Endogenous Omega (n)-3 Fatty Acids in Fat-1 Mice Attenuated Depression-Like Behavior, Imbalance between Microglial M1 and M2 Phenotypes, and Dysfunction of Neurotrophins Induced by Lipopolysaccharide Administration
- PMID: 30248907
- PMCID: PMC6213921
- DOI: 10.3390/nu10101351
Endogenous Omega (n)-3 Fatty Acids in Fat-1 Mice Attenuated Depression-Like Behavior, Imbalance between Microglial M1 and M2 Phenotypes, and Dysfunction of Neurotrophins Induced by Lipopolysaccharide Administration
Abstract
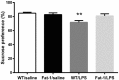
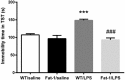
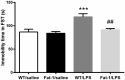
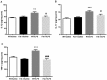
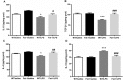
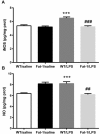
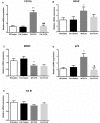
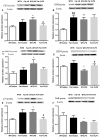
n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) have been reported to improve depression. However, PUFA purities, caloric content, and ratios in different diets may affect the results. By using Fat-1 mice which convert n-6 to n-3 PUFAs in the brain, this study further evaluated anti-depressant mechanisms of n-3 PUFAs in a lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced model. Adult male Fat-1 and wild-type (WT) mice were fed soybean oil diet for 8 weeks. Depression-like behaviors were measured 24 h after saline or LPS central administration. In WT littermates, LPS reduced sucrose intake, but increased immobility in forced-swimming and tail suspension tests. Microglial M1 phenotype CD11b expression and concentrations of interleukin (IL)-1β, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and IL-17 were elevated, while M2 phenotype-related IL-4, IL-10, and transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 were decreased. LPS also reduced the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and tyrosine receptor kinase B (Trk B), while increasing glial fibrillary acidic protein expression and pro-BDNF, p75, NO, and iNOS levels. In Fat-1 mice, LPS-induced behavioral changes were attenuated, which were associated with decreased pro-inflammatory cytokines and reversed changes in p75, NO, iNOS, and BDNF. Gas chromatography assay confirmed increased n-3 PUFA levels and n-3/n-6 ratios in the brains of Fat-1 mice. In conclusion, endogenous n-3 PUFAs may improve LPS-induced depression-like behavior through balancing M1 and M2-phenotypes and normalizing BDNF function.
Keywords: BDNF; Fat-1 transgenic mice; depression; microglial M1 and M2 phenotypes; n-3 fatty acids; neurotrophins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endogenous ω-3 fatty acids in Fat-1 mice attenuated depression-like behaviors, spatial memory impairment and relevant changes induced by olfactory bulbectomy.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2021 Aug;171:102313. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2021.102313. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2021. PMID: 34246927
-
Dietary eicosapentaenoic acid normalizes hippocampal omega-3 and 6 polyunsaturated fatty acid profile, attenuates glial activation and regulates BDNF function in a rodent model of neuroinflammation induced by central interleukin-1β administration.Eur J Nutr. 2018 Aug;57(5):1781-1791. doi: 10.1007/s00394-017-1462-7. Epub 2017 May 18. Eur J Nutr. 2018. PMID: 28523372
-
Transgenic increase in n-3/n-6 fatty acid ratio protects against cognitive deficits induced by an immune challenge through decrease of neuroinflammation.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015 Feb;40(3):525-36. doi: 10.1038/npp.2014.196. Epub 2014 Aug 5. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015. PMID: 25228141 Free PMC article.
-
The role of polyunsaturated fatty acids in the neurobiology of major depressive disorder and suicide risk.Mol Psychiatry. 2024 Feb;29(2):269-286. doi: 10.1038/s41380-023-02322-6. Epub 2023 Nov 22. Mol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 37993501 Review.
-
Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Neuroinflammation in Depression: Targeting Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns and Neural Biomarkers.Cells. 2024 Oct 29;13(21):1791. doi: 10.3390/cells13211791. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39513898 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Didang Tang inhibits intracerebral hemorrhage-induced neuronal injury via ASK1/MKK7/JNK signaling pathway, network pharmacology-based analyses combined with experimental validation.Heliyon. 2022 Nov 5;8(11):e11407. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11407. eCollection 2022 Nov. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36387497 Free PMC article.
-
Isoginkgetin treatment attenuated lipopolysaccharide-induced monoamine neurotransmitter deficiency and depression-like behaviors through downregulating p38/NF-κB signaling pathway and suppressing microglia-induced apoptosis.J Psychopharmacol. 2021 Oct;35(10):1285-1299. doi: 10.1177/02698811211032473. Epub 2021 Jul 19. J Psychopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34281416 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the study of IL-17 in neurological diseases and mental disorders.Front Neurol. 2023 Nov 16;14:1284304. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1284304. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 38046578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevention of colitis-induced liver oxidative stress and inflammation in a transgenic mouse model with increased omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids.Redox Biol. 2023 Aug;64:102803. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102803. Epub 2023 Jun 26. Redox Biol. 2023. PMID: 37392516 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the microbiota-gut-brain axis in neuropsychiatric disorders.Braz J Psychiatry. 2021 May-Jun;43(3):293-305. doi: 10.1590/1516-4446-2020-0987. Braz J Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 32667590 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Perez-Urrutia N., Mendoza C., Alvarez-Ricartes N., Oliveros-Matus P., Echeverria F., Grizzell J.A., Barreto G.E., Iarkov A., Echeverria V. Intranasal cotinine improves memory, and reduces depressive-like behavior, and gfap+ cells loss induced by restraint stress in mice. Exp. Neurol. 2017;295:211. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2017.06.016. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

