Extracellular matrix and the maintenance and loss of peripheral immune tolerance in autoimmune insulitis
- PMID: 30248522
- PMCID: PMC6286219
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coi.2018.09.006
Extracellular matrix and the maintenance and loss of peripheral immune tolerance in autoimmune insulitis
Abstract
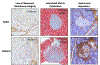
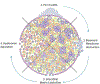
There is a growing appreciation that the extracellular matrix (ECM) contributes to both the maintenance of immune tolerance in healthy tissues and to its loss at sites of autoimmunity. Here, we review recent literature on the role of ECM and particularly the glycosaminoglycans hyaluronan and heparan sulfate in the development of autoimmune, type 1 diabetes (T1D). Data from transplant models suggest that healthy islets are embedded within an intact ECM that supports beta-cell homeostasis and provides physical and immunoregulatory barriers against immune infiltration. However, studies of human insulitis as well as the non-obese diabetic (NOD) and DORmO mouse models of T1D indicate that autoimmune insulitis is associated with the degradation of basement membrane structures, the catabolism of the islet interstitium, and the accumulation of a hyaluronan-rich, pro-inflammatory ECM. Moreover, in these models of autoimmune diabetes, either the pharmacologic inhibition of heparan sulfate catabolism, the reduction of hyaluronan synthesis, or the targeting of the pathways that sense these ECM changes can all prevent beta-cell destruction. Together these data support an emerging paradigm that in healthy islets the local ECM contributes to both immune tolerance and beta-cell homeostasis while in chronic inflammation the islet ECM is permissive to immune infiltration and beta-cell destruction. Therapies that support ECM-mediated 'barrier tolerance' may have potential as adjunctive agents in combination regimens designed to prevent or treat autoimmunity.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interest
PLB and NN are co-founders of Hyalos Therapeutics, a company developing novel small molecules to inhibit HA synthesis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Unexpected new roles for heparanase in Type 1 diabetes and immune gene regulation.Matrix Biol. 2013 Jun 24;32(5):228-33. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2013.02.007. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Matrix Biol. 2013. PMID: 23499527 Review.
-
Extracellular matrix components in the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes.Curr Diab Rep. 2014 Dec;14(12):552. doi: 10.1007/s11892-014-0552-7. Curr Diab Rep. 2014. PMID: 25344787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular composition of the peri-islet basement membrane in NOD mice: a barrier against destructive insulitis.Diabetologia. 2008 Sep;51(9):1680-8. doi: 10.1007/s00125-008-1085-x. Epub 2008 Jul 17. Diabetologia. 2008. PMID: 18633594 Free PMC article.
-
The role of hyaluronan and the extracellular matrix in islet inflammation and immune regulation.Curr Diab Rep. 2012 Oct;12(5):471-80. doi: 10.1007/s11892-012-0297-0. Curr Diab Rep. 2012. PMID: 22810951 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyaluronan: A Mediator of Islet Dysfunction and Destruction in Diabetes?J Histochem Cytochem. 2015 Aug;63(8):592-603. doi: 10.1369/0022155415576542. J Histochem Cytochem. 2015. PMID: 26216136 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nomograms Based on Fibrinogen, Albumin, Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio, and Carbohydrate Antigen 125 for Predicting Endometrial Cancer Prognosis.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 16;14(22):5632. doi: 10.3390/cancers14225632. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36428725 Free PMC article.
-
High levels of serum hyaluronan is an early predictor of dengue warning signs and perturbs vascular integrity.EBioMedicine. 2019 Oct;48:425-441. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.09.014. Epub 2019 Sep 13. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 31526718 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in research on the interaction between inflammation and cancer.J Int Med Res. 2020 Apr;48(4):300060519895347. doi: 10.1177/0300060519895347. Epub 2019 Dec 29. J Int Med Res. 2020. PMID: 31885347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pancreatic Tissue Proteomics Unveils Key Proteins, Pathways, and Networks Associated with Type 1 Diabetes.Proteomics Clin Appl. 2020 Nov;14(6):e2000053. doi: 10.1002/prca.202000053. Epub 2020 Oct 14. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2020. PMID: 33007151 Free PMC article.
-
4-Methylumbelliferone suppresses hyaluronan and adipogenesis in primary cultured orbital fibroblasts from Graves' orbitopathy.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2020 May;258(5):1095-1102. doi: 10.1007/s00417-019-04528-3. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 31900640
References
-
- Ziegler A-G, Nepom GT. Prediction and pathogenesis in type 1 diabetes. Immunity (2010) 32:468–478. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2010.03.018. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rosenblum MD, Remedios KA, Abbas AK. Mechanisms of human autoimmunity. J Clin Invest (2015) 125:2228–2233. 10.1172/JCI78088. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Atkinson MA, Herrath von M, Powers AC, Clare-Salzler M. Current concepts on the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes--considerations for attempts to prevent and reverse the disease. Diabetes Care (2015) 38:979–988. 10.2337/dc15-0144. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Atkinson MA, Leiter EH. The NOD mouse model of type 1 diabetes: as good as it gets? Nat Med (1999) 5:601–604. 10.1038/9442. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

