Melatonin Can Strengthen the Effect of Retinoic Acid in HL-60 Cells
- PMID: 30248940
- PMCID: PMC6213950
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19102873
Melatonin Can Strengthen the Effect of Retinoic Acid in HL-60 Cells
Abstract
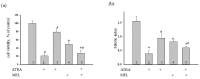
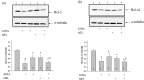
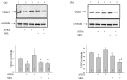
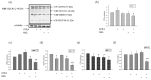
Melatonin is produced by the pineal gland. It can be regarded as an anticancer agent and used for combined therapy, owing to its oncostatic, antioxidant, and immunoregulatory activities. Retinoic acid is widely used for the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia; however, it has adverse effects on the human organism. We investigated the effect of melatonin and reduced concentrations of retinoic acid on the activation of proliferation in acute promyelocytic leukemiaon a cell model HL-60. The combined effect of these compounds leads to a reduction in the number of cells by 70% and the index of mitotic activity by 64%. Combined treatment with melatonin and retinoic acid decreased the expression of the Bcl-2. The mitochondrial isoform VDAC1 can be a target in the treatment of different tumors. The combined effect of and retinoic acid at a low concentration (10 nM) decreased VDAC1 expression. Melatonin in combination with retinoic acid produced a similar effect on the expression of the translocator protein. The coprecipitation of VDAC with 2',3'-cyclonucleotide-3'-phosphodiesterase implies a possible role of its in cancer development. The combined effect of retinoic acid and melatonin decreased the activity of the electron transport chain complexes. The changes in the activation of proliferation in HL-60 cells, the mitotic index, and Bcl-2 expression under combined effect of retinoic acid (10 nM) with melatonin (1 mM) are similar to changes that are induced by 1 μM retinoic acid. Our results suggest that MEL is able to improve the action the other chemotherapeutic agent.
Keywords: 2′,3′-cyclonucleotide-3′-phosphodiesterase; HL-60 cells; acute promyelocytic leukemia; apoptosis; melatonin; retinoic acid; translocator protein; voltage dependent anion channel-1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Stehle J.H., Saade A., Rawashdeh O., Ackermann K., Jilg A., Sebesteny T., Maronde E. A survey of molecular details in the human pineal gland in the light of phylogeny, structure, function and chronobiological diseases. J. Pineal Res. 2011;51:17–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2011.00856.x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

