Ocular torsion responses to electrical vestibular stimulation in vestibular schwannoma
- PMID: 30248625
- PMCID: PMC6206273
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clinph.2018.08.023
Ocular torsion responses to electrical vestibular stimulation in vestibular schwannoma
Abstract
Objectives: We determined if eye movements evoked by Electrical Vestibular Stimulation (EVS) can be used to detect vestibular dysfunction in patients with unilateral vestibular schwannoma (VS).
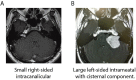
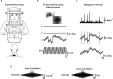
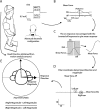
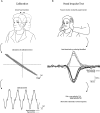
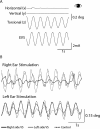
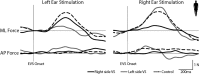
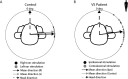
Methods: Ocular torsion responses to monaural sinusoidal EVS currents (±2 mA, 2 Hz) were measured in 25 patients with tumours ranging in size from Koos grade 1-3. For comparative purposes we also measured postural sway response to EVS, and additionally assessed vestibular function with the lateral Head Impulse Test (HIT). Patient responses were compared to age-matched healthy control subjects.
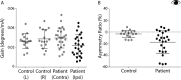
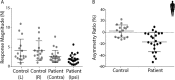
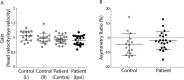
Results: Patients exhibited smaller ocular responses to ipsilesional versus contralesional EVS, and showed a larger asymmetry ratio (AR) than control subjects (19.4 vs. 3.3%, p < 0.05). EVS-evoked sway responses were also smaller in ipsilesional ear, but exhibited slightly more variability than the eye movement response, along with marginally lower discriminatory power (patients vs. controls: AR = 16.6 vs 2.6%, p < 0.05). The HIT test exhibited no significant difference between groups.
Conclusions: These results demonstrate significant deficits in the ocular torsion response to EVS in VS patients.
Significance: The fast, convenient and non-invasive nature of the test are well suited to clinical use.
Keywords: Asymmetry ratio; Electrical vestibular stimulation; Head impulse test; Vestibular schwannoma.
Copyright © 2018 International Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Aw S.T., Todd M.J., Aw G.E., Weber K.P., Halmagyi G.M. Gentamicin vestibulotoxicity impairs human electrically evoked vestibulo-ocular reflex. Neurology. 2008;71:1776–1782. - PubMed
-
- Baldissera F., Cavallari P., Craighero L., Fadiga L. Modulation of spinal excitability during observation of hand actions in humans. Eur J Neurosci. 2001;13:190–194. - PubMed
-
- Clemis J.D., Ballad W.J., Baggot P.J., Lyon S.T. Relative frequency of inferior vestibular schwannoma. Arc Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1986;112:190–194. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

