The Multifaceted Role of Pectin Methylesterase Inhibitors (PMEIs)
- PMID: 30248977
- PMCID: PMC6213510
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19102878
The Multifaceted Role of Pectin Methylesterase Inhibitors (PMEIs)
Abstract
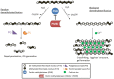
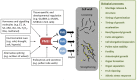
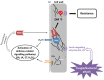
Plant cell walls are complex and dynamic structures that play important roles in growth and development, as well as in response to stresses. Pectin is a major polysaccharide of cell walls rich in galacturonic acid (GalA). Homogalacturonan (HG) is considered the most abundant pectic polymer in plant cell walls and is partially methylesterified at the C6 atom of galacturonic acid. Its degree (and pattern) of methylation (DM) has been shown to affect biomechanical properties of the cell wall by making pectin susceptible for enzymatic de-polymerization and enabling gel formation. Pectin methylesterases (PMEs) catalyze the removal of methyl-groups from the HG backbone and their activity is modulated by a family of proteinaceous inhibitors known as pectin methylesterase inhibitors (PMEIs). As such, the interplay between PME and PMEI can be considered as a determinant of cell adhesion, cell wall porosity and elasticity, as well as a source of signaling molecules released upon cell wall stress. This review aims to highlight recent updates in our understanding of the PMEI gene family, their regulation and structure, interaction with PMEs, as well as their function in response to stress and during development.
Keywords: applications; cell wall properties; degree of methylesterification (DM); development; homogalacturonan (HG); pectin methylesterase inhibitor (PMEI), pectin; stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

