IL-6: a cytokine at the crossroads of autoimmunity
- PMID: 30248523
- PMCID: PMC6286200
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coi.2018.09.002
IL-6: a cytokine at the crossroads of autoimmunity
Abstract
IL-6 is implicated in the development and progression of autoimmune diseases in part by influencing CD4 T cell lineage and regulation. Elevated IL-6 levels drive inflammation in a wide range of autoimmune diseases, some of which are also characterized by enhanced T cell responses to IL-6. Notably, the impact of IL-6 on inflammation is contextual in nature and dependent on the cell type, cytokine milieu and tissue. Targeting the IL-6/IL-6R axis in humans has been shown to successfully ameliorate a subset of autoimmune conditions. In this review, we discuss recent studies investigating how IL-6 regulates the CD4 T cell response in the context of autoimmune disease and highlight how blocking different aspects of the IL-6 pathway is advantageous in the treatment of disease.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

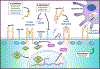
References
-
- Hirano T, Matsuda T, Turner M, Miyasaka N, Buchan G, Tang B, Sato K, Shimizu M, Maini R, Feldmann M, et al. : Excessive production of interleukin 6/B cell stimulatory factor-2 in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Immunol 1988, 18:1797–1801. - PubMed
-
- Linker-Israeli M, Deans RJ, Wallace DJ, Prehn J, Ozeri-Chen T, Klinenberg JR: Elevated levels of endogenous IL-6 in systemic lupus erythematosus. A putative role in pathogenesis. J Immunol 1991, 147:117–123. - PubMed
-
- Maimone D, Guazzi GC, Annunziata P: IL-6 detection in multiple sclerosis brain. J Neurol Sci 1997, 146:59–65. - PubMed
-
- Hunter CA, Jones SA: IL-6 as a keystone cytokine in health and disease. Nat Immunol 2015, 16:448–457. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

