Children and adolescents with sickle cell disease have worse cold and mechanical hypersensitivity during acute painful events
- PMID: 30247266
- PMCID: PMC6768435
- DOI: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001407
Children and adolescents with sickle cell disease have worse cold and mechanical hypersensitivity during acute painful events
Abstract
Sickle cell disease (SCD) pain associates with cold temperature and touch. Patients and murine models with SCD have baseline thermal and mechanical pain. In SCD mice, the baseline hypersensitivity is exacerbated by experimental vaso-occlusive crises. We hypothesized that patients with SCD will similarly experience increased hypersensitivity to thermal and mechanical stimuli during acute painful events compared with baseline health. We conducted a prospective study of 24 patients with SCD aged 7 to 19 years. Patients underwent quantitative sensory testing to thermal (cold/heat) and mechanical stimuli on the thenar eminence of the nondominant hand (glabrous skin) and the lateral dorsum of the foot (hairy skin) during baseline health and within 48 hours of hospitalization for acute pain. Primary outcomes were changes in: (1) cold pain threshold (°C), (2) heat pain threshold (°C), and (3) mechanical pain threshold (g). Median age was 10.5 (interquartile range [IQR] 9-14.8) years, 67% were females, and 92% were on hydroxyurea. Patients with SCD had increased cold pain sensitivity in the hand during hospitalization compared with baseline (25.2°C [IQR 18.4-27.5°C] vs 21.3°C [IQR 4.9-26.2°C]; P = 0.011) and increased mechanical pain sensitivity in the foot during hospitalization (0.32 g [IQR 0.09-1.1 g] vs 1.7 g [IQR 0.4-8.3 g]; P = 0.003). There were no differences in heat pain sensitivity. The increased cold (P = 0.02) and mechanical (P = 0.0016) pain sensitivity during hospitalization persisted after adjusting for age, sex, hydroxyurea use, opioid consumption, and numeric pain score. Thus, cold and mechanical pain is significantly worse during an acute SCD painful event as compared to baseline health in patients with SCD.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no financial arrangements that represent a conflict of interest.
Figures
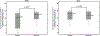
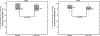
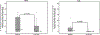
Similar articles
-
Patients with sickle cell disease have increased sensitivity to cold and heat.Am J Hematol. 2013 Jan;88(1):37-43. doi: 10.1002/ajh.23341. Epub 2012 Oct 31. Am J Hematol. 2013. PMID: 23115062 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Thermal pain and sensory processing in children with sickle cell disease.Clin J Pain. 2014 Mar;30(3):244-50. doi: 10.1097/AJP.0b013e318292a38e. Clin J Pain. 2014. PMID: 23629596
-
Clinical Interpretation of Quantitative Sensory Testing as a Measure of Pain Sensitivity in Patients With Sickle Cell Disease.J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2016 May;38(4):288-93. doi: 10.1097/MPH.0000000000000532. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26907660 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Modifiers Associated with Vaso-Occlusive Crises and Acute Pain Phenomena in Sickle Cell Disease: A Scoping Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 7;26(9):4456. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094456. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362693 Free PMC article.
-
Pain in sickle cell disease: current and potential translational therapies.Transl Res. 2021 Aug;234:141-158. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2021.03.007. Epub 2021 Mar 9. Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 33711512 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neuropathic pain in sickle cell disease: measurement and management.Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2020 Dec 4;2020(1):553-561. doi: 10.1182/hematology.2020000142. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2020. PMID: 33275730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence of neuropathic pain in adolescents with sickle cell disease: A single-center experience.Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2022 Apr;69(4):e29583. doi: 10.1002/pbc.29583. Epub 2022 Feb 11. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35147289 Free PMC article.
-
Cold exposure induces vaso-occlusion and pain in sickle mice that depend on complement activation.Blood. 2023 Nov 30;142(22):1918-1927. doi: 10.1182/blood.2022019282. Blood. 2023. PMID: 37774369 Free PMC article.
-
Implementing ASH's guidelines for acute medical care for incarcerated children and adults with sickle cell disease.Blood Adv. 2025 Jun 10;9(11):2744-2750. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2023012546. Blood Adv. 2025. PMID: 39969208 Free PMC article.
-
Gabapentin alleviates chronic spontaneous pain and acute hypoxia-related pain in a mouse model of sickle cell disease.Br J Haematol. 2019 Oct;187(2):246-260. doi: 10.1111/bjh.16067. Epub 2019 Jun 27. Br J Haematol. 2019. PMID: 31247672 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Medoc TSA-II NeuroSensory Analyzer, Vol. 2011. pp. http://www.medoc-web.com/medoc_en_tsaII_analyzer.aspx.
-
- Arendt-Nielsen L, Curatolo M, Drewes A. Human experimental pain models in drug development: translational pain research. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 2007;8(1):41–53. - PubMed
-
- Backonja MM, Walk D, Edwards RR, Sehgal N, Moeller-Bertram T, Wasan A, Irving G, Argoff C, Wallace M. Quantitative sensory testing in measurement of neuropathic pain phenomena and other sensory abnormalities. Clin J Pain 2009;25(7):641–647. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

