Building Kidney Exchange Programmes in Europe-An Overview of Exchange Practice and Activities
- PMID: 30247314
- PMCID: PMC6613834
- DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000002432
Building Kidney Exchange Programmes in Europe-An Overview of Exchange Practice and Activities
Abstract
Background: Considerable differences exist among the living donor Kidney Exchange Programmes (KEPs) that are in use and being built in Europe, contributing to a variation in the number of living donor transplants (Newsletter Transplant; International figures on donation and transplantation 2016). Efforts of European KEPs to exchange (best) practices and share approaches to address challenges have, however, been limited.
Methods: Experts from 23 European countries, collaborating on the European Network for Collaboration on Kidney Exchange Programmes Cooperation on Science and Technology Action, developed a questionnaire to collect detailed information on the functioning of all existing KEPs in Europe, as well as their opportunities and challenges. Following a comparative analysis, results were synthesized and interpreted by the same experts.
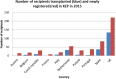
Results: The practices, opportunities and challenges reported by 17 European countries reveal that some of the 10 operating programs are mature, whereas others are in earlier stages of development. Over 1300 transplants were performed through existing KEPs up to the end of 2016, providing approximately 8% of their countries' living kidney donations in 2015. All countries report challenges to either initiating KEPs or increasing volumes. Some challenges are shared, whereas others differ because of differences in context (eg, country size, effectiveness of deceased donor program) and ethical and legal considerations (eg, regarding living donation as such, nonrelated donors, and altruistic donation). Transnational initiatives have started in Central Europe, Scandinavia, and Southern Europe.
Conclusions: Exchange of best practices and shared advancement of national programs to address existing challenges, aided by transnational exchanges, may substantially improve access to the most (cost) effective treatment for the increasing number of patients suffering from kidney disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Klarenbach S, Barnieh L, Gill J. Is living kidney donation the answer to the economic problem of end-stage renal disease? Semin Nephrol. 2009;29:533–538.. - PubMed
-
- Smith CR, Woodward RS, Cohen DS, et al. Cadaveric versus living donor kidney transplantation: a Medicare payment analysis. Transplantation. 2000;69:311–314.. - PubMed
-
- McFarlane PA. Should patients remain on intensive hemodialysis rather than choosing to receive a kidney transplant? Semin Dial. 2010;23:516–519.. - PubMed
-
- U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network Web site. https://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/. Accessed April 18, 2018.
-
- GODT. Global Observatory on Donation and Transplantation Web site. http://www.transplant-observatory.org/. Accessed April 18, 2018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical