Chronic Insulin Infusion Down-Regulates Circulating and Urinary Nitric Oxide (NO) Levels Despite Molecular Changes in the Kidney Predicting Greater Endothelial NO Synthase Activity in Mice
- PMID: 30249002
- PMCID: PMC6213653
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19102880
Chronic Insulin Infusion Down-Regulates Circulating and Urinary Nitric Oxide (NO) Levels Despite Molecular Changes in the Kidney Predicting Greater Endothelial NO Synthase Activity in Mice
Abstract
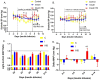
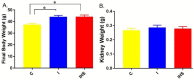
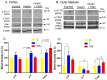
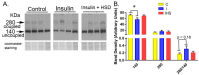
Insulin therapy is often needed to overcome insulin receptor resistance in type 2 diabetes; however, the impact of providing additional insulin to already hyperinsulinemic subjects is not clear. We infused male TALLYHO/Jng (TH) mice (insulin resistant) with insulin (50 U/kg·bw/d) or vehicle (control) by osmotic minipump for 14 days. One group of insulin-infused mice was switched to 4% NaCl diet (high-sodium diet, HSD) in the second week. Blood chemistry revealed a significantly higher anion gap and blood sodium concentrations with insulin infusion, i.e., relative metabolic acidosis. Systolic BP and heart rate were slightly (~5 mm Hg) higher in insulin-infused versus control mice. HSD resulted in a modest and transient rise in mean arterial blood pressure (BP), relative to control or insulin-infused, normal-NaCl-fed mice. In kidney, insulin infusion: (1) increased total and phosphorylated (serine-1177) endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) band densities; (2) reduced band density of the uncoupled form of eNOS; and (3) increased renal homogenate nitric oxide synthase (NOS) activity. Despite this, plasma and urine levels of nitrates plus nitrites (NOx) fell with insulin infusion, by day 14 (40⁻50%) suggesting worsening of resistance. Overall, insulin infusion ramps up the cellular means in kidney to increase vasodilatory and natriuretic NO, but in the long term may be associated with worsening of insulin receptor resistance.
Keywords: blood pressure; heart rate; hypertension; metabolic syndrome; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Song J., Hu X., Riazi S., Tiwari S., Wade J.B., Ecelbarger C.A. Regulation of blood pressure, the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC), and other key renal sodium transporters by chronic insulin infusion in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2006;290:F1055–F1064. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00108.2005. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

