi: 10.1111/jocd.16027. Epub 2023 Nov 1. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 37909853
-
Effect of zinc pyrithione shampoo treatment on skin commensal Malassezia.Med Mycol. 2021 Feb 4;59(2):210-213. doi: 10.1093/mmy/myaa068. Med Mycol. 2021. PMID: 32785575
-
Targeting Malassezia species for Novel Synthetic and Natural Antidandruff Agents.Curr Med Chem. 2017;24(22):2392-2412. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170404110631. Curr Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28393697 Review.
-
Anti-acne, anti-dandruff and anti-breast cancer efficacy of green synthesised silver nanoparticles using Coriandrum sativum leaf extract.J Photochem Photobiol B. 2016 Oct;163:69-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2016.08.005. Epub 2016 Aug 7. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2016. PMID: 27541567
-
[How I treat dandruff].Rev Med Liege. 2013 Sep;68(9):436-9. Rev Med Liege. 2013. PMID: 24180197 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Cationic Liposomes with Different Lipid Ratios: Antibacterial Activity, Antibacterial Mechanism, and Cytotoxicity Evaluations.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Dec 14;15(12):1556. doi: 10.3390/ph15121556. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36559007 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Microwave Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanomaterials: Reactants, Process Parameters and Morphoslogies.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020 May 31;10(6):1086. doi: 10.3390/nano10061086. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32486522 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Faergemann J.: ‘Lipophilic yeasts in skin disease’, Semin. Dermatol., 1985, 4, pp. 1173 –1184
-
- Gupta A.K. Batra R. Bluhm R. et al.: ‘Skin diseases associated with Malassezia species’, J. Am. Acad. Dermatol., 2004, 51, (5), pp. 785 –798 - PubMed
-
- Joshi P. Bonde S. Gaikwad S. et al.: ‘Comparative studies on synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Fusarium oxysporum and Macrophomina phaseolina and it's efficacy against bacteria and Malassezia furfur ’, J. Bionanosci., 2013, 7, (4), pp. 378 –385
-
- Agarwal U.P. Prajakta S. Patki S. et al.: ‘Evaluation of clinical efficacy and safety of ‘anti dandruff hair cream’ for the treatment of dandruff’, Antiseptic, 2009, 106, pp. 37 –39
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

